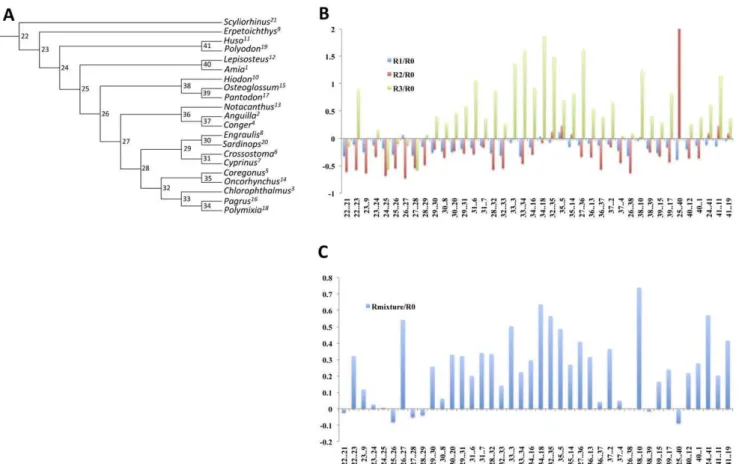
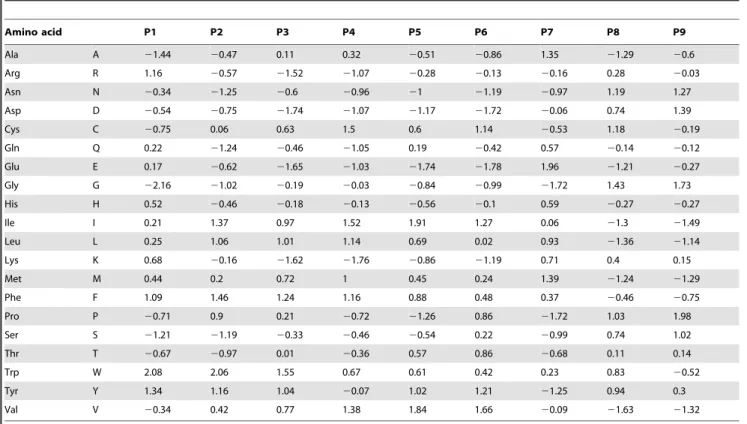
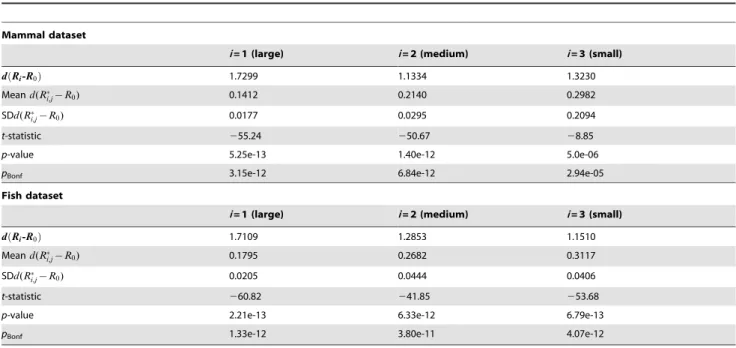
Improving evolutionary models for mitochondrial protein data with site-class specific amino acid exchangeability matrices.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
For matrices with real entries, orthogonal matrices and symmetric matrices play an important role in the orthogonal diagonalization problem.. For matrices with complex entries,
Although the current NRC (2007) increases calcium and phosphorus intakes for mature horses receiving light exercise, it did not do the same for two year old horses that are
This experiment was conducted with the objective of evaluating the solubility of nepheline syenite and glauconite as a function of three organic matrices, humic acid, citric acid
Comparison of N-terminal amino acid sequence of Neisseria meningitidis class 1 (C1) protein with deduced and translated meningococcal class 1 proteins... of the organism in
A prominent class of these matrices over the simplest finite or Galois field GF (2) is the class of involutory or Self-Inverse (SI) matrices, which are matrices for
Também a questão da heteronímia constitui o cerne das reflexões de Nuno Ribeiro, já agora voltadas para uma interessante relação estabelecida entre os fundamentos da criação
O objetivo deste estudo foi revisar na literatura atual os métodos e variáveis do consumo máximo de oxigênio/potência aeróbia e aspectos relacionados com a capacidade aeróbia