Predictive Value of Carotid Distensibility Coefficient for Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis.
Texto
Imagem

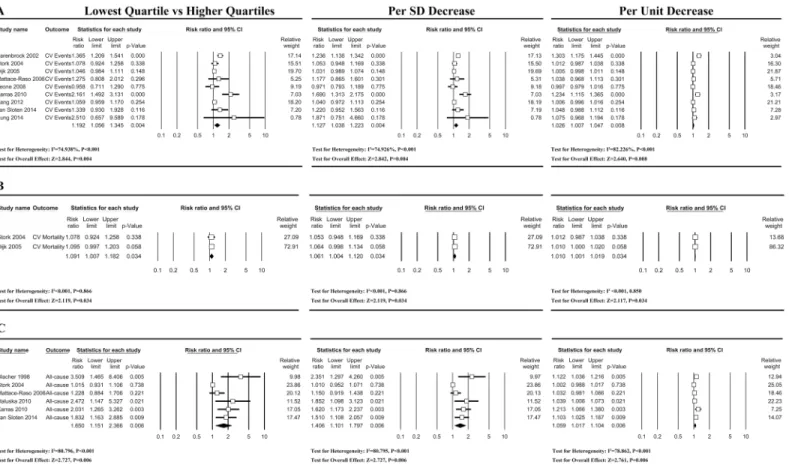
Documentos relacionados
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the beneits (such as reductions in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, major cardiovascular events, MI and stroke; and slow progression of CKD to
OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the beneits (such as reductions in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, major cardiovascular events, MI and stroke; and slow progression of CKD
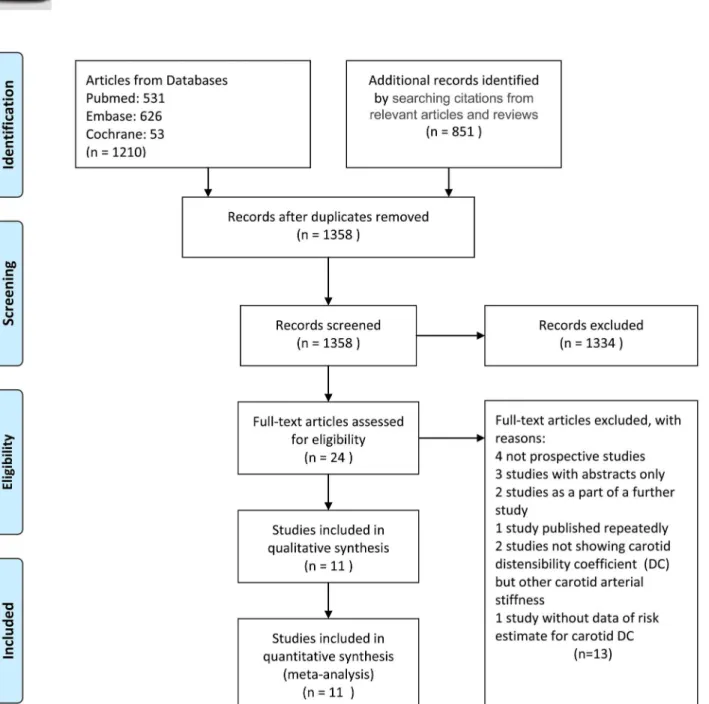
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they reported the long-term all-cause or cardiovascular mortality of chronic kidney disease patients with abnormally elevated serum
further study of mortality due to CRF, which was performed from 2000-2004, found that diabetes and cardiovascular diseases were the main un- derlying causes of death due to CRF;
In adults, an active lifestyle is associated to a reduction in the incidence of many chronic diseases, and a reduction in cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. In children
This study sought to evaluate the predictive value of resting (pre-exercise) heart rate for cardiovascular and all- cause mortality, establishing a cut-off value
In the present study, all questionnaires and evaluations were performed face-to-face, by a trained and qualified monitor. The dependent variable was the presence of
Thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism and risk of all-cause mortality, major bleeding, and intracranial hemorrhage: a meta-analysis.. Thrombolysis for acute submassive