Review of Survey activities 2006: A multi-disciplinary study of Phanerozoic landscape development in West Greenland
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
The geophysical model for the floor of the intrusion has the same dip as the regional strata of 10–20°S but also shows a dip of around 15° towards the east that is unexpected from
In 2004 the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (GEUS) initiated a study of the origin and tectono-meta- morphic evolution of greenstone belts and important regio- nal
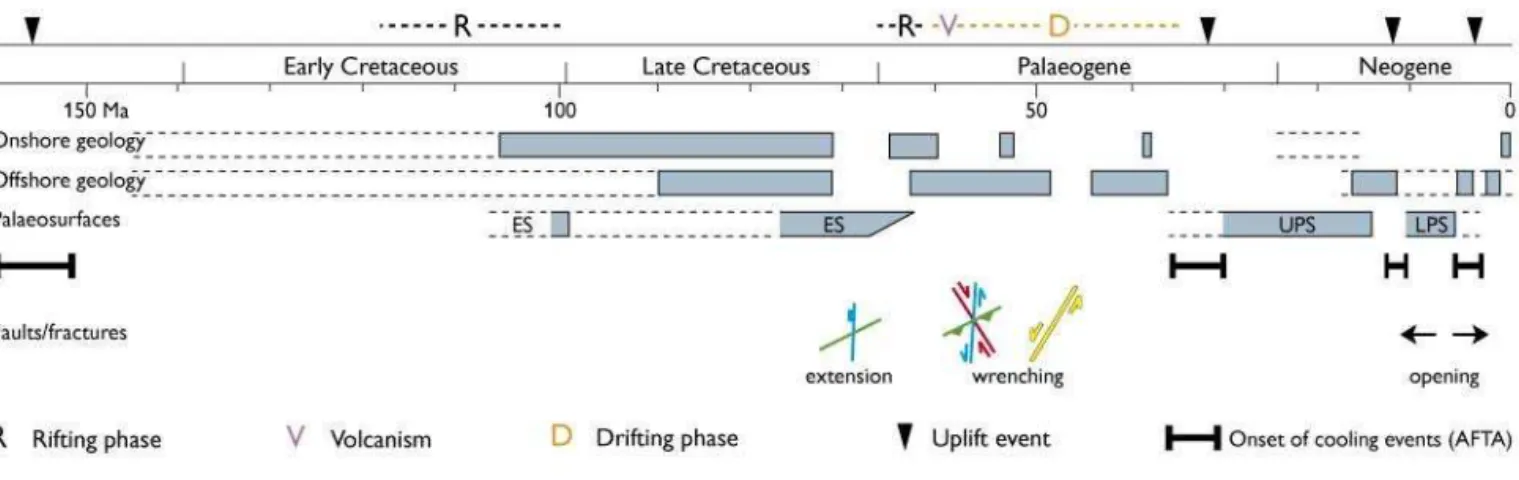
In East Greenland, the Rhaetian – Early Bajocian time interval was characterised by regional subsidence fol- lowing rift events in the Late Permian and Early Triassic (Surlyk
However, farther south, in the central part of the Nagssugtoqidian orogen, Palaeoproterozoic granulite facies metamorphism has led to U loss in Archaean rocks, resulting in
(ed.) 2005: Greenstone belts in the central Godthåbsfjord region, southern West Greenland: Geochemistry, geochronology and petrography arising from 2004 field work, and digital
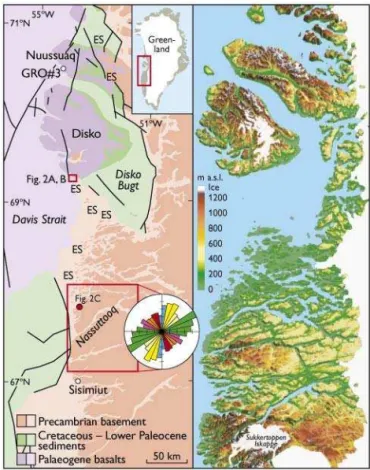
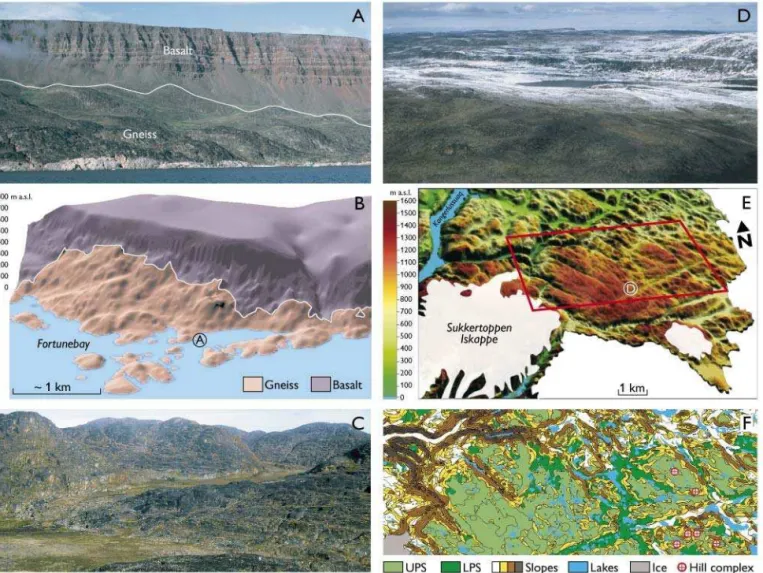
Our new observations show that such Archaean basement gneiss in the Kangerluarsuk area is heavily incised, and that Palaeoproterozoic palaeovalleys were filled in with
The aim of the GLISN project is to cover all of Greenland and surrounding areas with as regular a seismological network as feasible (Fig. The stations will be upgraded to a common
A vertical section north of Denmark Strait shows, that just above the shelf break of west Iceland, the southward flowing branch of the East Greenland Current forms a distinct front