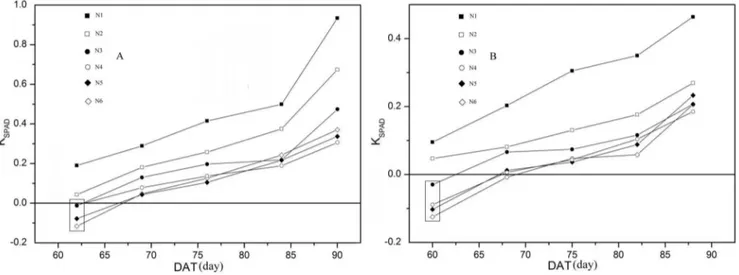
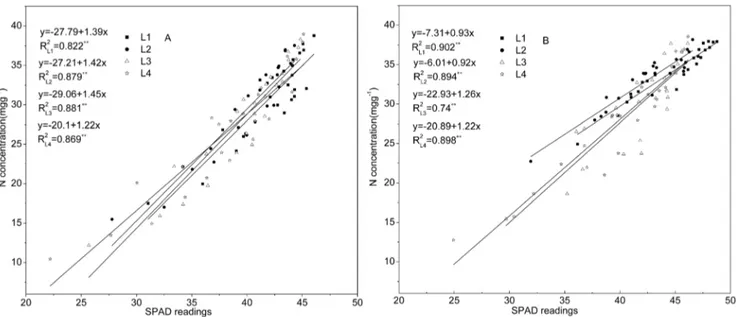
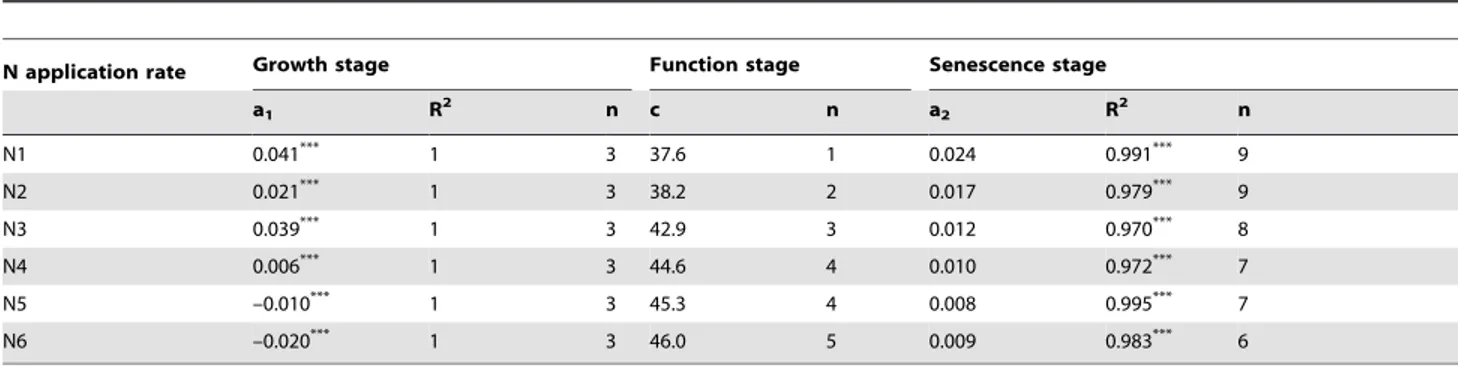
Effects of nitrogen application rate and leaf age on the distribution pattern of leaf SPAD readings in the rice canopy.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Relationship between plant top dry mass yield and nitrate reductase activity taken on the newly expanded lamina leaf (NL), in the first ( ) and second ( ) growth of the ‘Mombaça’
Abstract – The objective of this work was to determine the effects of rainfall, temperature, predators, parasitoids, plant age, leaf chemical composition, levels of leaf nitrogen
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of height of leaves in the canopy of plants, leaf organic compounds, concentrations of leaf nitrogen and potassium,
The objective of this study was to determine the effects of predators and parasitoids, height of canopy, plant age, leaf areas, organic compounds leaves, levels of leaf nitrogen
The probability of attending school four our group of interest in this region increased by 6.5 percentage points after the expansion of the Bolsa Família program in 2007 and
Tiller dynamics, number of green leaf blades, leaf blade length, leaf appearance rate according to the evaluation periods of ryegrass... In this case, as the blades were smaller
The distribution of leaf nitrogen, rubisco capacity (V cmax ) and electron transport (J max ) in the canopy is taken to decrease exponentially with cumulative leaf area index from
Effect of canopy height and leaf face on leaf damage (%) and on the numbers of thrips Frankliniella schulzei , Pseudococcidae and Coccidae leaf -1 face in Dimorphandra mollis