Extracellular Matrix Molecular Remodeling in Human Liver Fibrosis Evolution.
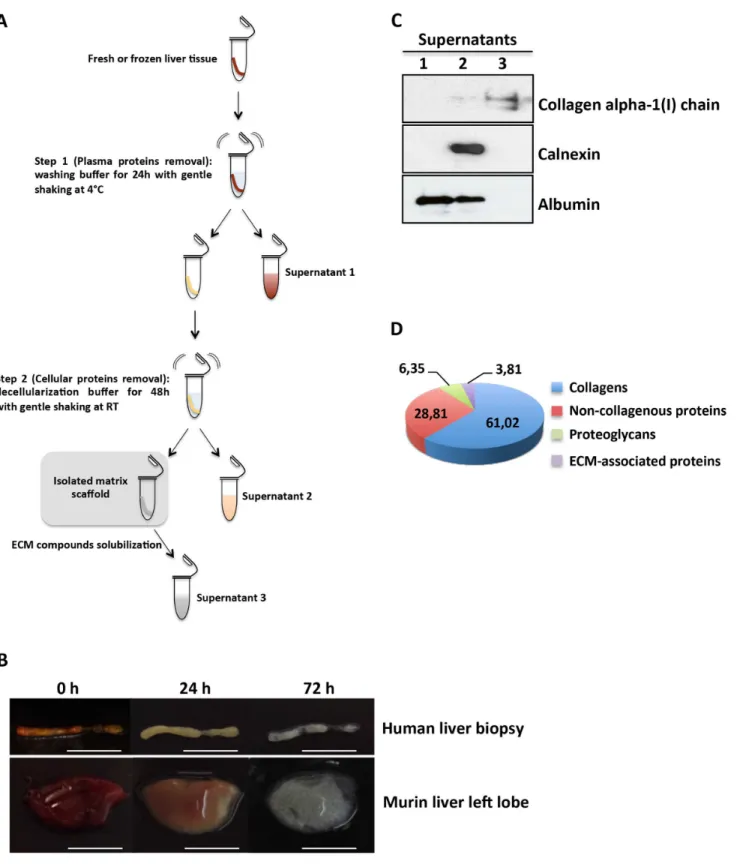
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
To further investigate this possibility, a com- parative study of size, appearance and matrix com- position of granulomas formed in three different organs of mice (liver, intestine
Alternatives to the stimulation of active pro- liferation and functional islets in vitro are based on cell culture strategies, namely the use of extracellular matrix (ECM) elements
Noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis should be performed in cases of (i) contraindication or difficult access to liver biopsy, (ii) the need for such monitoring in order to
In conclusion, we have shown that APRI could identify significant fibrosis and cirrhosis at a high degree of accuracy in studied patients compared with liver biopsy..
Noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis should be performed in cases of (i) contraindication or difficult access to liver biopsy, (ii) the need for such monitoring in order to
Biologic scaffold materials composed of mammalian extracellular matrix are commonly used in regenerative medicine and in surgical procedures for the reconstruction of numerous
Right: quantitative analysis of the extracellular matrix of cryopreserved pulmonary cusps and subjected to decellularization process.. A - Control: cryopreserved and not subjected
Acoustic radiation force impulse is equivalent to liver biopsy to evaluate liver ibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rockey
