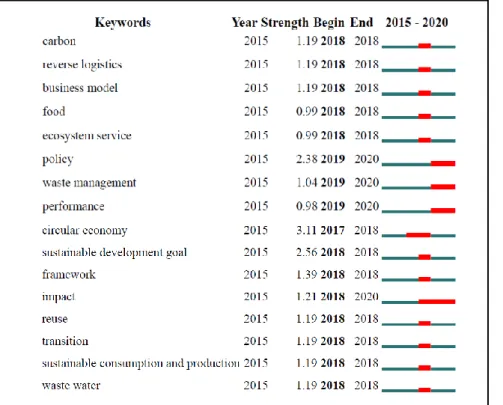
This brings forth the purpose of the study, which is to analyze the scientific literature related to the circular economy and the sustainable development goals in order to identify its main research trends. The concept of circular economy originates according to Martins-Rodrigues et al. 2020), in the thinking theory of the Economics of Sustainable Development (eco-development), based on the balance between economy and environment, called green economy and related to green jobs (Sulich, Rutkowska, & Popławski, 2020). Although, we can consider its peak in 2015 which was fundamentally characterized by the circular economy action plan of the European Union, the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement.
In this sense, companies must include circular economy guidelines in their mission: the promotion of research, sustainable development, innovation and cooperation strategies, which are the basis of a circular economy. It is clear that the transition from a linear economy to a circular economy requires changes at the heart of the company. Based on these practices, the circular economy can contribute to sustainability by affecting the reduction and reuse of resources and environmental degradation (Babbitt et al., 2018).
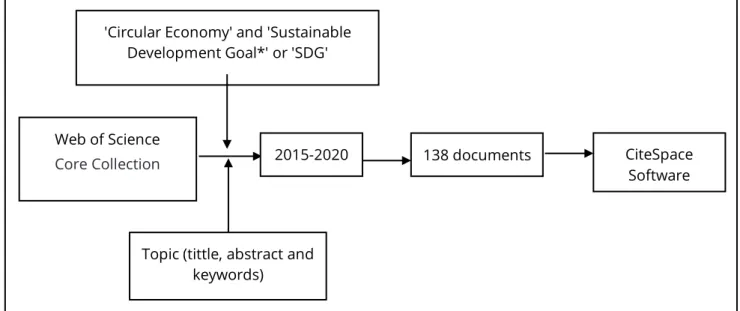
However, it is important to note that in recent years, the circular economy has gained increasing attention as a tool for an integrative and multidisciplinary approach, presenting itself as a solution to some of the most pressing challenges globally in the context of sustainability. development. The bibliometric analysis should be systematic, having a fundamental role for Greenhalgh (1997), Café & Bräscher (2008) and Pimenta, et al. 2017) in the analysis of the performance and behavior of the production of scientific knowledge, and should be derived from primary studies;. The term is used in quotation marks to ensure that the terms appear identically in search results.
CiteSpace software was used as it is one of the most prominent tools for network analysis.
4 RESULTS
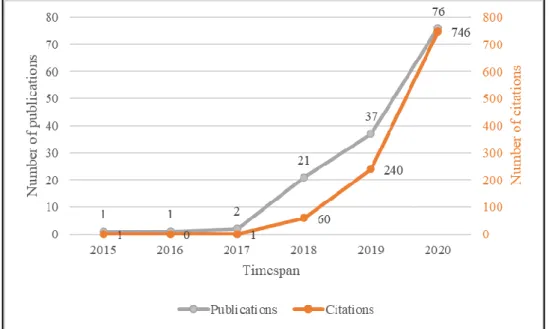
- Temporal distribution
- Research categories
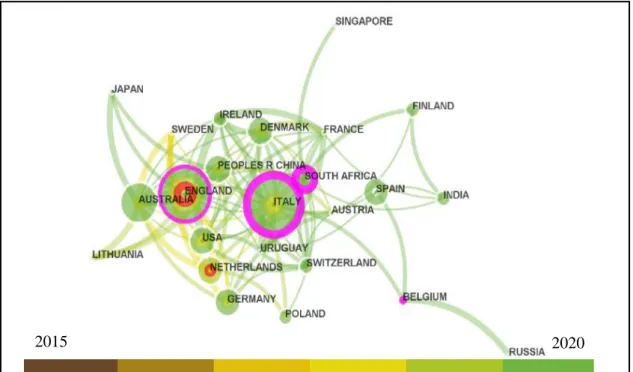
- Countries
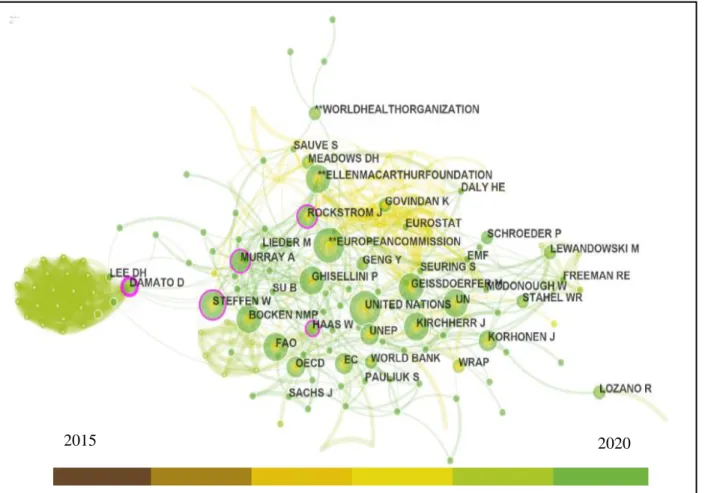
- Authors co-citation analysis
- Main keywords
- Thematic clusters
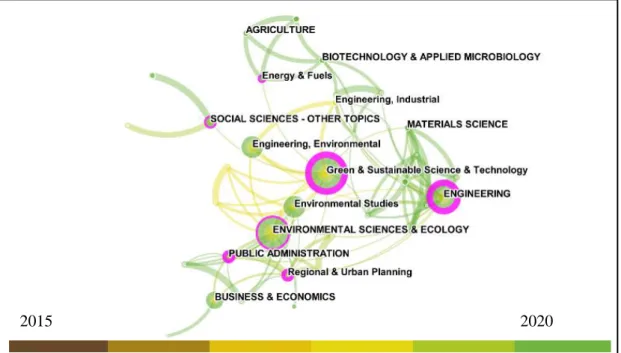
First, we analyze the thematic areas of circular economy and sustainable development topics in the period 2015-2020. According to Figure 3, the main research categories in circular economy studies and sustainable development goals demonstrate a multidisciplinary field, marked by research areas such as engineering, sustainable sciences and green technologies, environmental sciences and ecology, public administration , urban and regional planning, social sciences and energy and fuels. In view of this, it is evident that researchers of the circular economy and sustainable development goals must consider the need to articulate multiple scientific knowledge.
The most cited articles in the environmental science and technology category are: (Schroeder et al., 2019) with 136 citations and (Nosratabadi et al.,. In the business and economics category the most cited article is by (Goyal et al. , 2018), with 36 citations. The article by authors of Italian origin with the highest number of citations deals with food waste (Corrado & Sala, 2018); the article with the highest number of citations with at least one English author (Schroeder, Patrick) deals with the intersection of circular economy for sustainable development goals (Schroeder et al., 2019) and finally, the article, one of the authors of which is South Africa (Dhir & Amandeep), deals with bibliometrics and content analysis discussions on sustainable manufacturing practices (Bhatt et al., 2020).
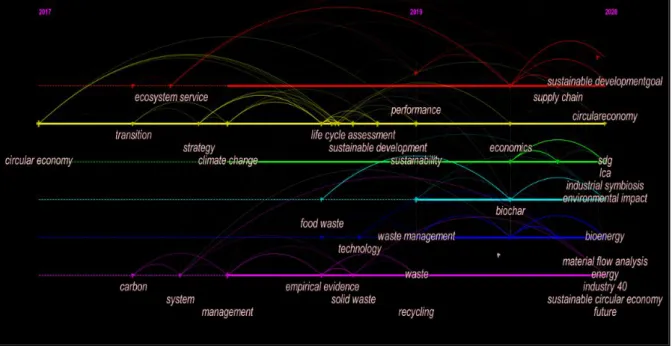
This analysis aims to verify the intellectual structure of the field of study in circular economy and SDGs, and they differ from co-authored maps in that the ACA has as its object of analysis the works found in the references of the examined works, and not the authors of the study. With this, it is clear that the keyword that has the most use in terms of citations is "circular economy", which is relatively expected when you consider that it was one of the words used in the study. In addition, the keywords in the thematic clusters and in the timelines represent research trends in circular economy studies and sustainable development goals.
circular economy; environment; resource recovery; commercialization; techno-economics; waste; circular practices; material flow analysis; urban environment;. circular economy; sanitation; wetlands; treatment of wet areas; resource; life cycle management; sustainable development goals; electronic equipment; sustainable waste management; municipal solid waste, sustainability; sustainable development. To this end, the use of information and communication technology and big data tools is becoming apparent, culminating in Industry 4.0 as a catalyst of the circular economy in favor of achieving the SDGs.
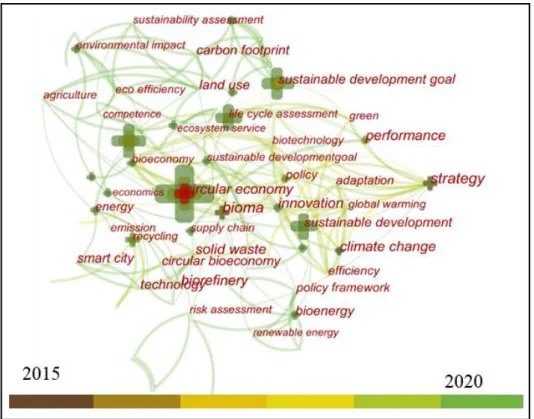
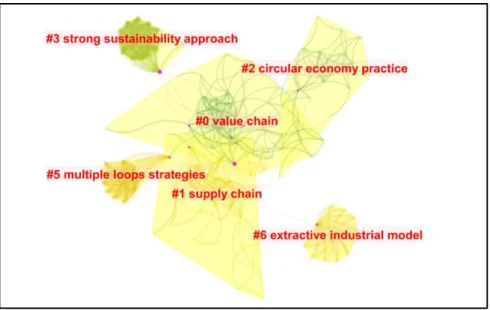
In the field of studies on circular economy and SDGs, 43 clusters have been identified, six of which are described in Figure 9 and will be discussed. In group 1, the supply chain is considered essential to reduce impacts, to enable the functioning of the circular economy in favor of the SDGs, where one of the most recent works addresses discussions on future demand for copper, recycling and gas emissions. To this end, works in this cluster, the work of Priyadarshini & Abhilash (2020) deal with waste management and policies capable of promoting circular economy practices in waste and energy sectors.
The work of Barroso et al. 2020), shows research on circular economy practices in the context of agricultural waste, given that the reuse of agricultural waste is very important for a circular economy. Finally, cluster 6 concentrates studies in which the circular economy is seen as confronting the current waste-based extractive industry model, such as the work of Schroeder et al.
5 FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
Regarding cluster 3, sustainability is the main theme, the most important work of which in terms of citations is that of Bhatt et al. The analysis of keywords and groupings shows that the intersection between environmental education, practices favoring waste reduction and the use of technologies for cleaner production is central to studies on circular economy and SDGs. This work achieves the goal of presenting an overview and characteristics of this field in the international context, enabling researchers to investigate trends in new themes and opportunities.
This study is the first that we are aware of to perform a skenometric and bibliometric analysis aligning the two topics, SDG and CE. Thus, we contribute to the literature while revealing key research trends, identifying research potential. Although this paper contains advances, it also has limitations, among which the use of a smaller amount of pure bibliometric indicators stands out, since the analysis of social networks was prioritized.
With the pandemic process, future studies will come out and for the next few years, important results can be published in leading journals, in particular, topics related to: 'SDG 3 - Health and well-being' as the coronavirus pandemic has done. affected the health and quality of life of the world's population; 'SDG 4 - Quality Education' can be addressed in light of the impacts of the pandemic on formal education; "SDG 9 - Industry, innovation and infrastructure" and "SDG 17 - Partnerships and means of implementation" could represent an area in which innovation processes and cooperation for vaccines are investigated.
In Ulas Akkucuk, (ed.) The circular economy and its implications for sustainability and the green supply chain (66-83). 2015), A Carbon Market Sensitive Optimization Model for Integrated Forward-Reverse Logistics, International Journal of Production Economics. Accounting for food waste along global and European food supply chains: state of the art and prospects.
An overview of the circular economy: the expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. Achieving Sustainable Development Goals by Identifying and Analyzing Barriers to the Industrial Sharing Economy: A Framework Development. Business models of the circular economy in emerging economies: lessons from India on reduce, recycle and reuse paradigms.
A new holistic conceptual framework for performance evaluation of green supply chain management based on the circular economy, Journal of Cleaner Production. Green jobs, defining issues and youth employment: An analysis of three European Union countries. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: "Our Common Future". United Nations General Assembly.
Institution: Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro Santana Canoas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasilien. Institution: Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brasilien. Doctor in Business Administration fra Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro Orcid: https://orcid.org.
Master i Business Administration fra Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro Orcid: https://orcid.org.