This work proposes to determine, through an exploratory study, digital natives' perceptions regarding companies' internal social media use. Internal social media therefore offers many opportunities for organizations, but at the same time presents many challenges.
Research delimitation and justification
The search results show that there are a significant number of studies related to digital natives or Gen Z. It should be noted that some authors refer to digital natives but do not necessarily consider the same birth period as Gen Z, which could mean a lower number of studies for the specific cohort of this research.
Objectives
First, a brief overview of social media and digital natives is presented to explore the context in which this research is conducted. In the following, the literature on internal social media is presented, providing a definition and a brief history of the topic, followed by a collection of recent studies on various research areas within internal social media.
Social Media, the Bright and Dark side
Although their history is still relatively short in terms of time, social media have permanently taken over people's lives and influenced them both positively and negatively. The way social media is used has also evolved significantly over the last decade, reflecting changes in how, why and when people use it.
Generation Z, the digital natives
Organizations and Digital Natives
In terms of communication, digital natives value face-to-face communication over all other forms, including emails and social networks. In parallel, academic researchers began the journey to study digital natives within the workplace.
Organization Internal Communication and Social Media
Internal social media definition, evolution and academic advancement
In a similar literature review, Leonardi et al. 2013) acknowledged that these studies have focused little on the implications of internal social media use for organizational action. In this way, a brief review of the academic literature on internal social media funding is presented in a separate item below.
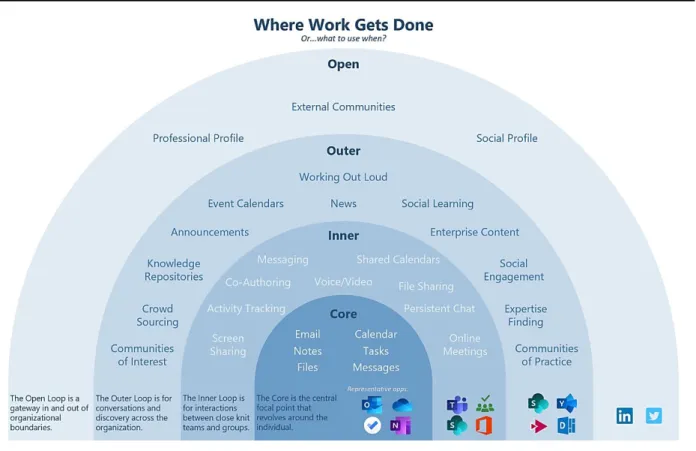
Internal Social Media in Light of Internal Communication
Moreover, using Barzilai-Nahon's network gatekeeping theory, Verheyden (2017) found that internal social media tools influence the gatekeeper role of internal communication. Then there is the knowledge sharing arena, in which internal social media is developing a multi-directional communication mainly used for sharing knowledge.
Internal Social Media in Light of Knowledge Management
Next, the authors looked at how involvement in knowledge sharing in the workplace can be changed through the use of social media from an affordable perspective. The research identified three main activities of social media applications that differentiate them from traditional forms of knowledge sharing and communication behavior: knowledge seeking, knowledge contribution, and social interactivity. Nevertheless, the authors conclude that to promote work-related knowledge sharing, managers should facilitate non-work-related interactions on social media.
Possibly, some theories and models that specifically address internal social media in the light of knowledge management appear shyly in the literature.
Internal Social Media in Light of HRM
Men and Hung-Baesecke (2015) initiated a research stream to examine the effect of social media on employee engagement based on transparency and authenticity. For example, Charoensukmongkol (2014) studied the consequences of using social media at work and found a positive relationship between job satisfaction and job performance and the use of social media at work. 2016) examined the influence of social media on employee job performance, which found that using social media at work could increase employee social capital, facilitating knowledge transfer and leading to better job performance.
Finally, according to the scholars covered, the use of internal social media is positively related to performance, apparently mediated by knowledge management.
Internal Social Media in Light of Generations
Specifically regarding internal social media, Shami et al. 2014) developed a longitudinal study that found that some indicators of social media use (number of forum posts, forum post length, and status update length) were positively related to performance ratings. Later, Ali-Hassan et al. 2015) examined the effect of three categories of social media use—social, hedonic, and cognitive—on job performance as mediated by three dimensions of social capital. According to Boughzala (2014) and Boughzala (2016), private use of social media by millennials is no guarantee of effective workplace adoption.
Older workers and those who did not have significant experience with social media outside of work were largely optimistic about the potential utility of internal social media.
Literature Review Summary
They could view it as different from public social media and perceive the technology as potentially useful for organizational activities. It can be seen that the academic literature confirms that people's perception of the usefulness of technology is formed differently when the technology is used in the workplace rather than outside it, as suggested by O'Mahony and Barley (1999). Similarly, while pointing out some of the disadvantages of its use, a clear understanding of the potential negative consequences for individuals and organizations is lacking.
However, the literature reviewed provides significant insights for this research and forms the basis of the analysis and discussions presented here.
Research Approach
The purpose of this section is to explicitly present the methodological aspects of this study and the basic assumptions on which it is based.
Context, Universe and Unit of Operation
Data Collection
However, despite the structure, the interview process is still flexible and also allows room to pursue topics of particular interest to the interviewees. In preparation, an interview guide was created following a protocol consisting of seven main topics, as summarized below. As such, the interview guide reflected the research specific objectives to ultimately answer the research question.
Organizational context that approximates the nature of the interaction between the interviewees and internal social media;.
Data Coding and Analysis
- Private Usage of Social Media
- Nature of the Interaction with Internal Social Media
- Initial Perceptions of Internal Social Media
- Internal Social Media Outside of Working Hours
- Knowledge Management Aspects
- Internal Communication Aspects
- Corporate Surveillance Aspects
Thus, the following categories were proposed to explore digital natives' use of private social media: use, motivation, and behavior. The following categories were therefore proposed to explore the beginnings of digital natives. perceptions of internal social media: characteristics, comparison with private and personal data. Thus, the following categories were proposed to explore digital natives' perceptions of social media related to internal communication aspects: employee voice and behavior shaping.
Therefore, the following categories were proposed to examine digital natives' perceptions of social media in relation to corporate surveillance: monitoring, privacy, and obligation to share.
Before Getting to Organizational Context
Analysis of the interviews and the main findings of the study are presented in the following paragraphs. Each section addresses one of the seven main content areas of the interview, with a general analysis of the responses and conclusions of the main findings and a table of excerpts from the interviews. Finally, the eighth section provides a holistic analysis of the interviews, compiling the findings from the earlier topics and providing a larger picture of the themes that are individually addressed in each of the topics.
Motivation – I use social media to connect more with my friends, to learn more about their lives and what they do.
Nature of the Interaction with Internal Social Media
I didn't choose when I'm there and when I'm not there, I just go on social media whenever I feel bored for example, so I've reduced my usage today. Although with a reduced awareness of the platform, the internal impact of social media on their professional life was expressed positively by the respondents at this initial point of the interview. Familiarity - I am very familiar with those social media because I use them in the company where I work.
I am familiar with all social media tools within our organization that are named as such, such as the Yammer, SharePoint, Teams, Stream.
Initial Perceptions on Internal Social Media
Characteristics - The main characteristic of social media of these modern means of communication is the easy and sometimes standard interface that they have, which does not make it a complicated way to use it. When we compare social networks in the workplace and social networks in our private lives, I see that there are many common points, but they have different purposes. I believe that on an internal work social media I would not feel comfortable sharing my private information because I think it is important that information is shared.
I don't think I would be very comfortable sharing private life details in social media tools at work.
Blurring Lines Between Rest and Work Times
I have most of the organization apps installed on my cell phone and I think it definitely helps you remove that barrier between work life and personal life. So if you were always aware of what is going on at work, it can spoil some of the entertainment or relaxation you have and add some stress to your personal life. If something is urgent and I really need to do it, I give myself time and I get the message almost immediately because I have it on my phone.
The positive impact is that I'm very aware of what's going on even when I leave work, and it certainly helps me plan what I'm going to do to solve some problems or what are the most urgent requests I need to make in the next one. Work day.
Knowledge Management Aspects
This may indicate that digital natives think that information reliability is a problem separate from them, caused by other private social media users—and that they can resolve reliability issues in a more controlled environment, i.e., the work environment. I think the fact that I know that any information I share within my company's social media tools is visible to literally everyone in the company is a bit scary. I think the key to making social media work in a work environment is to control the information that is posted.
I agree with the fact that the availability of information has really helped people to access things that they could only get from experts before, but I still believe that you get the information but only the experts will know how to interpret it. do, and really understand how to use that information.
Employee Voice, Organizational Authenticity and Transparency
I believe that internal social media gives many opportunities to employees and especially raises their voice because they have the opportunity to contact other people who would otherwise be very inaccessible. I do think that perhaps with a wrong use of that internal social media, the organization can also control certain aspects of the employees' daily private life if they use it to the power that should not be used, which also happens in the workplace. I do think that social media has a lot of power to change our emotions and how we feel and then in the second moment it also changes our behavior.
Perhaps with the misuse of that internal social media, the organization can also control certain aspects of the daily private life of the employees if they use it with power that should not be used.
Corporate Surveillance
Visibility and competition seem to be the reason behind this behavior as they believe that people who will use more social media are more likely to be valued by the organization. However, it is not clear whether the pressure is the result of the company's culture or just a projection of the competition that is already present on the private social media. They have to, not they can, they always have to post something, they always have to be connected on the social media of the company.
People who will use social media more are more likely to be appreciated, seen and remembered for putting themselves in the foreground.
Discussions and insights
Indeed, if we move to the organizational context, we first notice that internal social media is not a specific topic that deals with digital natives. Although with a limited view of the topic, the internal impact of social media on professional life is positively expressed. Internal social media is not a specific topic on the top of interviewers' minds.
Although there is agreement from the respondents that internal social media raise individual voices, aspects regarding Corporate social media: Definition, history, and perspectives for the study of social technologies in organizations. Does social media amplify the constructive employee voice all the time or only sometimes.