Fish Community Composition and Habitat Use in the Eg-Uur River System, Mongolia
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Andean species present in our analysis, was recovered as the sister group to species distributed in the Amazon, São Francisco, and Paraná River Basins, which are discussed
(42). are the most common plant species, which are highly important nutritional forage value for sheep and cattle in the Inner Mongolia steppe. This study focused on
Abstract: This work aimed to study the composition and distribution of fish species at four sites along Cabec ¸ a River, an affluent of Corumbataı´ River, tributary of Tieteˆ
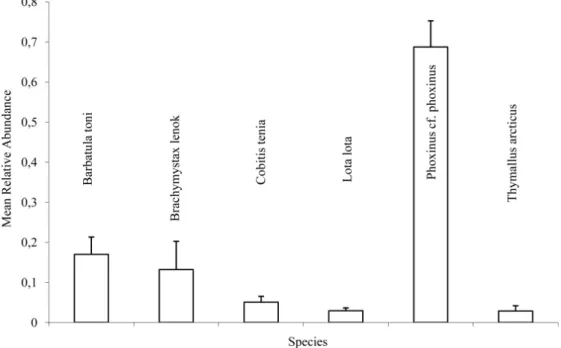
Species list, number of specimens, and body size (minimum and maximum in mm) of the fish species registered in the main river channel at the two studied sections (mid and
The main objectives of this study were: (i) to develop habitat suitability curves of microhabitat use for three fish species representative of the fish community in
are to 1) document the trophic position of species of Chirostoma in relation to other fish species and food web components in Lake Chapala based on stable isotope data,
The present study is the first that used RAPD to estimate genetic variability in fish species from the upper Uruguay River basin.. RAPD markers are efficient in
Besides all impacts caused by the damming and introduction of exotic species, the middle and lower courses of the Tietê River also suffer with different sources of