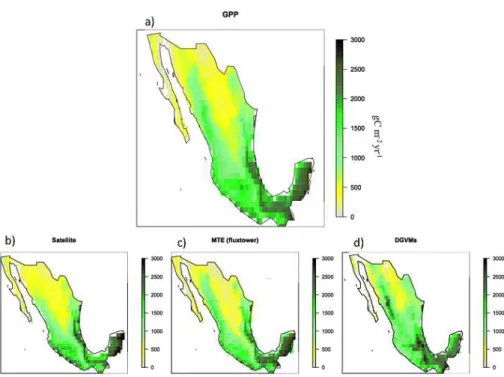
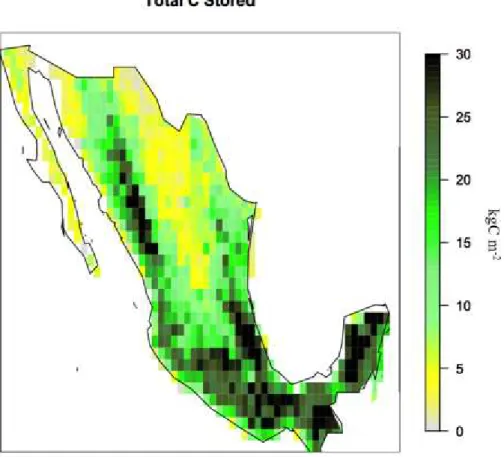
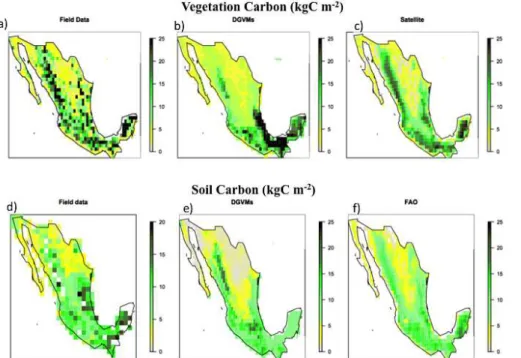
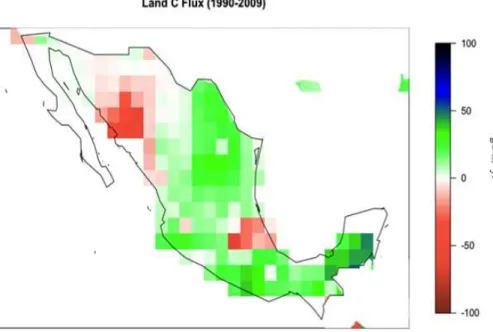
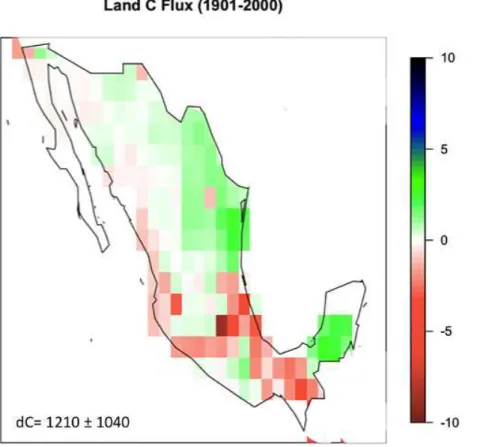
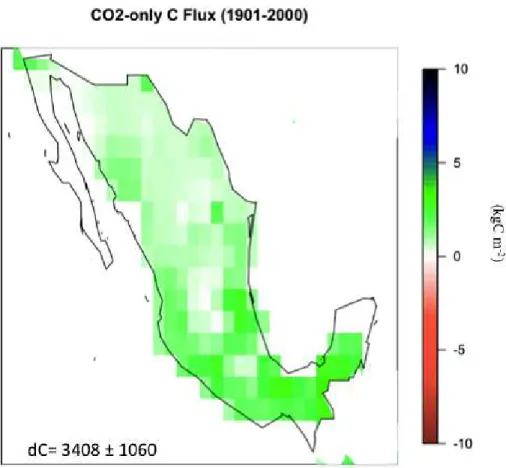
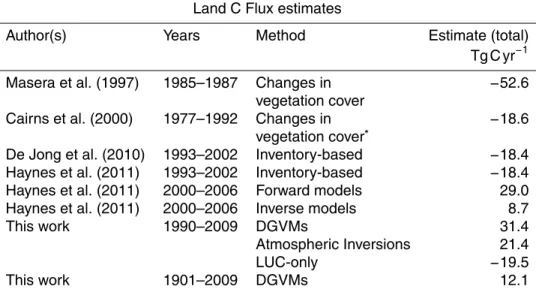
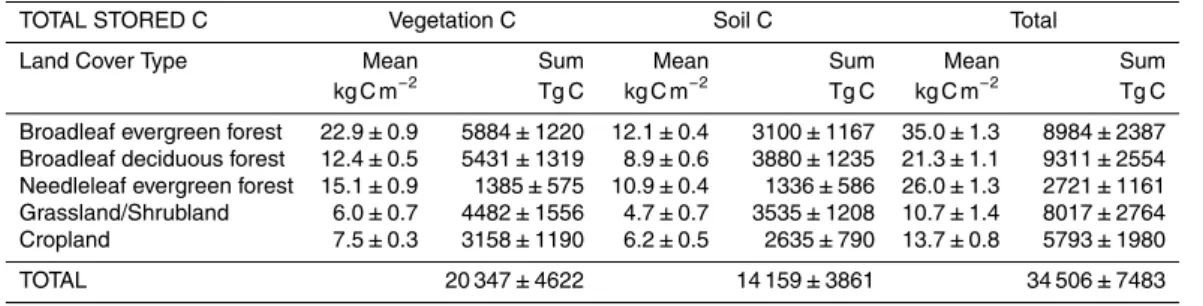
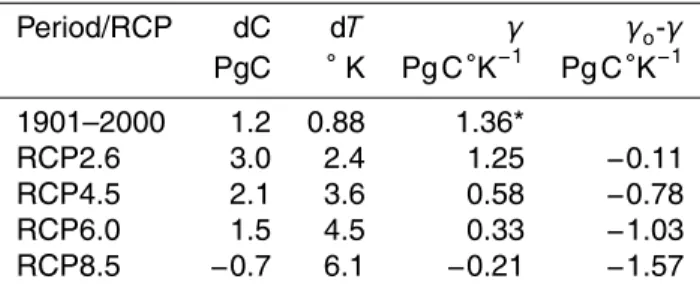
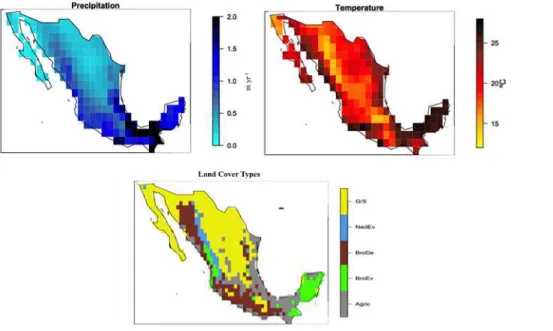
The carbon cycle in Mexico: past, present and future of C stocks and fluxes
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
In a di ff erent study with a di ff erent model, inclusion of tropospheric bromine, iodine and chlorine chemistry led to topical tropospheric marine average O 3 columns to decrease
Ratio of calculated to measured CCN number concentrations as a function of organic mass fraction for seven di ff erent data sets and di ff erent assumptions of hygroscopicity and
The future challenge is to detect rapid changes in surface composition and land cover of saline environments, with adequate precision and at di ff erent temporal and spatial
o ff sets between di ff erent surface types and small thermal o ff sets in general (exclud- ing wetlands and peat), (ii) a clear influence of the micro-topography at wind exposed
accumulation time: time for increase of stocks from zero to 95% of equilibrium stock In the equilibrium experiment we prescribed di ff erent current assimilation rates and
Accumulated chemical loss in column ozone for di ff erent altitude intervals and di ff er- ent months in winter 1991–1992, derived using ER-2 aircraft measurements, HALOE
hence the incorporation of trace gases, vary between di ff erent laboratory experiments, and presumably between the di ff erent conditions encountered in clouds and in snow-
Summary of the di ff erent formulae used to estimate BGE, directly from data points (experimental) or with three models (Monod, Marr-Pirt and DEB models) for the pulse (P) and batch