In the US, the greatest perceived benefits of university involvement in the field were related to education and advancement of the field, while in E.U. 2 Introduction to the TUNRail project and rail transport in the European Union (E.U.) and the United States (USA).
Background
Introduction to TUNRail
The purpose of Task 1 was to develop a comprehensive inventory of current rail higher education programs and activities in the US. This task also examined the synergies between the rail systems and rail higher education programs in the US.
Limitations of the Study
Comparison of Rail Systems in the U.S. and E.U
Introduction to the E.U. and the U.S
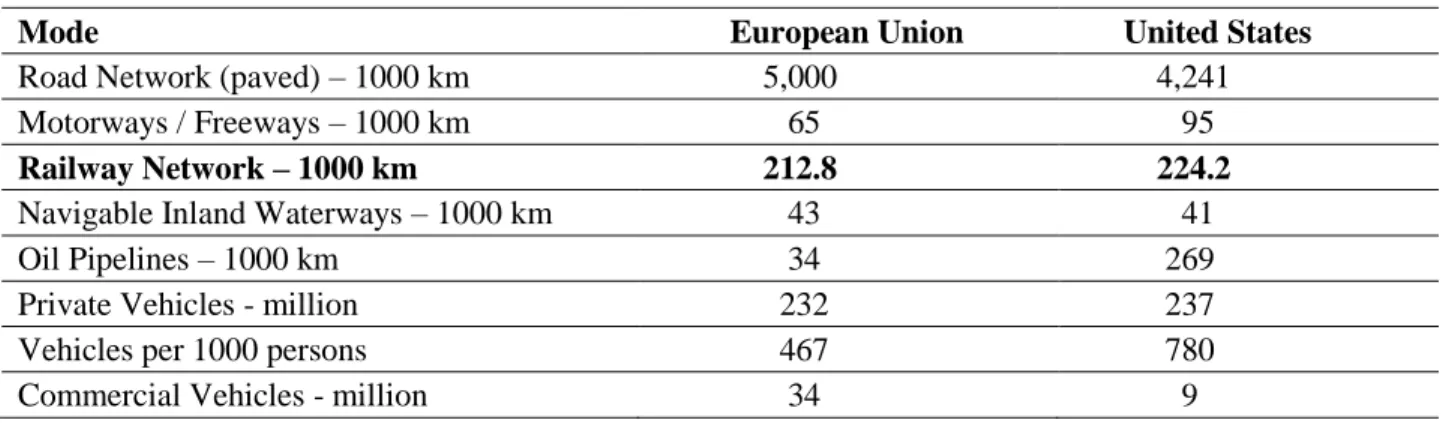
The United States of America (USA) is the third largest country in the world by population and the fourth largest country by land area. In terms of population, Germany, France and Great Britain are the three largest countries in the EU.
Transportation in the E.U. and the United States
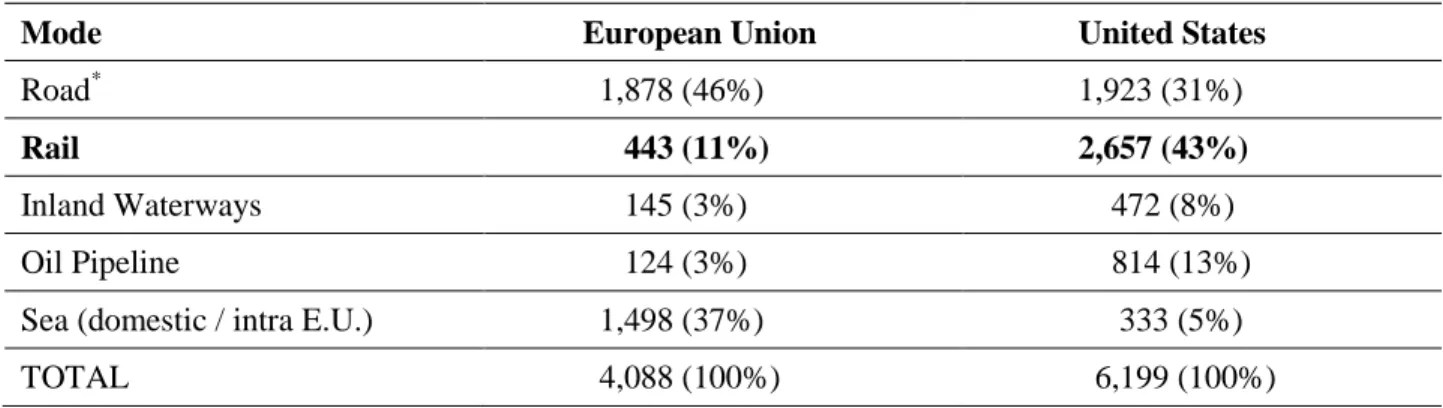
In the 1950s, the share of freight carried by railroads was similar and declined in both the United States and Europe. By 2008, rail's share of freight (measured in tonne-kilometres) had risen to 43% in the United States, while in Europe it had fallen to 11%.
Railroad Systems in the E.U. and the United States
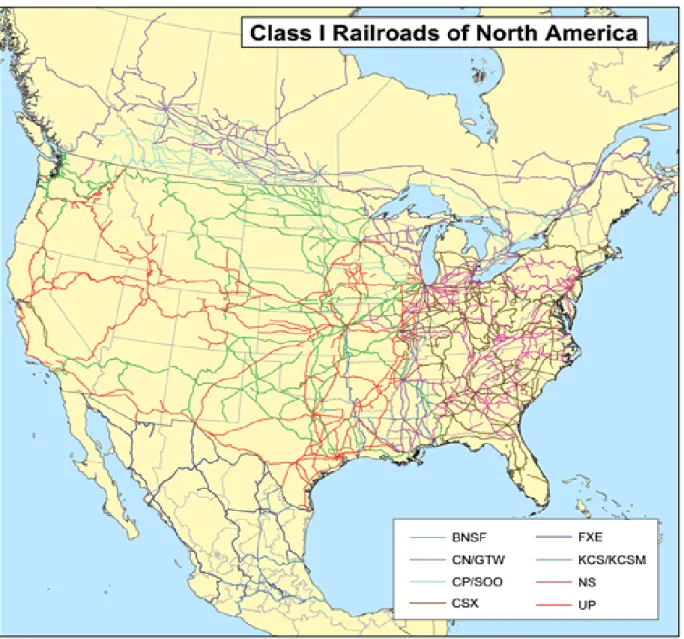
Freight Railroads
In the United States there are 565 railroad companies and all but two of the major railroad companies are owned by private investors. For example, railroads in the United States now carry less than 1 percent of all intercity passenger traffic.
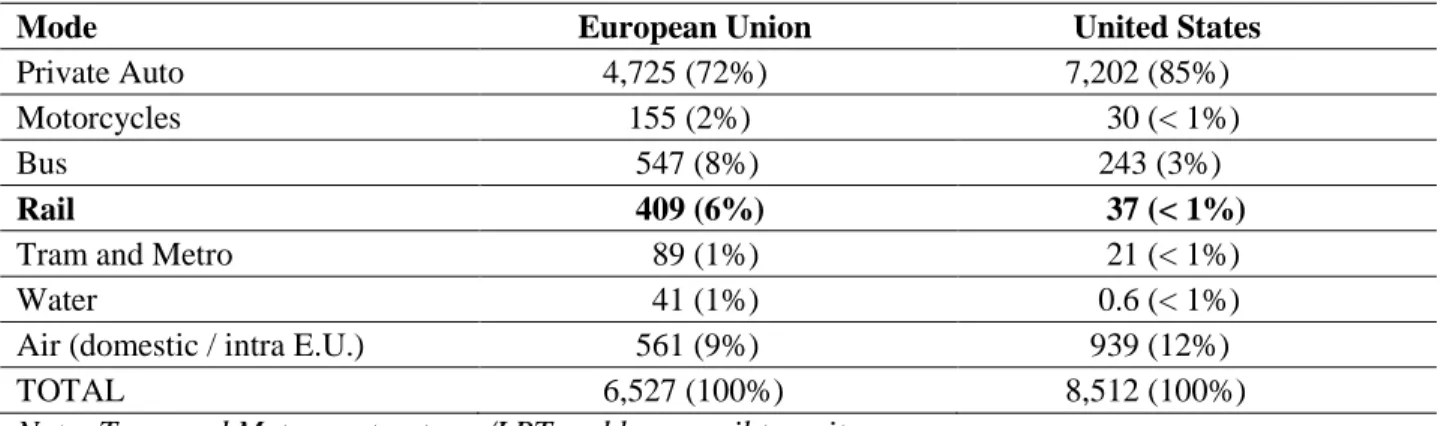
Urban Rail/Public Transit
Light rail is a mode of transportation in which passenger cars of one, two or three cars are operated on fixed rails in a street or on rights-of-way separated from other traffic. Light rail vehicles are typically operated by a driver and power is drawn from an overhead wire or pantograph.

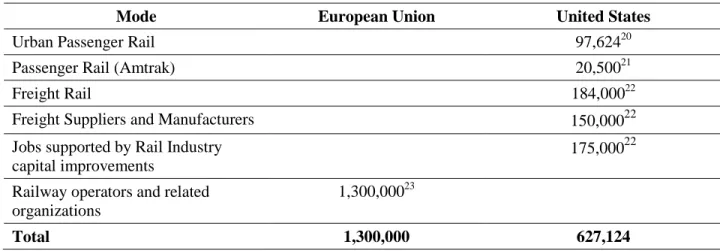
Rail Industry Employment
This makes it difficult to obtain a clear and unambiguous picture of the development of employment in the past and of current employment levels23. In the UK, Project Brunel was set up to address the same concerns about an aging workforce.
Methodology
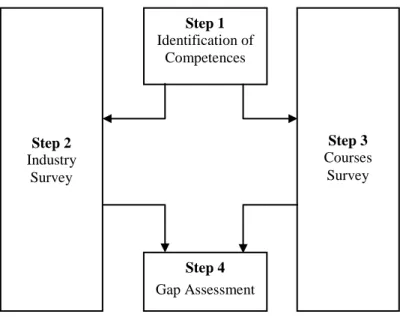
There is no central data source for such programs which has made the data collection effort very challenging. There may also be weaknesses in the data set (in EU data) due to language barriers and other sources of potential inaccuracies (in both EU and US data).
U.S. Railway Programs and Courses
History
However, despite the word "transportation" in the title, the content of these courses is almost entirely highway oriented. But until recently, both industry and government have largely neglected the role of academia in helping rail transport fulfill its potential in the 21st century.
Existing U.S. University Programs and Courses
In addition to the rail transportation and engineering programs described in this chapter, the team identified that a few universities have research funding from the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) and other sources, but they do not offer any courses in railroad engineering. The rail industry is used to competing with the highway sector for traffic, but now it must also compete for faculty and students interested in transportation careers.
U.S. Case Studies
The program became a foundation for further development of railroad activities at Michigan Tech, culminating in the establishment of a Rail Transportation Program (RTP) under the Michigan Tech Transportation Institute (MTTI). Pasi Lautala is the program director and the website for rail transportation activities at Michigan Tech is www.rail.mtu.edu.
E.U. Railway Programs and Courses
History
In the 1990s, after the end of the Soviet empire, some Eastern European countries maintained this model while others did not. In Dresden, the former transport college became a department of the Dresden Technical University and it still offers a comprehensive railway program.
Existing E.U. Programs and Courses
It is assumed that these differences are equalized by the large number of courses, so that the results will not differ significantly from a more detailed analysis. Here, as before, it is also assumed that the large number of courses will equalize these uncertainties.
E.U. Case Studies
Among the Portuguese engineering schools, the best known are the Instituto Superior Técnico of the Technical University of Lisbon (Lisbon), the Technical Faculty of the University of Porto (Oporto), the Faculty of Science and Technology of the University of Coimbra (Coimbra) and the School of Engineering of the University of Minho (Guimarães). The supervisor is a professor from one of the Portuguese universities and the co-supervisor is a professor from MIT.
U.S. and E.U. Railway Program and Course Comparison
However, this is not the case in the US, where it would be unique for a student to receive railroad training as part of a traditional civil engineering curriculum. As university railway education has been well established in the EU for decades, there is no general trend towards further growth.
Industry Survey
Survey Part I – All Professionals
The study then sought to determine the types of exposure to the railroad industry while at university, and Figures 4.8 and 4.9 show the variety of approaches in the United States. Over half of the respondents noted that their organization cooperated with universities, and almost all respondents agreed on the benefits of transatlantic cooperation (Figure 4.11).
Survey Part II – Recruitment/Development Managers
University Education
One of the goals of TUNRail was to evaluate how well today's education meets industry demands and needs. The methodology used for the assessment was a competency gap analysis where outcomes from university course surveys were compared with outcomes from the industry survey.
Background
University career advancement does not require interaction with the corporate world, and many faculty members have never held a position outside of the university environment; The need for training delays the market entry of the students and increases the costs for the employers.
Basic Definitions
Motor skill is related to an individual's ability to perform motor related behaviors such as speed and accuracy of physical movements or dexterity. Problem-solving skill is related to an individual's ability to solve new (or unfamiliar) tasks.
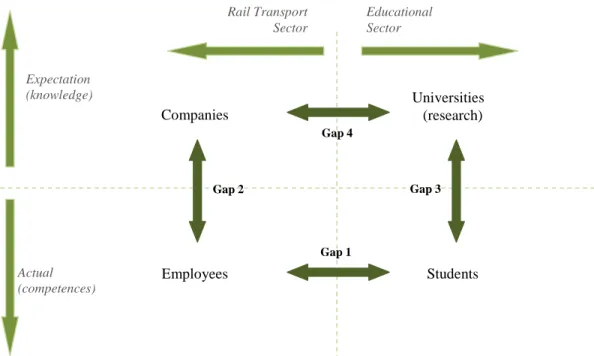
Competence Gap Analysis Framework
Using the four gaps assessment framework, it helps to identify the four gaps and better understand the location and origin of the competency gap (gap) (Figure 4.19). TUNRail researched rail teaching and the state of the industry in the European Union and the United States.
Assessment of the Gap
Methodology
In the EU, railway-related courses were found in programs in the field of railways (and transport) (111 courses), mechanical engineering (4 courses), electrical and electronic engineering (1 course), civil engineering (127 courses), industrial engineering (9 courses) and automotive engineering (2 courses). In the EU, courses were found in six domains (out of sixteen), and two of them covered more than 90% of the courses (Civil Engineering and Railways).
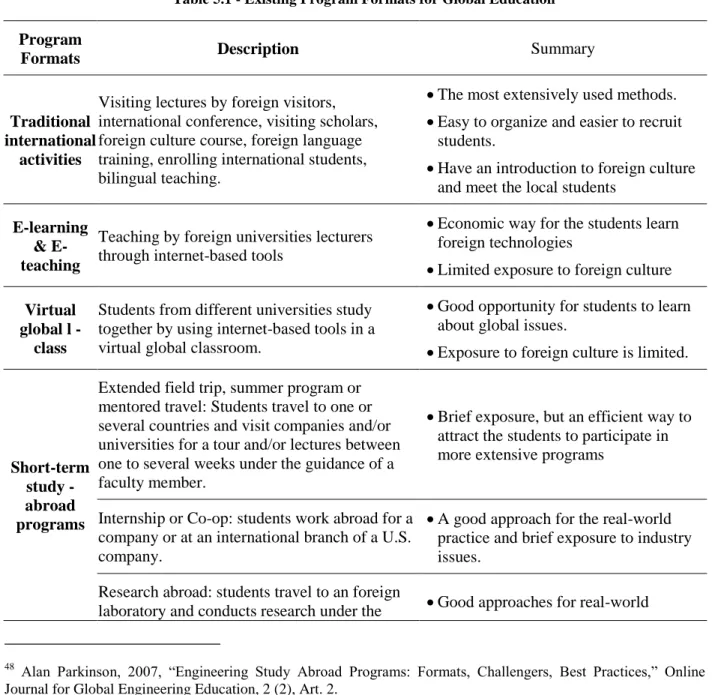
Global Education Program Formats
Many innovative approaches to global engineering education have been developed, and these approaches can be grouped into several categories. Extension: The home university operates a pseudo-extension campus in the other country at a permanent facility.
Teaching Railway Engineering
HPL transforms teaching from traditional teacher-centered to learner-centered with a greater emphasis on self-directed and active learning. Some innovative methodologies include problem-based, project- and challenge-based learning and collaboration, and context-based learning styles.
Railway Operations Laboratories
It is very typical for a railway operations laboratory to provide different generations of control technology. New users of rail operation laboratories outside the rail training area have also been identified.

Rail Traffic Control Simulations
The most challenging use of simulations is to let students run simulations to try out rail traffic control. By using simulations, the subject of operating rules is taught with a fun factor and students get an incredible level of knowledge about the railway traffic control process and the operating rules of a specific railway.
Recent Developments in Innovative Laboratory and Simulator Teaching
In the opposite direction, a train leaving the virtual network will trigger a train waiting in the hidden storage yard to start moving and appear in the visible part of the modeled area. While the tracks of the modeled area may be controlled by local control stations, the virtual area must be CTC territory.
Beijing Jiaotong University Simulation Software
The model control system will operate trains according to plans and provide dynamic feedback. Students will create a train operation adjustment plan based on feedback data and commit it to the mode system.
Railway Infrastructure Education
Railroad Track Engineering and Design Course - Michigan Tech University
The course introduces students to the design and development of construction documents for railway projects, particularly the construction of a new, or modification of an existing track. They also gained practical experience in how to use MicroStation and Geopak software in the design part of the project.
Infrastructure Engineering at University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign
Examples of these software packages are the Association of American Railroads (AAR) Train Energy Model, used to calculate train fuel consumption and resistance, the Rail Traffic Controller (RTC) (shown in Figure 5.7), used to modeled network capacity, as well as Bentley Systems MicroStation, used to design railway infrastructure. The macro level of the project is developed in a course known as "Railway Project Design and Construction", where students focus on determining the right alignment from different alternatives, carry out some elements of track design and span the entire project management and construction management steps needed to complete the project.

Use of Web Technologies in Railway Education and Training
The French National Railway Company (SNCF) has recently chosen a change management approach within the company that allows project managers to share their knowledge and experiences through an IT device called "knowledge server". By "knowledge server", "is meant an information system that allows users to improve their practice".
Current Research and Curriculum Development Projects
Skillrail - Education and Training Actions for High Skilled Job Opportunities in the
RiFLE - Rail Freight and Logistics Curriculum
But the research for the TUNRail project indicates that practical knowledge based on a comprehensive railway higher education program has considerable value. To provide the greatest benefit to the rail industry, a comprehensive rail higher education program should cross the line between academic and practical knowledge.
Data Collection/Research Activities
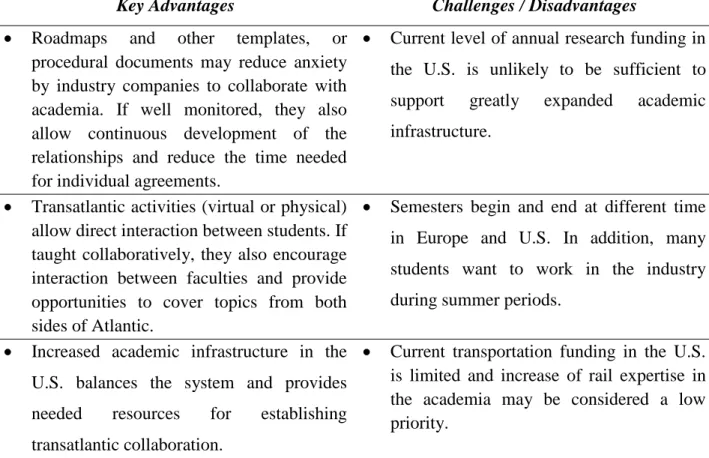
As more companies operate on both sides of the Atlantic and as system synergies continue to develop, the environment is becoming ready for transatlantic research collaboration in areas considered a high priority for both parties. Collaborative research allows for the utilization of expertise and experiences on both sides of the Atlantic and provides potential level of investment through economies of scale.
Education and Technology Development
The surveys and related competence gap analysis have shown that current higher education in rail transport is mainly limited to civil engineering and transport domains, while some of the most important subjects may lie outside these areas. Since the number of students for such specialized courses may be limited, collaboration agreements between institutions should be explored as part of implementation.
University/Industry and Transatlantic Collaboration
Consider rail education through research, such as joint master's or doctoral programs that include mandatory visits for candidates on the other side of the Atlantic. The joint MIT/IST MS program is an excellent example of such collaboration, and additional programs with similar goals should be considered in the future.
On-line Industry Survey Questions
Do you think that employees with university degrees in the following areas will add value to your organization? For each competence, can you assess its relevance to your organisation's activities in the railway sector.