Prevalence and Epidemiological Determinants of Malnutrition Among Under-Fives in an Urban Slum, Nagpur
Texto
Imagem
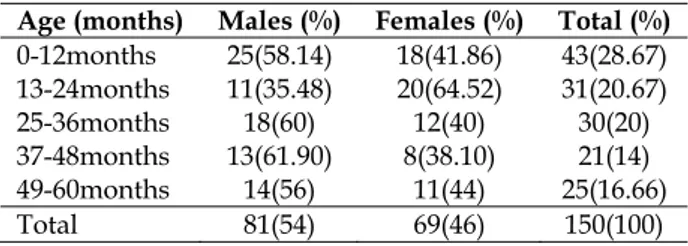
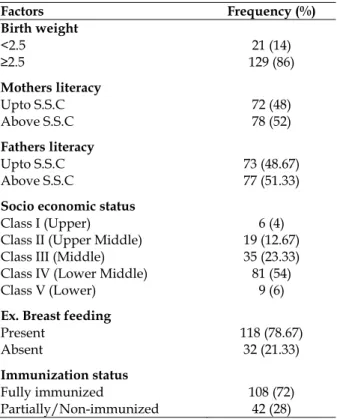

Documentos relacionados
Objective: The present study aimed to estimate the prevalence of falls among institutionalized elderly persons and identify associated factors.. Method: A cross-sectional study
OBJECTIVE: This is a cross-sectional epidemiological survey designed to estimate the prevalence of dizziness among the adult population of the city of Sa˜o Paulo, Brazil, and
In 1987, indicators of child malnutrition were signif- icantly associated with several variables related to child’s characteristics, to health care, and to the socio-
The aim of this study was to describe and compare findings regarding the prevalence and severity of dental caries when using ICDAS and DMFT/dmft in an epidemiological study
Objective: This cross sectional study was carried out to investigate the existence or not of an association between haptoglobin genotypes and prevalence of ischemic
To estimate the prevalence of tuberculosis infection among these workers, a cross-sectional study was carried out at Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade
In response to this, this literature review was conducted to provide an overview of the prevalence rates and factors associated with stunting and excess weight among children
This study describes the prevalence of self-medication and associated factors among nursing workers.. This epidemiological sectional study included 1,509 working nurses from two