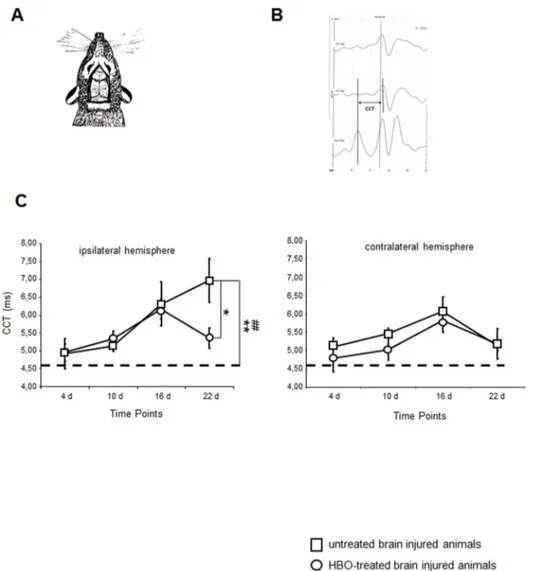
Repetitive long-term hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) administered after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats induces significant remyelination and a recovery of sensorimotor function.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
To: Measurement of intracranial pressure and short-term outcomes of patients with traumatic brain injury: a propensity-matched analysis.. LETTER TO
Tal circunstância, além de ser vista como penosa para os próprios AO’s (responsáveis pelo transporte e distribuição deste tipo de produtos pelas várias unidades do
Em Java, esses conteineres são denominados panels (Painéis em português), e são representados pela classe JPanel. No exemplo, serão usados dois panels, um para o campo do Visor,
However, weight drop impact dramatically increased brain water content which was observed as early as 3 hours and peaked at 24 hour after injury, suggesting a
Effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on mitochondrial function of neuronal cells in the cortex of neonatal rats after hypoxic-ischemic brain damageL. Hu
Changes in cardiac aldosterone and its synthase in rats with chronic heart failure: an intervention study of long-term treatment with recombinant human brain natriuretic
Within hyperbaric therapies, Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is the administration of pure oxygen (100%) at pressures greater than atmospheric pressure for therapeutic reasons
High risk of hypopituitarism after traumatic brain injury: a prospective investigation of anterior pituitary function in the acute phase and 12 months after trauma. Cernak