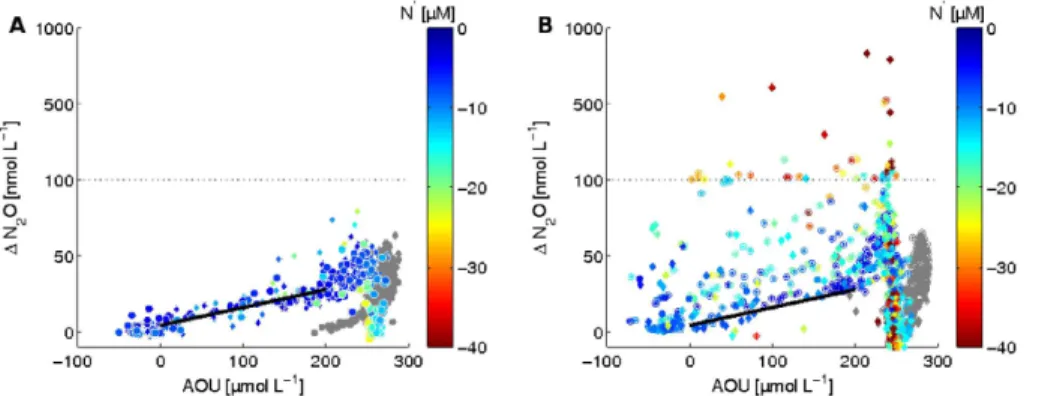
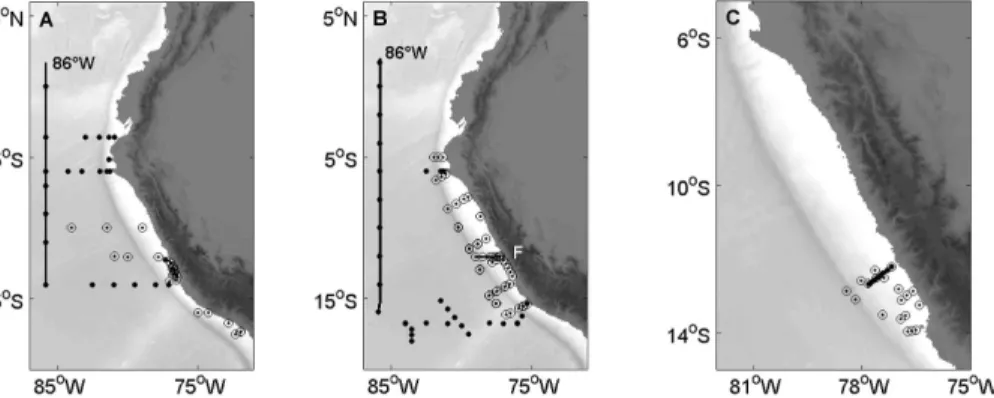
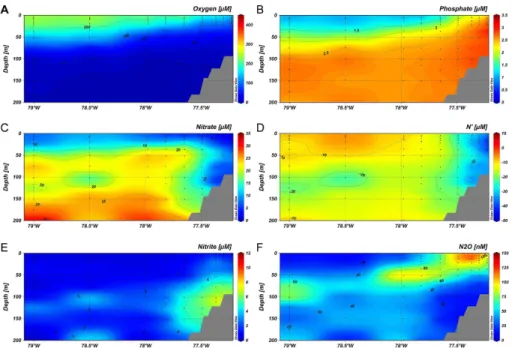
Differences between coastal and open ocean distributions of N<sub>2</sub>O in the oxygen minimum zone off Peru
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
To validate results obtained from a local scale off Chile for the OMZs at the global scale (Paulmier and Ruiz-Pino, 2008), the DIC structure was determined in the permanent OMZs in
The methods detailed in section 2 were used to measure OH product yields for the reactions of a number of other substituted peroxy radicals with HO 2. Note that simulation of
no differences between our two groups in terms of the minimum SaO 2 or oxygen desaturation, the mean SaO 2 was lower in the NREM-related OSA group than in the REM-related
The middle section is characterized by a mixing zone with higher turbidity and chlorophyll- a concentrations, medium concentrations of DIN and dissolved oxygen;
We present in situ benthic phosphate fluxes, particulate matter C / P ratios for water-column particles and surface sediments and P burial fluxes, and relative abundances of
The framework is based on a mass balance ap- proach and given that for Europe most of the components have been independently estimated, di ff erent accounting schemes may be used
Here, we investigate the potential evolution of marine N 2 O emissions in the 21st century in response to anthropogenic climate change using the global ocean biogeochemical
PAN is the most possible compound to interfere the TD-CIMS measurements in this study, not only due to its relatively high ambient abundances but also because it can escape