The full text of the thesis is available in the relevant libraries in the Faculty of Science at Charles University. The main focus of my thesis is on the role and expression of P2X and P2Y receptors in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) of the hypothalamus, which produces the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin, and the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which controls the circadian rhythm in many physiological functions. The second part of my thesis is focused on the role of P2X7 and P2Y receptors in the mechanism of circadian ATP release from SCN astrocytes.
Ivetic M, Bhattacharyya A and Zemkova H (2019) P2X2 receptor expression and function are up-regulated in the rat supraoptic nucleus stimulated through refeeding after fasting.
Úvod
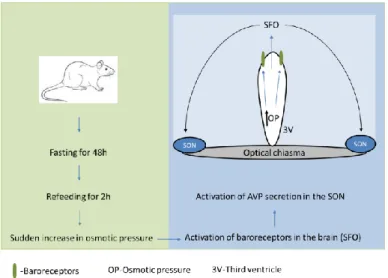
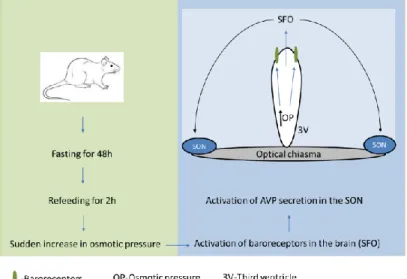
8 Dokrmování po hladovění představuje komplexní stimulaci sekrece hormonů zahrnující objemové/baroreceptory a periferní/centrální osmoreceptory (obrázek 2). Potravinová deprivace po dobu 48 hodin způsobuje pokles hladiny AVP v SON, zatímco zvýšená osmolalita plazmy s příjmem potravy (po 48 hodinách hladovění) stimuluje baroreceptory v neuronech mozkového subfornálního orgánu promítajícího se do SON (obr. 2). ) a způsobuje zvýšení plazmatických hladin AVP (Lucio-Oliveira et al., 2015) a oxytocinu (Lucio-Oliveira a Franci, 2012). Tento typ signalizace je široce používán v somatických a nervových tkáních (Khakh a North, 2006; Illes et al., 2021) a přispívá také k vysoce komplexní regulaci endokrinního systému (Stojilkovic a Zemkova, 2013; Burnstock, 2014). . ).
Vysoká hladina exprese podtypů P2X2, P2X4 a P2X7 byla dokumentována v supraoptickém (SON) a suprachiasmatickém (SCN) jádru (Vavra et al., 2011; Bhattacharya et al., 2013), ale fyziologický význam těchto receptorů v hypotalamu stále není dobře pochopeno.
Cíle práce
Materiál a metody
Řezy byly kultivovány v neurobazálním médiu po dobu 7 dnů pro stabilizaci před zahájením měření extracelulární akumulace ATP (Svobodová et al., 2003). Primární kultury astrocytů SCN: Novorozené krysy ve věku 2–5 dnů byly usmrceny dekapitací, oblast SCN byla vyříznuta z ~600 μm tlustých hypotalamických řezů a buňky byly disociovány po inkubaci s trypsinem podle publikované metody (Watanabe et al., 1993; Svobodová a kol., 2003). Záznamy náplastí: ATP-evokované proudy a membránové potenciály byly zaznamenány z řezů SON pomocí standardní techniky náplasti s celobuněčnou náplastí za použití zesilovače Axopatch-200B (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA, USA).
ATP-stimulované proudy a spontánní miniaturní postsynaptické proudy (mPSC) byly zaznamenány z napěťově upnutých buněk v přítomnosti 0,5 μM tetrodotoxinu (TTX), který blokuje akční potenciály.
Výsledky a diskuse
Za druhé, ATP uvolněný ze zadní hypofýzy během elektrické stimulace depolarizuje nervová zakončení a zvyšuje sekreci AVP (Knott et al., 2008). 16 na druhé straně elektronová mikroskopie ukázala, že ne všechny axony v potkaním SON vykazují imunoreaktivitu P2X2 (Loesch et al., 1999). Je zajímavé, že glutamátem stimulované zvýšení [Ca2+]i v intaktních astrocytech zrakového nervu je významně inhibováno u myší P2X7 knock-out (Hamilton et al., 2008).
For example, food deprivation for 48 h and refeeding for 2–6 h reliably stimulate vasopressin synthesis and release (Burlet et al., 1992). The SON of mice was identified by position relative to the chiasma opticum ( Vavra et al., 2011 ). Slices were cultured in Neurobasal medium for 7 days before starting ATP accumulation assays to allow slices to stabilize ( Svobodova et al., 2003 ).
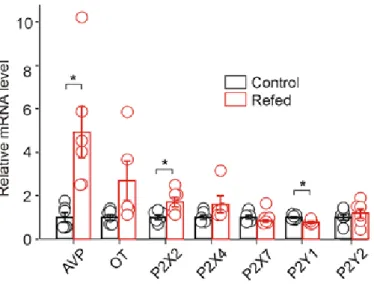
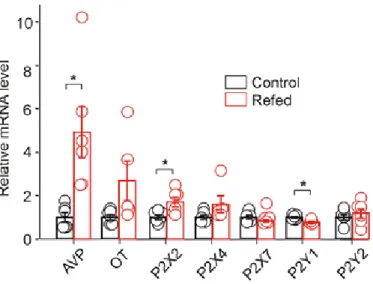
We examined the effect of 2 h of food intake after 48 h of starvation (Fig. 2) (Lucio-Oliveira et al., 2015) on AVP, oxytocin, P2X and P2Y mRNA expression and ATP-induced electrophysiological responses in SON neurons. in brain slices. P2X2 activation increases AVP release from explants of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system (Gomes et al., 2009; Troadec et al., 1998; Song and Sladek, 2006) and evokes somatic current in SON neurons from hypothalamic slices (V. alvraet). . , 2011). Second, endogenously released ATP from the posterior pituitary during electrical stimulation depolarizes nerve terminals and potentiates AVP secretion ( Knott et al., 2008 ).
Both P2X and P2Y participate in the ATP-induced increase in intracellular calcium in the SON cells ( Song et al., 2007 ) and P2Y has been reported in rat SON astrocytes ( Espallergues et al., 2007 ). On the other hand, electron microscopy observation showed that not all axons in the rat SON display immunoreactivity to P2X2 (Loesch et al., 1999). GABA innervation appears to play a role in patterning the pulsatile discharge of oxytocin neurons (Voisin et al., 1995; . Moos, 1995; Brussaard and Kits, 1999).
Several P2Y receptors (P2Y1, P2Y2 and P2Y12) have been detected in the SCN at the transcriptional level (Bhattacharya et al., 2013). ATP application was previously found to modulate the synaptic activity of SCN neurons and potentiate GABA release via presynaptic P2X2Rs ( Bhattacharya et al., 2013 ). Surprisingly, the glutamate-evoked increase in astrocytic [Ca2+]i in the intact optic nerve is significantly reduced in P2X7R knockout mice (Hamilton et al., 2008).
Závěr
Introduction
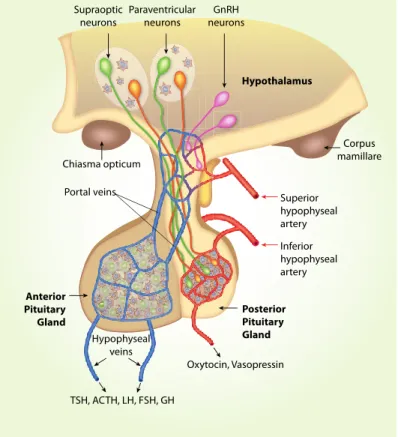
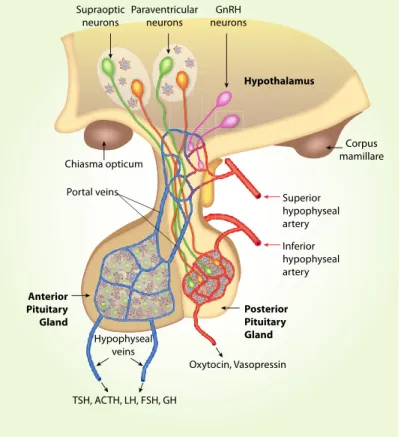
The hypothalamus contains many small nuclei involved in various specific endocrine functions and the regulation of circadian rhythms. One of the main systems involved in endocrine functions is the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system (Figure 1), which produces the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin. Through the action of its hormones at the level of the central nervous system, it establishes control over related behaviors such as maternal care (Taylor et al., 2017; Iovino et al., 2021).
The hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system exhibits considerable plasticity as a function of endocrine state, and is often used as a model system for investigating neuropeptide secretion. 25 Refeeding after fasting represents a complex stimulation to hormone secretion involving the volume/baroreceptors and peripheral/central osmoreceptors (Fig. 2). Food deprivation for 48 hours causes a decrease of AVP level in the SON, while increased plasma osmolality by food intake (after 48 hours of fasting) stimulates baroreceptors in neurons of the brain subfornical organ projecting to the SON (Fig. 2), and elicits elevation of plasma AVP (Lucio-Oliveira et al., 2015) and oxytocin (Lucio-Oliveira and Franci, 2012).
Extracellular ATP (adenosine-5'-triphosphate) and its degradable products ADP (adenosine-5'-diphosphate) and adenosine, together with purinergic receptors are involved in the signaling network called "purinergic signaling" which is widely used as in both somatic and neuronal tissues. (Khakh and North, 2006; Illes et al., 2021), and also contributes to the highly complex regulation of the endocrine system (Stojilkovic and Zemkova, 2013; Burnstock, 2014). ATP and its metabolites act as extracellular ligands for two specific receptor families called P1, if activated by adenosine, or P2, if activated by ATP or ADP (Burnstock, 2006a). Hypothalamic and pituitary cells release ATP and express multiple P2X and P2Y receptors (Stojilkovic, 2009; Stojilkovic and Zemkova, 2013; Burnstock, 2014).
The high level of expression of P2X2, P2X4 and P2X7 subtypes has been documented in the supraoptic (SON) and suprachioasmatic nuclei (SCN) (Vavra et al., 2011; . Bhattacharya et al., 2013), but the physiological importance of these receptors in the hypothalamus is still not well understood. Refeeding after fasting represents a complex stimulation of hormone secretion involving volume/baroreceptors and peripheral/central osmoreceptors.
Aims of the study
Material and methods
Organotypic culture preparation: Coronal hypothalamic sections (~350 μm thick) were cut from approximately 1x1 mm tissue blocks containing the SCN using a vibratome (DTK-1000, D.S.K. Dosaka, Japan). Three slices were cut from one animal and then transferred to one 0.001 mm pore size cell culture cartridge (BD Falcon, Tewksbury, MA, USA). 3-slice culture inserts, hereafter referred to as organotypic cultures, were placed in 6-well plates (BD Falcon) and immersed in 1 ml of Neurobasal A-based medium saturated with a mixture of 95% air and 5% CO2.
During this time, organotypic SCN cultures retain the clear organization of SCN cells along the dorsoventral axis. SCN regions were dissected from ∼600-μm-thick hypothalamic slices, and cells were detached after treatment with trypsin, according to published methods ( Watanabe et al., 1993 ; Svobodova et al., 2003 ). Cells were then purified on a discontinuous protein gradient and approximately 100,000 cells were plated on coverslips coated with a 1% poly-L-lysine solution (Sigma) in 35 mm culture dishes (BD Falcon) and cultured in Neurobasal A medium with 2. % B27 supplement and 0.5 mM L-Glutamine in a humidified CO2 atmosphere at 37°C until use (14-21 days).
Patch clamp recordings: ATP-induced currents and membrane potentials were recorded from SON slices using standard whole-cell patch clamp techniques with an Axopatch-200B amplifier (Axon Instruments, Union City, CA, USA). Average cell capacitance was 6–8 pF, 50–80% series resistance compensation was used, and the liquid junction potential (~4 mV) calculated with CLAMPEX 9 was corrected offline when determining the resting membrane potential of the SON cell . Data were captured and stored using the pClamp 9 software package in conjunction with a Digidata 1322A A/D converter (Axon Instruments).
The ATP-induced currents and spontaneous miniature postsynaptic currents (mPSCs) were recorded from voltage-clamped cells in the presence of 0.5 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX) used to block action potentials. In the case of multiple groups, comparison was made using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test in SigmaStat 2000 v9.0 (Systat Software, San Jose, CA, USA, RRID:SCR_ 010285), for comparison with a single control.
Results and discussion
P2X2, P2X4, P2X7, P2Y1, and P2Y2 receptors and AVP and oxytocin (OT) expression in the SON were normalized to the control group. In the presence of 0.5 µM TTX, whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings showed that under our experimental conditions both mEPSCs and mIPSCs could be recorded as small inward currents differing in their amplitudes and decay time constants (Vavra et al., 2011) . The difference between control and fasted/refed rats in the ATP-induced increase in mIPSC frequency was significant (two-way ANOVA, p<0.05), but there was no difference in the ATP-induced increase in mIPSC amplitude.
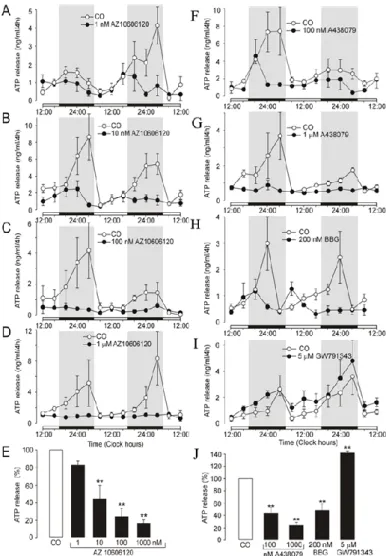
34 changes in the pattern of the discharge of AVP neurons in vivo, such that the synthesis and release of AVP is increased. In the second part of the thesis, we tested the hypothesis that P2X7 and P2Y receptors play a role in circadian ATP release from SCN astrocytes. Extracellular ATP accumulation was incompletely inhibited in the presence of selective inhibitor of the mitochondrial Na + -Ca 2+ exchange transporter CGP37157 (not shown), indicating that ATP is released as a transmitter, not as a metabolite.
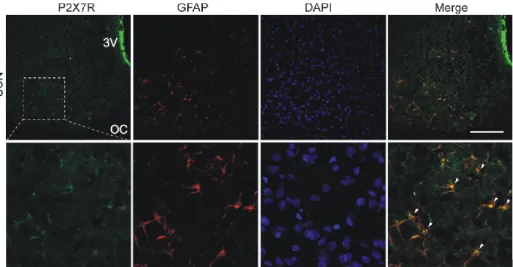
These results indicated that P2X7 receptors play an important role in circadian accumulation of extracellular ATP in SCN organotypic cultures, and astrocytes represent a source of P2X7-dependent circadian ATP release. The results in the second part of my thesis showed that the circadian rhythm of ATP release peaked in the opposite phase of the day, during the previously described AVP secretory rhythm, which peaked at about 12:00. These results also indicated that the P2X7 receptor, pannexin-1 hemichannels, and metabotropic P2Y receptors participate in circadian ATP release in the SCN.
On the other hand, extracellular ATP and its metabolites may act as paracrine modulators in the SCN. Currently, no evidence has been reported to suggest day-night variability in the expression of P2X7R mRNA or protein in the SCN. Refeeding after fasting upregulates P2X protein levels on cell somata and presynaptic nerve terminals that release GABA on putative AVP neurons in the SON.
Loesch A, Miah S, Burnstock G (1999) Ultrastructural localization of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system.
Conclusions