SPECTRUM SENSING IN COGNITIVE RADIO NETWORKS: QOS CONSIDERATIONS
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
distance vector are not well suited to be applied to CRNs. The main reason is that there are frequent dynamic changes in the CRN that may trigger a large number of
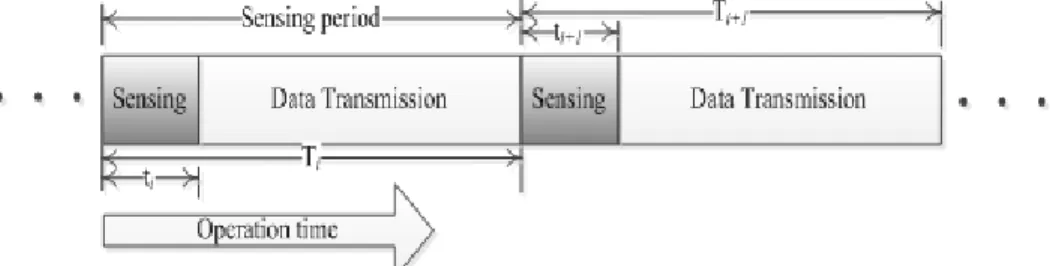
The overhead contains additional sensing time, delay, energy and sensing actions dedicated to cooperative sequential sensing any also contains any performance degradation that
The fact that the MI considers collocates with very low isolated frequency in the corpus to be the more significant ones can be misleading, like in the case of the collocation
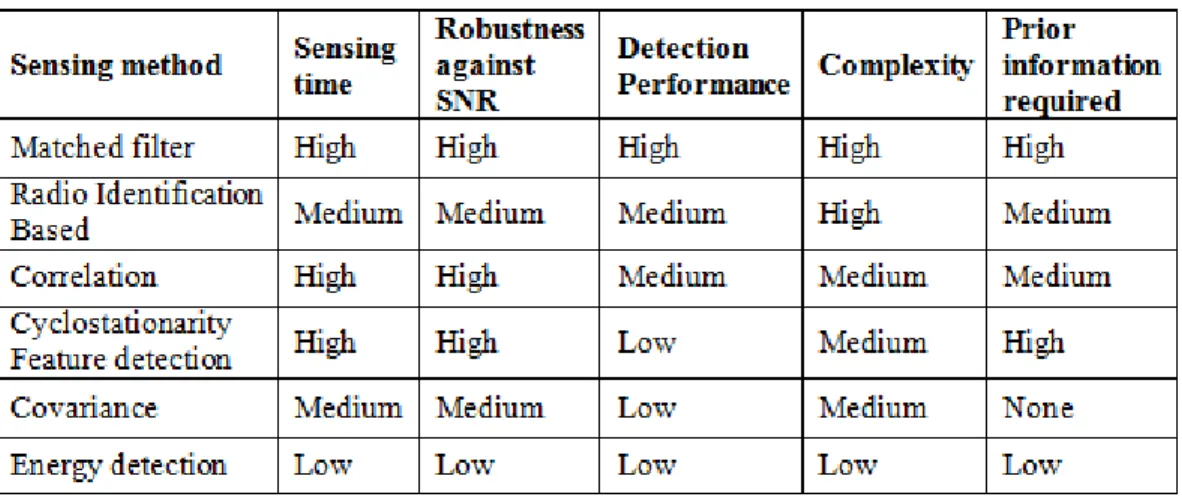
This scheme was proposed as a solution to the problem of noise uncertainty, fading and shadowing. This scheme decreases the probabilities of false detection and false
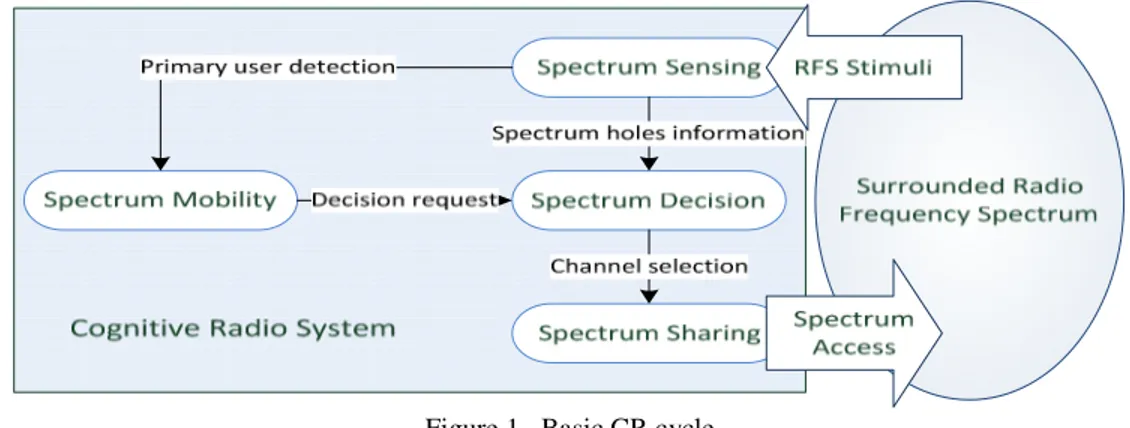
Cognitive Radio (CR) is a developing technology to overcome the problem of using the spectrum inefficiently by improving idle spectrum utilization in both temporally and spatially.
The observation chain (GSM data capture) used for the performance evaluation of the dynamic Bayesian network (DBN) in the modeling and prediction of channel usage
CR is an persuasive resolution to the spectral congestion crisis by establishing the opportunistic exploitation of unused frequency bands that are not significantly engaged through
By introducing the trust scheme into the fuzzy logic scheme to represent the reliability of the nodes, a cooperative spectrum sensing scheme based on trust and fuzzy logic for