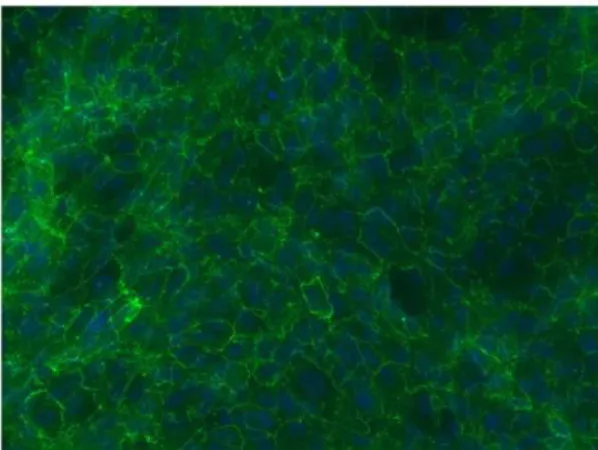
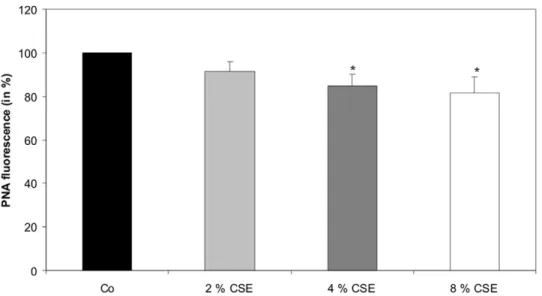
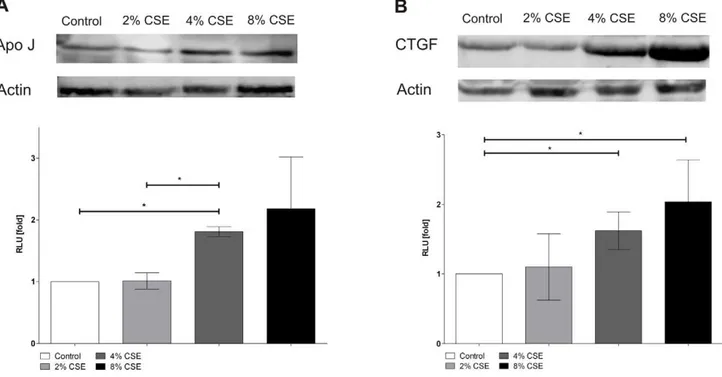
Biological effects of cigarette smoke in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
In this study, we showed that cigarette smoke exposure, even without the presence of tobacco, promoted lung inflammatory injury, as indicated by the presence of inflammatory cells
Objective: To investigate the acute effects of intravenous administration of cigarette smoke extract (CSE) on histological, inflammatory, and respiratory function parameters in
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of cigarette smoke on the production and characterization of exopolysaccharides (EPSs) produced by Bifidobacterium.. Cigarettes
The implanted bone matrix improved the process of reconstitution of the injured bone tissue in rats submitted to passive inhalation of cigarette smoke, mainly
The animal groups were as follows: Group I – 20 animals subjected to daily inhalation of cigarette smoke in the exposure chamber.. Animals in this group were subjected to smoke
The current knowledge regarding the effects of maternal smoking on the placenta suggests that exposure of placental villous explants to cigarette smoke extract results in
Embora nenhuma destas empresas atue no setor vinícola foi, em todo o caso, possível evidenciar as mais-valias da utilização de uma ferramenta de cálculo do custo total
present study, we evaluated the effect of chronic exposure to cigarette smoke on CK activity in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice, and the protective effect of