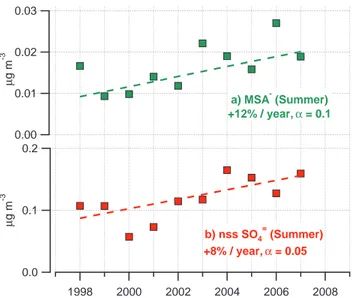
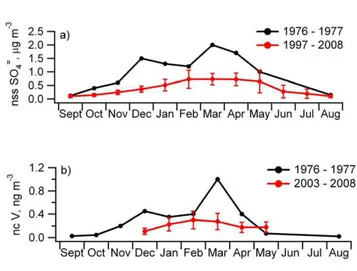
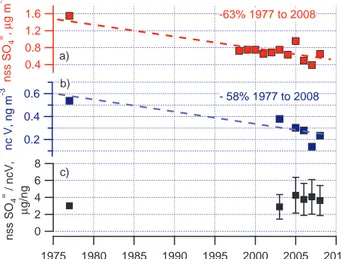
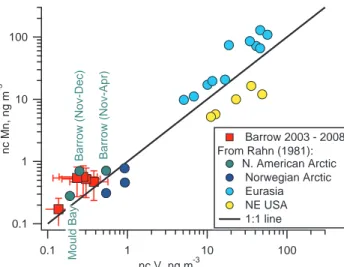
Decadal trends in aerosol chemical composition at Barrow, AK: 1976–2008
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
changes in wind speed over the ocean on aerosols characteristics using collocated measurements of aerosol number size distribution, mass concentration, and spectral aerosol
aerosol chloride signal was observed during sea sweep experiments when the source of the aerosol chloride was NaCl present in artificially generated sea salt aerosols even though
In addition to the comparison with hourly concentrations of AMS-derived marine or- ganic aerosol at an inland site, we have also evaluated terrestrial and total organic
The spatial distribution of aerosol chemical com- position and the evolution of the Organic Aerosol (OA) fraction is investigated based upon airborne measurements of aerosol
Measurements of aerosol chemical composition and aerosol optical depth in the Nepal Himalaya have clearly shown the build up of aerosols in the pre-monsoon season during the winter
(a) MODIS mean aerosol optical depth at 550 nm over Amazonia during the dry season (b) and mean direct aerosol radiative forcing of aerosols (DARF24h) during the peak of the
There was no, or only marginal, influence of continental or anthropogenic nss-SO 2− 4 south of the ITCZ and the variation in concentration was attributed to variation in the
The well- predicted aerosol quantities, such as aerosol number, mass composition and optical properties, and the inclusion of full aerosol-cloud couplings lead to