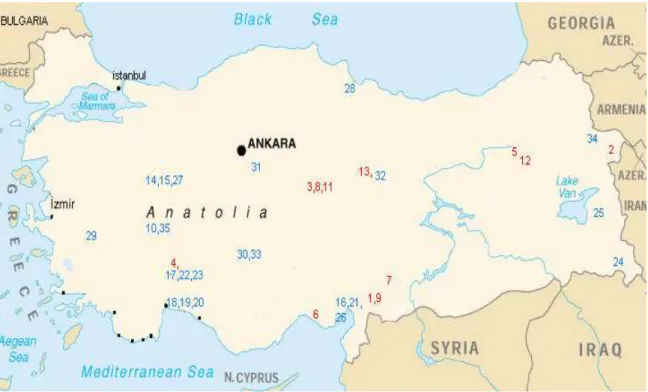
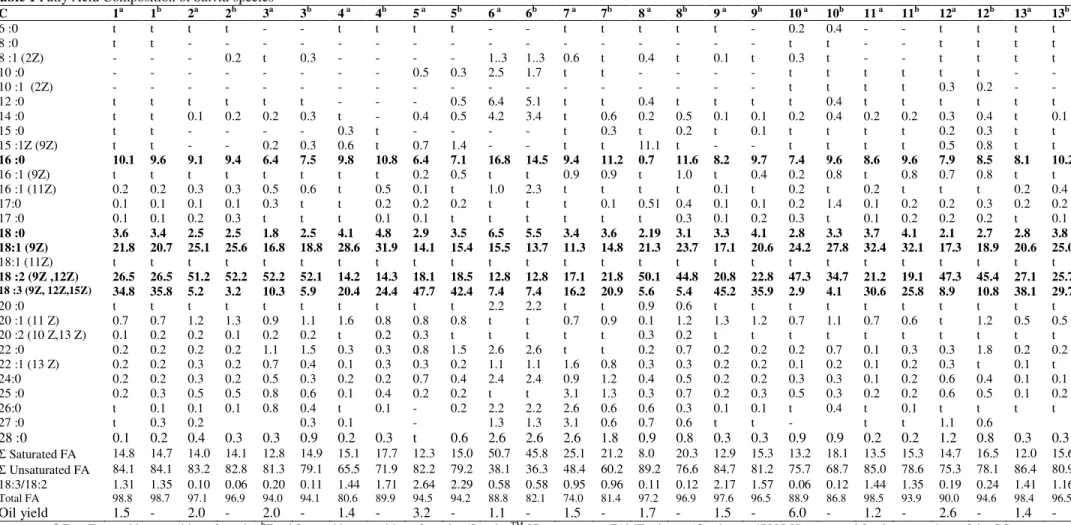
Chemotaxonomic Evaluation of Species of Turkish Salvia: Fatty Acid Composition of Seed Oils. II
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Esta conceção, inicialmente elaborada por Umberto Eco na obra Apocalípticos e Integrados, suscitou desde logo um profundo debate: os últimos viam a cultura de massas como
The retention capacity of encapsulated glucose solutions in lipid microparticles with lipid mixtures of solid-liquid fatty acids (stearic acid – oleic acid) in relation
There was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the two methods of cultivation studied in terms of the palmitic, linoleic, oleic and stearic fatty acid contents,
The fatty acid profile showed that linoleic acid, palmitic acid, oleic acid, stearic acid and linolenic acid (above 0.55 g/100 g) as the most abundant fatty acids followed
Considering the PUFA/SFA ratio and omega-6/omega-3 ratio, our data suggest that, among the peppers of the genus Capsicum evaluated in this work, the bell pepper and orange
(2009), Quantitation of alpha-linolenic acid elongation to eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid as affected by the ratio of n6/n3 fatty acids... (2000), Dietary
palmitic and linolenic acid, N194 and A680 for oleic acid, A632 and FR13 for linoleic acid, and A619 for stearic acid contents are of higher values compared to the other
Evaluation of new Turkish hybrid hazelnut ( Corylus avellana L.) varieties: fatty acid composition, a -tocopherol content, mineral composition and stability. Fatty acid, tocopherol