Direct radiative effect of aerosols emitted by transport: from road, shipping and aviation
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
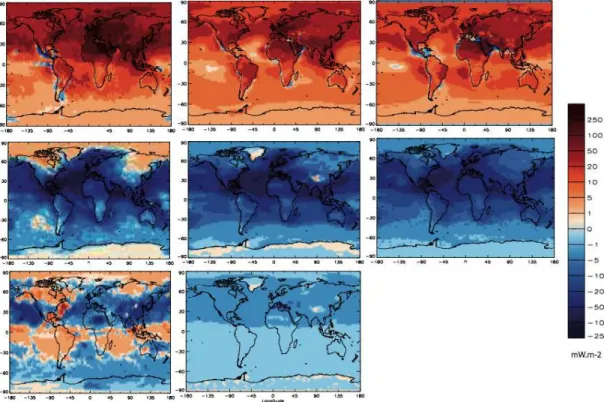
Here we assess the aerosol optical depth ( τ ), direct radiative effect (DRE) by natural and anthropogenic aerosols, and direct climate forcing (DCF) by anthropogenic aerosols,
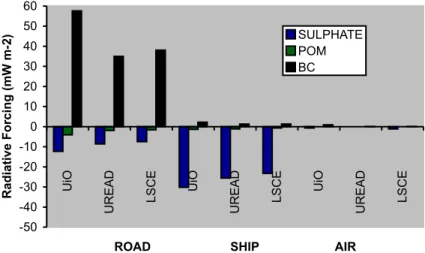
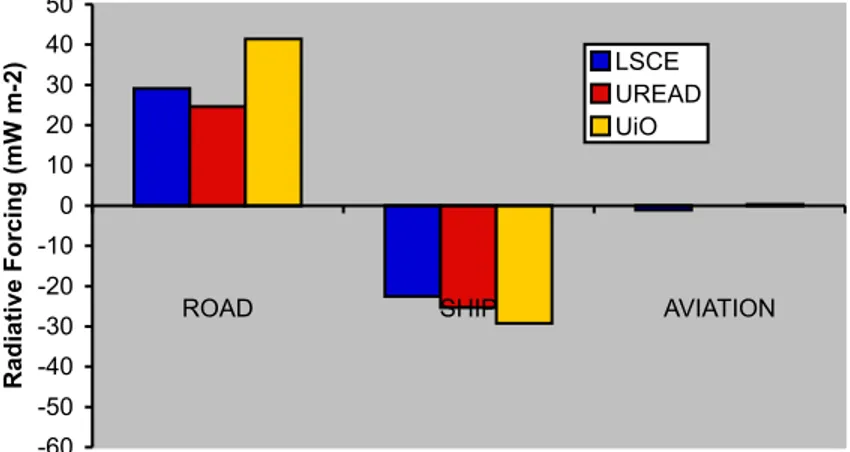
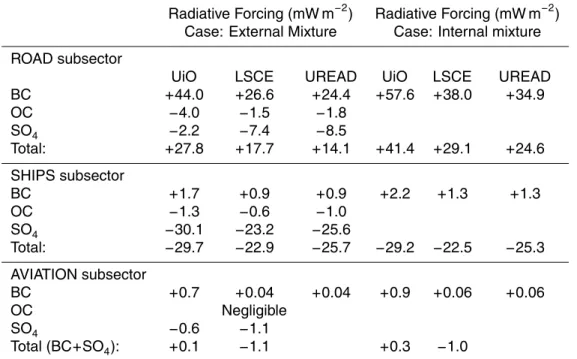
In this section, we present values of the Specific Forcing Pulse for black carbon (BC) and organic matter (OM) par- ticles emitted from different regions, obtained from a single
With the help of a global climate model (CAM5) in which black carbon (BC) emitted from different source regions can be explicitly tracked, we are able to characterize BC
Anthropogenic aerosols are typically composed of various inorganic and organic species (IPCC, 2007), among which sulfate, nitrate, and carbonaceous aerosols including black carbon
These are: elemental carbon from combustion of biomass (EC bb ) and fossil fuel (ECff), organic carbon from combus- tion of biomass (OC bb ), fossil fuel (OCff), primary
variations in the atmospheric circulation, expressed as variations in the frequencies of the transport from four source regions with di ff erent emission rates, can explain
Surface measurements of carbon dioxide mixing ratio from a global network can be combined with atmospheric transport models and a priori estimates of anthropogenic and oceanic
The comparison of the specific road transport ERs, relative to acetylene derived from near-field measurements, to ERs from ACCMIP and EMEP emission inventories for the road