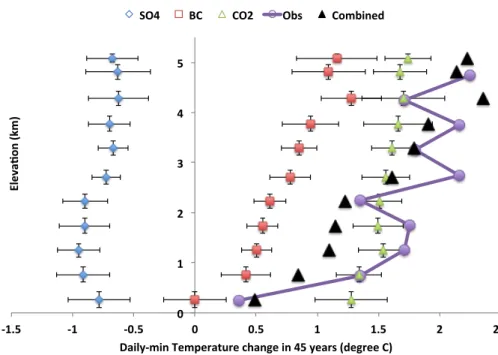
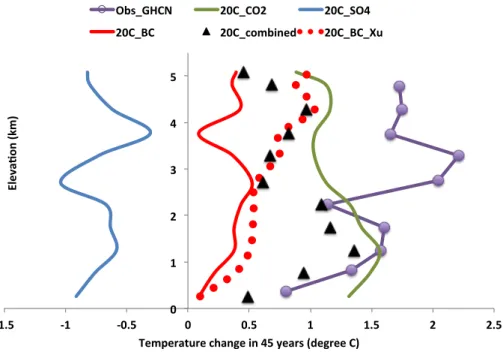
Observed high-altitude warming and snow cover retreat over Tibet and the Himalayas enhanced by black carbon aerosols
Texto
Imagem
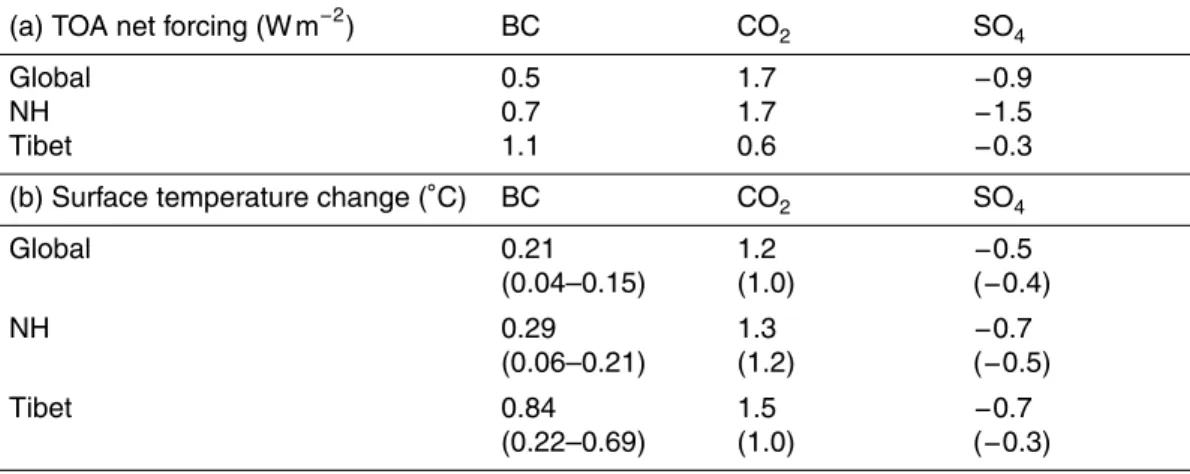

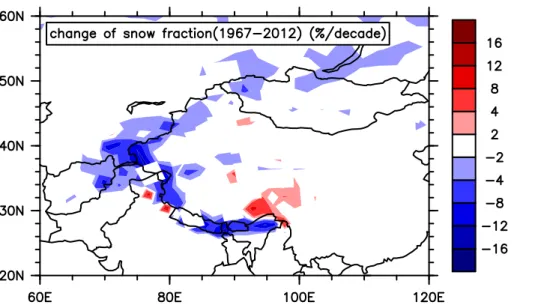

Documentos relacionados
Anthropogenic aerosols are typically composed of various inorganic and organic species (IPCC, 2007), among which sulfate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols including black carbon
Centre Global Climate Model, comparing it to an ob¬ served climatology, for the present period 1961-1990. The differences between the GCM and
As these basic aerosol properties (chemistry, size, shape and mixing state) can seriously affect the optical proper- ties calculation, in the following sections we discuss: (1)
The modelled campaign- mean total particle number concentration is within a factor of 2 of the PCASP observations in the model-defined size range of coated BC particles, which is
The main aerosol components produced from road, shipping and aircraft transport are: black carbon (or soot) which we will refer as BC, organic carbon (OC) and sulphate.. A recent
To establish the extent to which a snow cover will mitigate the albedo e ff ect of black carbon in sea ice two di ff erent Arctic snow types (also described by Grenfell and
According to China Energy Statistics Yearbook 2006, percentage of diesel ve- hicles in Shanghai area was about 2 times higher than that in Beijing, and diesel fuel consumption was
mean (middle right) surface albedo changes due to BC in snow from the 1950s to 2000s, and annual mean (bottom left) and spring mean (bottom right) surface albedo changes due to