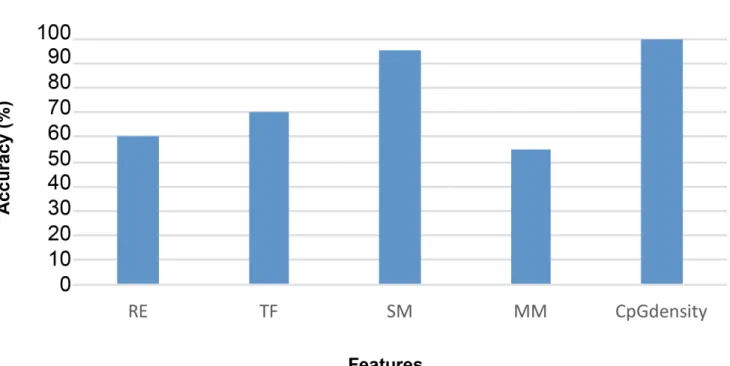
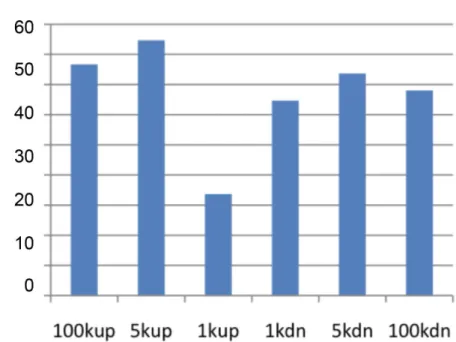
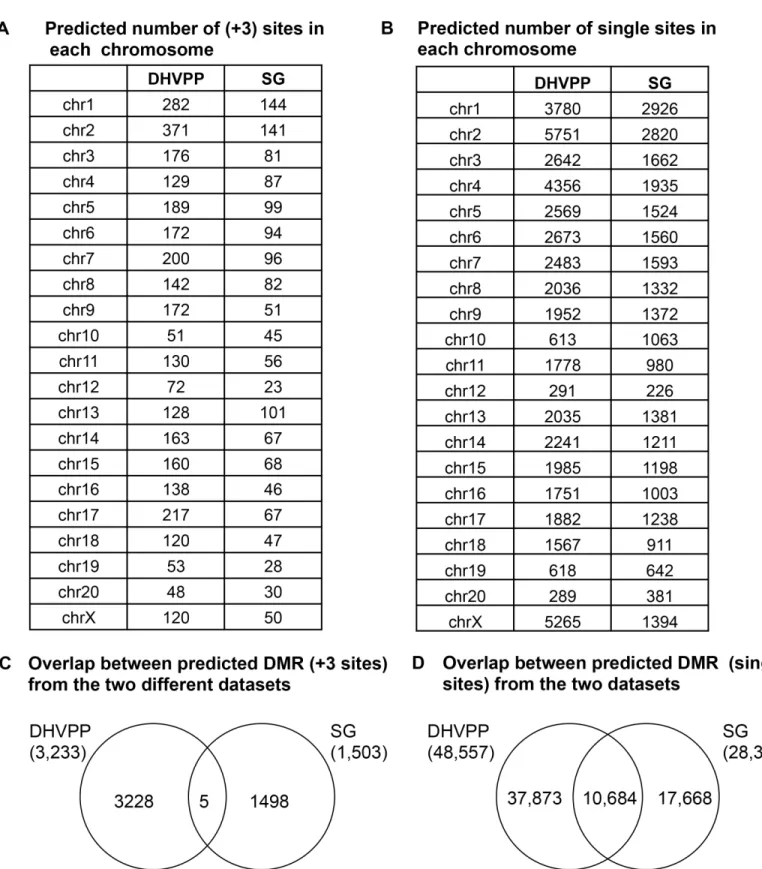
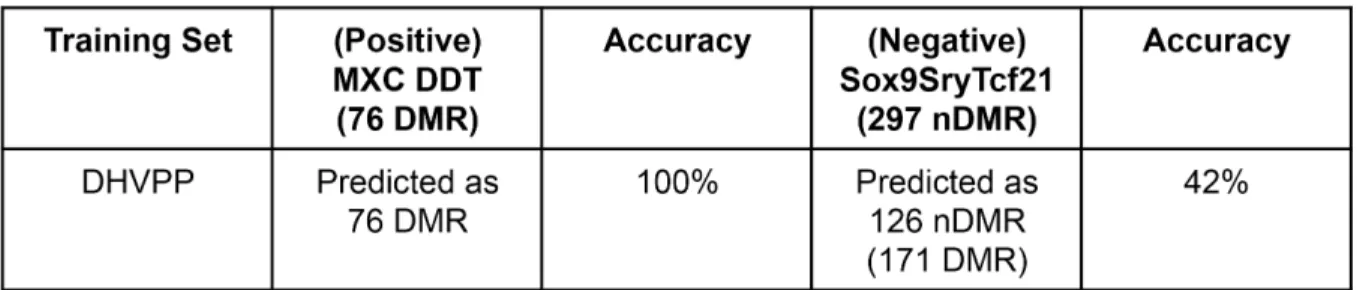
Genome-Wide Locations of Potential Epimutations Associated with Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Disease Using a Sequential Machine Learning Prediction Approach.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
We performed a genome wide analysis of 164 urothelial carcinoma samples and 27 bladder cancer cell lines to identify copy number changes associated with disease characteristics,
In the discovery meta-analysis of 19,509 subjects from seven cohorts, we identified 11 genome-wide significant associations with six white cell phenotypes (total WBC,
Gene network of known relationships among those genes differentially expressed in control- compared to vinclozolin lineage F3 generation germ cells.. Gene node shape code: oval
RNA-Seq was performed on the same RNA pools used to quantify hypoxic enhancer activity in order to identify putative target genes proximal to identified enhancer
To perform association tests between gene expression variation and SNP variation, we selected 374 of the 630 tested genes that had probe hybridization signals significantly above
For the detection of mimicry candidates we focused on human-pathogenic endoparasites known for their mastery in immune evasion, namely Brugia malayi , Schistosoma mansoni ,
The genome-wide promoter target sites of miRNAs were predicted, organized, and integrated with a number of publicly available annotated sequence databases including the database
The first analysis of fox populations using genome-wide distributed SNPs (48,294 SNPs) re- vealed the genetic structure of the tame and aggressive strains and identified several