Vol-7, Special Issue3-April, 2016, pp1090-1099 http://www.bipublication.com
Case Report
The roles of factors affecting learning spaces with an emphasis on primary
schools (Case study: Schools located in Sari –provincial capital of
Mazandaran, Iran)
Shaqayeq Najafi Bayekolaie*, Somayeh Zakiyan Galogahi**, Majid Alishah***and Seied Rasool Rasooli****
*schoolteacher of Iranian High schools, Graduate student, department of architecture, Sari University, Sari, Iran
** MSc in architecture engineering,
instructor of Sama technical and vocational college, Islamic Azad University, Sari Branch, Sari, Iran. *** Graduate student, department of architecture,
Sari University of Science and Research **** Graduate student, department of architecture,
Sari University of Science and Research SomayehZakiyanGalogahi** s_zakiann@yahoo.com
ABSTRACT
Education and creatingincentives forlearningare important educational and cognitive issues to be consideredingrowing the country's futuregeneration. This research aimed to study the creation of learning spaces that are desirable qualitatively and quantitatively, also to identify standards through which the relations between visual quality and structural features could be promoted to the highest level. This is a descriptive – analytical research study that can be classified as applied research. In this research, 389 primary school teachers and workers (in Sari), involving 60% women and 34% men, were selected by cluster sampling and the analyses were conducted using SPSS 16. The results indicate that individual and social factors (developing a sense ofcalm in students by building relationshipsbetweenteachers and students 56%, the effect of individual factors and understanding the differences existing among students 53.7% , and the effect of current limitations in learning spaces compared with homes 52%, as well as qualitative factors (attention to aesthetic qualities in school building and furniture compared with traditional simple schools 49%, the availability of educational facilities including salons with equipment necessary for doing visual arts and various sports and availability of modernrecreational facilities designed in schools for different contests 48.7%, and the effect of colors used in the design of external and internal walls specifically happy colors 43.4%)are the most determining factors affecting the extent to which students welcome schools. However, individual and social factors showed to have a little more effect on learning spaces than qualitative variables.
Keywords: learning environment, behavior, learning spaces, designing indicators.
INTRODUCTION
Educational and learning centers are social institutions thatreflect theunique cultureofdifferentcommunities and transfer certainworldview, habits, customs, skills and knowledge to learners (Lotf Ata, 2008, 73) and students' understanding of social constructionism learning environment is in relationship with their learning consequences.
desirability, enthusiasm, and charisma. Accordingly, attention to Islamic aesthetic principles and social bonds are the most effective factors (NasrAbadi et al. 2013) and the second most effective factor is interest in physical comfort (Azemati et al. 2013) that leads to and understanding of the environment. For this aim, by analyzing thefine structureof spaces andspatial hierarchy, andthe generalarchitecture oflearning spaces built using Iranian architecture, ideas and strategies involved to meet human's hierarchical needs from psychological viewpoints can be extractedand then used as designing strategies for contemporary learning spaces (Yazdanfar et al, 2013). In addition, involving students directly in creation and operation of a multifunctional community center equipped with state-of-the-art technology not only can create active interaction in school environment, but also students can be developed physically and emotionally and their environmental creativity can be reinforced (Baqeri and Azemati, 2011), So that, by creating various dynamic opportunities for each student to perceive and correct his/her situation regarding local requirements and opportunities for participation in different levels of social activities designed to promote the performance of learning spaces (HajiBabaie2012), we can achieve learning spaces that are in parallel with the purposes ofcommunityeducation.
Statement of the problem
In recent yearsdueto the growingand breadth oflearningmethods oftraining,adapting thelearningcontextwithall aspects of thelearner's needs, has been in the spotlight of education experts. It is because of the fact that due toits structure, thephysical environmentcan reinforce or weaken interactionsand subsequently the learningprocesses. since "human'sconstant
interactionwith each other
andwithenvironmental resources" and"instructor-centric" paradigm shapethe essence oftraining systemsof today and
tomorrow, it is believedthatnew
approachesrequirestudents'movement,
teamworkand dynamism (Mardomi and Delshad, 2010, 109). Given thisfundamental pointthat learning isa central partof
everyperson'slife, even whenwe are not thinking of that, it happens; with this understanding thatbehavior doesn'toccurin a vacuum; therefore different ways of behavior arerelated tothe
physical environment. Learning
environmentswill becomposed of
elementsthataremeaningful when they are together. The qualitiesof each ofthese elementsare effectiveinthe formation ofdifferentbehaviors. Education and consequently learning environments are playing the most effective roles in communities'
mentality and civilization.
Educationreformationrequiresproviding an opportunity forstudents that isrelated to theiractivities; placesthatmeet conditions for physical, mental, emotional and social growth of children. This is achieved through detailed design of spaces according to people's behavioral patterns (Lotf Ata, 2008, 73). Andnowit is believedthat the most basicneeds inmodern education systemsare physical and mental activity andsocial morale improvement (Greeno, 1998, 9).Due to the fact that each person on average spendsabout 14thousand hoursof their life in learning spaces fromelementarytohigh schools, so learning environment should reflect the beauty that attracts individuals and asset that everyone feels the meaning, relevance and meaning. Teaching and learning environments should be like a garden. Different set of arrangements that although each one has its own voice, in general they can be smoothing or disturbing. The main problem is that the existing education system is putting moreemphasis oneducationthanfostering, i.e. scientificrevelation is taught to children rather than inner revelation ( Lotf Ata, 2008). However, in the design of learning spaces, there is a mistaken assumption that all learners learn the same way. Nevertheless the individual cognitive style in information processing practices puts large and significant effects on the efficiency and effectiveness of education (Yamanie et al, 2008, 114). Due toourgrowing community, making significant changesin the
learning processofournext
generationrequiresnew and
oflearningspaces. This research study aims to find out the roles of factors affecting learning spaces with an emphasis on primary school in the city of Sari; also in this research effort will be made to answer the following questions:
What are gooddesign principles(quality of learning spaces),leading to thesatisfactionof studentsinlearningenvironments?
What effects do individuals' psychological
conditions have on
attitudesandperceptionslearning spaces users?
Due to changesineducational technologyand educationin the modern world,how are
learning spaces criticizedin terms ofsymbolic andphysicalarchitecture?
Hypotheses
It seems that environmental variables (the quality of learning spaces) could be effective in students' satisfaction of learning environments.
It seems that there is significant relationship between users' conditions (individual psychology) and learning spaces.
It seems that there is significant relationship between educational conditions in developing communities and up-to-date changes in educational technology.
Literature
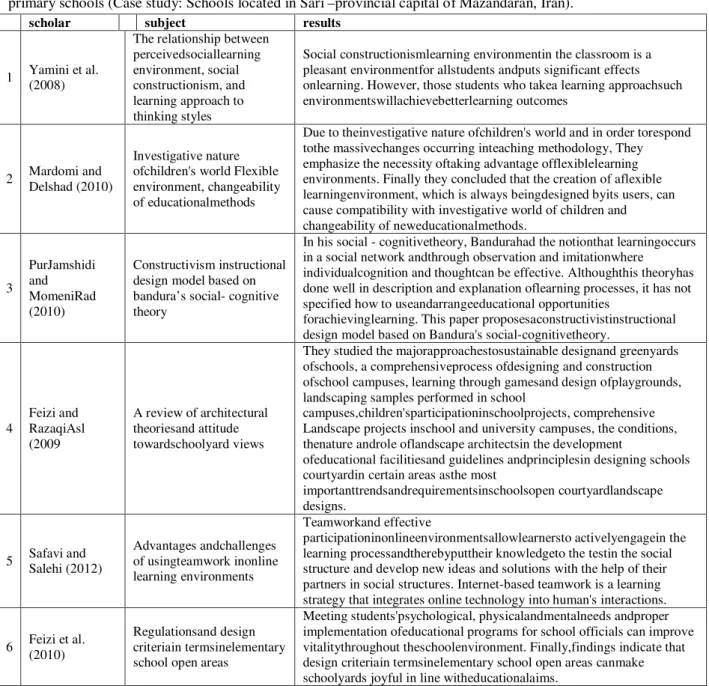
Table 1-Summary of studies in the field (The roles of factors affecting learning spaces with an emphasis on primary schools (Case study: Schools located in Sari –provincial capital of Mazandaran, Iran).
scholar subject results
1 Yamini et al. (2008)
The relationship between perceivedsociallearning environment, social constructionism, and learning approach to thinking styles
Social constructionismlearning environmentin the classroom is a pleasant environmentfor allstudents andputs significant effects onlearning. However, those students who takea learning approachsuch environmentswillachievebetterlearning outcomes
2 Mardomi and Delshad (2010)
Investigative nature ofchildren's world Flexible environment, changeability of educationalmethods
Due to theinvestigative nature ofchildren's world and in order torespond tothe massivechanges occurring inteaching methodology, They emphasize the necessity oftaking advantage offlexiblelearning environments. Finally they concluded that the creation of aflexible learningenvironment, which is always beingdesigned byits users, can cause compatibility with investigative world of children and changeability of neweducationalmethods.
3
PurJamshidi and MomeniRad (2010)
Constructivism instructional design model based on bandura’s social- cognitive theory
In his social - cognitivetheory, Bandurahad the notionthat learningoccurs in a social network andthrough observation and imitationwhere
individualcognition and thoughtcan be effective. Althoughthis theoryhas done well in description and explanation oflearning processes, it has not specified how to useandarrangeeducational opportunities
forachievinglearning. This paper proposesaconstructivistinstructional design model based on Bandura's social-cognitivetheory.
4
Feizi and RazaqiAsl (2009
A review of architectural theoriesand attitude towardschoolyard views
They studied the majorapproachestosustainable designand greenyards ofschools, a comprehensiveprocess ofdesigning and construction ofschool campuses, learning through gamesand design ofplaygrounds, landscaping samples performed in school
campuses,children'sparticipationinschoolprojects, comprehensive Landscape projects inschool and university campuses, the conditions, thenature androle oflandscape architectsin the development
ofeducational facilitiesand guidelines andprinciplesin designing schools courtyardin certain areas asthe most
importanttrendsandrequirementsinschoolsopen courtyardlandscape designs.
5 Safavi and Salehi (2012)
Advantages andchallenges of usingteamwork inonline learning environments
Teamworkand effective
participationinonlineenvironmentsallowlearnersto activelyengagein the learning processandtherebyputtheir knowledgeto the testin the social structure and develop new ideas and solutions with the help of their partners in social structures. Internet-based teamwork is a learning strategy that integrates online technology into human's interactions.
6 Feizi et al. (2010)
Regulationsand design criteriain termsinelementary school open areas
Meeting students'psychological, physicalandmentalneeds andproper implementation ofeducational programs for school officials can improve vitalitythroughout theschoolenvironment. Finally,findings indicate that design criteriain termsinelementary school open areas canmake schoolyards joyful in line witheducationalaims.
Theoretical foundations 1.1 How people learn
People learn as a result of an interaction between personality and environmental variables. Personality and environmental variables affecting learning are quite inseparable,because thepersonality variablesare
formed in environment and
environmentalvariablesthemselvesinfluencepers onality variables. Students learn by different methods. Some studentshavea strong desiretolearn and understand thematerial, while other studentsseem tolearnonlythe minimumnecessaryfor passingtheircourses. For example, peopleinasimilarposition, mayhave differentlearning, which canresult from differences inabilities,motivation ortheirthinking styles. (Yaminiet al, 2008).
1-2 Flexible learning environments
Flexible learningenvironmentissimilar to atheater, so thatteachers andstudents are its directors and actors, and they aredefininghow space should be used; therefore, the learning happeninginthisgamefits the needs ofthe learner, the subjectbeing learned andtools being used. This learning can happen in 3 ways:
1. Participationin activitiesafter there-arrangement of furniture. It brings childrenadvantages such asprogress and learning incentive, improvedphysical skills, increased self-confidenceandindependence, meeting needs and control over theenvironment.
2. Making classrooms as large as possible, so thatdifferent multipleactivities can occur. 3. Seamlesslearning: learning environment is not
a series of classes with the samesize, but the whole atmosphere of a learning center can be seen as a context for learning. (Mardomi and Delshad, 2010).
1-3Learning in learning environment
Students learn by different methods. Some studentshavea strong desiretolearn and understand thematerial, while some others
learnonlywhat is necessaryfor
passingtheircourses. In addition, those whostudied inmore appropriateenvironmentsare more efficientthanothers. In the designof learning spaces, educational leveland gender of
those using the spaceplay an important role inthe design practices and shaping ofitsconstituent elements(KamelNia, 2007).Behavioral processes in learning spaces are influenced by several factors including symbolic, organizational, physical, architectural and psychological factors. The effect of effective factors is not simple or direct, but they mutually influence and intensify each other (Mortazavi, 1997), which can be categorized as:
1. Symbolic factors: that is related tomental conceptsthatarerelative toa specific locationin mind. For example,large spaceswithexpensive furniture are a symbol ofsocialhierarchyand cancontain suchmessages.
2. Social - organizational dimensions: the restriction of movementbyorganizational rulesisemphasizedinlearningenvironments. These restrictionsweakenself-concept in students.
3. Architectural - physicalfactors: deal with the impact ofissuessuch as heat, cold, light, sound etc.(KamelNia, 2007).
1-4 learning through playing games in learning environments
Two theories have been developed by theorists about learning through playing games in learning environments:
a) Theoryof preparation foradulthood: playing games can provideopportunitiesto gainskills andfunctions thatare necessaryin adulthood. According to thistheory, playing gameis a uniquephenomenoninchildhoodthatimprovesph ysical andmentalcapacities.
b) Social-culturaltheory: Game is an incentive and a stimulus to imaginative thinking and way of doing things and to apply symbolic manner. Games can help recognizing therolespeopleplayin societyandsocial rules.This recognition is through playing theroles ofsocial figures, such as a doctor, mother, etc. (Mardomi and Delshad, 2010). Objective
2. Recognizing the effects users' characteristics (individual psychology) onthe desirability oflearning spaces.
3. Identifying the effects of educational status in developing communities and the necessity of designing new changesineducational technology.
Methodology
This articleisbased onresearchconductedduringa university project that due to its nature, subjectand purpose, it can be claimed thatthis is a descriptive-analytical research study and can be classified as applied research. Since inthisstudy, questionnairesandinterviews were
used to collectthe required
information,sofromanother point of view, this study can be said to besurvey research. Required information, in this study, was collected through documents (library) and surveys. This study examines theroles offactors affecting learning environmentsand learning spacesof Sari- provincial capital of Mazandaran, Iran. In this research, 389respondents, 65% womenand 34%men, were selected from teachers and school workers working in Sari Primary schools byclustersampling. Questioners were used to
collect information on variables and results were analyzed by Kolmogorov–Smirnov, Pearson and Friedman tests using SPSS 16.
HYPOTHESES AND DISCUSSION
Results are the most important part of research that lead to the development of hypotheses and add new information to past knowledge with the help of research theories (Hafeznia, 2003). After gaining a recognition offactors affecting the design oflearning spaces(with emphasis onprimary school), the questionnaires which were prepared by authors using Delphi method and were tested by10professorsandprofessionals inthis areawere distributed among research population(all elementary schools of Sari) in order to identify factors affecting student's welcome of learning spaces . it includes the following three parts:
Identifying qualitative
factorsaffectingstudents' welcome ofoptimal learning spaces.
Identifying individual and social factors affecting students' welcome of optimal learning spaces
Categorizing identified factors in terms of their importance and their efficacy.
Table 2- descriptive statistics of sample group
variable frequency percentage variable freque
ncy
percent age se
x
female 255 65.5
O
cc
upa
ti
on
st
at
us
governmental 296 76
male 134 34.5 Self-employed -
educ
at
ion
Under
diploma - retired 54 13.88
diploma - University student -
associate
degree - housewife -
Bachelor's
degree 302 77.63 jobless 39 10.2
Master's degree 87 22.37 student -
PhD - total 380 100
Source: the author (2015)
The normality of data distribution (Kolmogorov–Smirnovtest)
Most statistical tests including parametric tests are based upon the normality of data distribution and they are applied with this presumption that data distribution in a community or in samples selected from the community follows a normal distribution. Thus, before conducting any statistical analyses on variables, analyzers need to know variables type of distribution. Applying
distribution is considered to follow a normal distribution. Consequently, parametric tests have
been used for testing research hypotheses.
Table 3- Kolmogorov–Smirnov test results for evaluating the normal data distribution
variable Statistical indicator number Z Significance level Test result Factors affecting promotion of
museum design quality 389 0.695 0.531
Data are normal Source: the author (2015)
According to the statistical value in Kolmogorov–Smirnov test for variables, significance level was P > 0.05. Thus it can be concluded that above variables enjoy normal distribution and so we can apply Pearson test. The evaluation of research data using PearsonCorrelationCoefficient
Evaluation was conducted using
PearsonCorrelationCoefficient.
PearsonCorrelationCoefficient is a measurement in which correlation between two or more variables is studied. In this research, researcher aims to know if a change in a variable can cause a change in other variables, and if so, how and to what extent. Finally variables were ranked using Friedman test.
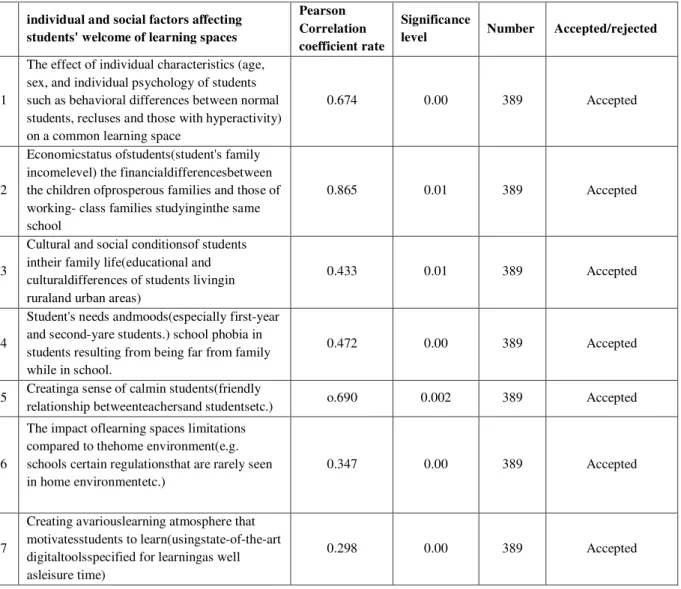
Table 4-1- Ranking of individual and social factors affecting students' welcome of learning spaces individual and social factors affecting
students' welcome of learning spaces
Pearson Correlation coefficient rate
Significance
level Number Accepted/rejected
1
The effect of individual characteristics (age, sex, and individual psychology of students such as behavioral differences between normal students, recluses and those with hyperactivity) on a common learning space
0.674 0.00 389 Accepted
2
Economicstatus ofstudents(student's family incomelevel) the financialdifferencesbetween the children ofprosperous families and those of working- class families studyinginthe same school
0.865 0.01 389 Accepted
3
Cultural and social conditionsof students intheir family life(educational and culturaldifferences of students livingin ruraland urban areas)
0.433 0.01 389 Accepted
4
Student's needs andmoods(especially first-year and second-yare students.) school phobia in students resulting from being far from family while in school.
0.472 0.00 389 Accepted
5 Creatinga sense of calmin students(friendly
relationship betweenteachersand studentsetc.) o.690 0.002 389 Accepted
6
The impact oflearning spaces limitations compared to thehome environment(e.g. schools certain regulationsthat are rarely seen in home environmentetc.)
0.347 0.00 389 Accepted
7
Creating avariouslearning atmosphere that motivatesstudents to learn(usingstate-of-the-art digitaltoolsspecified for learningas well asleisure time)
0.298 0.00 389 Accepted
Source: the author (2015)
which shows that there is significant relationship between students' individual and social characteristics ant the extent to which they welcome a learning space.
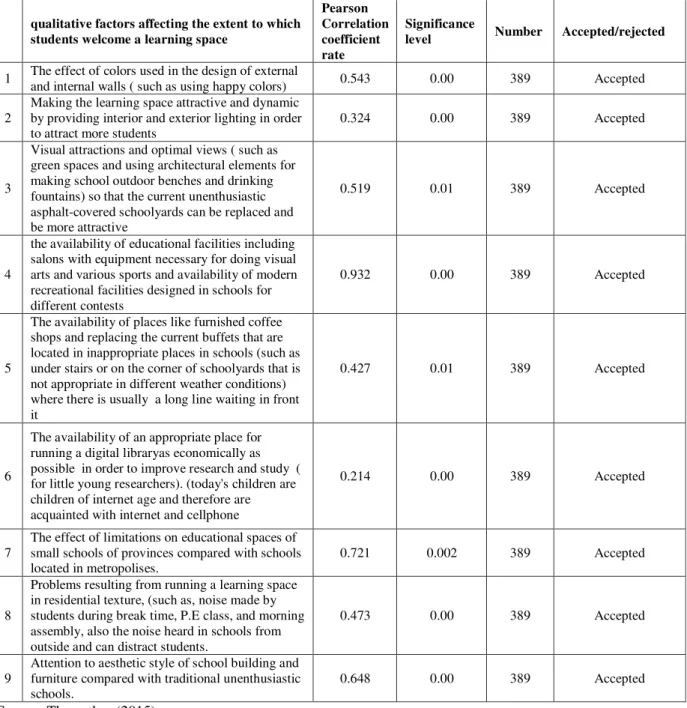
Table 4-2 - Ranking of qualitative factors affecting the extent to which students welcome a learning space
qualitative factors affecting the extent to which students welcome a learning space
Pearson Correlation coefficient rate
Significance
level Number Accepted/rejected
1 The effect of colors used in the design of external
and internal walls ( such as using happy colors) 0.543 0.00 389 Accepted
2
Making the learning space attractive and dynamic by providing interior and exterior lighting in order to attract more students
0.324 0.00 389 Accepted
3
Visual attractions and optimal views ( such as green spaces and using architectural elements for making school outdoor benches and drinking fountains) so that the current unenthusiastic asphalt-covered schoolyards can be replaced and be more attractive
0.519 0.01 389 Accepted
4
the availability of educational facilities including salons with equipment necessary for doing visual arts and various sports and availability of modern recreational facilities designed in schools for different contests
0.932 0.00 389 Accepted
5
The availability of places like furnished coffee shops and replacing the current buffets that are located in inappropriate places in schools (such as under stairs or on the corner of schoolyards that is not appropriate in different weather conditions) where there is usually a long line waiting in front it
0.427 0.01 389 Accepted
6
The availability of an appropriate place for running a digital libraryas economically as possible in order to improve research and study ( for little young researchers). (today's children are children of internet age and therefore are acquainted with internet and cellphone
0.214 0.00 389 Accepted
7
The effect of limitations on educational spaces of small schools of provinces compared with schools located in metropolises.
0.721 0.002 389 Accepted
8
Problems resulting from running a learning space in residential texture, (such as, noise made by students during break time, P.E class, and morning assembly, also the noise heard in schools from outside and can distract students.
0.473 0.00 389 Accepted
9
Attention to aesthetic style of school building and furniture compared with traditional unenthusiastic schools.
0.648 0.00 389 Accepted
Source: The author (2015)
With regard toreliability(99%) anda significantlevel of Pearson correlation coefficient(0.000) inwhich research hypothesesvalue is less than default value(0.10). the null hypothesis (there is relationship between qualitative factors andthe extent to which learning spaces are welcomed) is accepted which shows that there is significant relationship qualitative factors the extent to which they welcome a learning space.
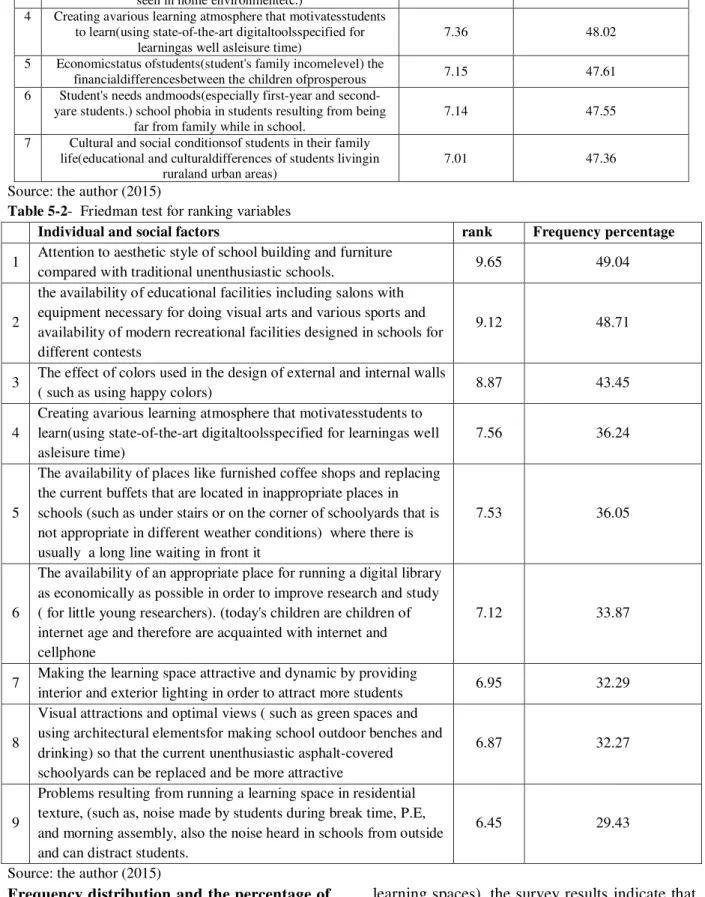
Table 5-1- Friedman test for ranking variables
Individual and social factors rank Frequency percentage
1 Creatinga sense of calmin students (friendly relationship
between teachersand studentsetc.) 9.11 56.02 2 The effect of individual characteristics (age, sex, and
individual psychology of students such as behavioral differences between normal students, recluses and those with
hyperactivity) on a common learning space
3 The impact oflearning spaces limitations compared to thehome environment(e.g. schools certain regulationsthat are rarely
seen in home environmentetc.)
8.45 52.08
4 Creating avarious learning atmosphere that motivatesstudents to learn(using state-of-the-art digitaltoolsspecified for
learningas well asleisure time)
7.36 48.02
5 Economicstatus ofstudents(student's family incomelevel) the
financialdifferencesbetween the children ofprosperous 7.15 47.61 6 Student's needs andmoods(especially first-year and
second-yare students.) school phobia in students resulting from being far from family while in school.
7.14 47.55
7 Cultural and social conditionsof students in their family life(educational and culturaldifferences of students livingin
ruraland urban areas)
7.01 47.36
Source: the author (2015)
Table 5-2- Friedman test for ranking variables
Individual and social factors rank Frequency percentage
1 Attention to aesthetic style of school building and furniture
compared with traditional unenthusiastic schools. 9.65 49.04
2
the availability of educational facilities including salons with equipment necessary for doing visual arts and various sports and availability of modern recreational facilities designed in schools for different contests
9.12 48.71
3 The effect of colors used in the design of external and internal walls
( such as using happy colors) 8.87 43.45
4
Creating avarious learning atmosphere that motivatesstudents to learn(using state-of-the-art digitaltoolsspecified for learningas well asleisure time)
7.56 36.24
5
The availability of places like furnished coffee shops and replacing the current buffets that are located in inappropriate places in schools (such as under stairs or on the corner of schoolyards that is not appropriate in different weather conditions) where there is usually a long line waiting in front it
7.53 36.05
6
The availability of an appropriate place for running a digital library as economically as possible in order to improve research and study ( for little young researchers). (today's children are children of internet age and therefore are acquainted with internet and cellphone
7.12 33.87
7 Making the learning space attractive and dynamic by providing
interior and exterior lighting in order to attract more students 6.95 32.29
8
Visual attractions and optimal views ( such as green spaces and using architectural elementsfor making school outdoor benches and drinking) so that the current unenthusiastic asphalt-covered schoolyards can be replaced and be more attractive
6.87 32.27
9
Problems resulting from running a learning space in residential texture, (such as, noise made by students during break time, P.E, and morning assembly, also the noise heard in schools from outside and can distract students.
6.45 29.43
Source: the author (2015)
Frequency distribution and the percentage of responses made by samples
Given the results obtained in Friedman test in which qualitative and individual- social factors were tested separately( in terms of their effects on the extent to which students welcome
the effect of current limitations in learning spaces compared with homes 52%, as well as qualitative factors (attention to aesthetic qualities in school building and furniture compared with traditional simple schools 49%, the availability of educational facilities including salons with equipment necessary for doing visual arts and various sports and availability of modern recreational facilities designed in schools for different contests 48.7%, and the effect of colors used in the design of external and internal walls specifically happy colors 43.4% )are the most effective factors contributing to an enthusiastic welcome from students.
RESULTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Results obtained from studying contributing factors and variables indicate that it is accepted that qualitative, individual, and socialfactors and the extent to which students welcome a learning space are correlated. However, according to responses, it can be claimed that, individual and social factors have had a little more effect on learning spaces than qualitative variables, so that it can be stated that results are different from the researcher's fist hypothesis ( qualitative variables are more effective) and it seems that appropriate strategies for designing learning spaces with regard to individual and environmental psychological principles can promote the sense of calm and therefore learning process in students. Thus, given the analytical findings, the following recommendations can be made:
1. Attention to the designof a novelformthat is in harmony with educational application. The study of results obtained from questionnaires completed in survey indicates that the design used in school appearance and furniture can put significant effects on the extent to which students welcome learning spaces, and in contrary to old unenthusiastic traditional schools, novel design of modern schools that meet students' needs can affect this extent. 2. The availability of modern and
state-of-the-art educational assistance spaces in learning spaces. Since educational assistance spaces (salons with equipment necessary for doing
visual arts and various sports and availability of modern recreational facilities designed in schools for different contests) are among the most important factors from respondents' point of view, attention to the design of learning spaces is of paramount importance and creating such spaces what mentioned above can increase desirability.
3. Creating a space that makes students feel a sense of calm. Creating a sense of calm in people and alleviating their everyday stress is an important factor to be considered in the design of learning spaces. This objective can be achieved by providing proper lighting, selecting appropriate colors in the design of interior and exterior walls (such as happy and energetic colors) and designing the interior space, as well as school yard according to environmental psychology strategies.
4. Creatingspaces that motivate students to learn. Learning spaces of Iran suffer from insufficient sociocultural facilities. In order to add variety to learning spaces, we can use state-of-the-art digitaltools specified for learningas well asleisure time such as furnished coffee shops rather than old buffets where there is a long line waiting in front of it and are located in inappropriate places (e.g. under stairs or on the corner of schoolyard ), digital libraries to promote research and study as cheap as possible (for little young researchers)(today's children are children of computer age and are acquainted with internet and cellphone applications). Moreover, designing such spaces can make educational level follow standards of the modern world and therefore mere displaying role of educational assistance spaces can be changed, and then this space becomes more practical.
REFRENCE
1 Azemati, HR, Sabah; Sabahi, Samaneh; Azemati, Saeed, (2012), "environmental factors affecting students' satisfaction of educational facilities", the Journal of Naqsh-e-Jahan, year 2, p. 31.
Journal of Curriculum Studies, No.22 , year 6, p. 163.
3 Faizi et al., (2010), " design criteria in terms of elementary school open areas ", National school renovation organization, Tehran. 4 Feizi, M; RazaqiAsl, S, (2009), "A review of
opinions and attitudes on architecture of schools open yard view", Journal of Utopia, No. 7, p. 59.
5 Greeno, J.G. (1998), The Situativity of Knowing, Learning, and Research, American Psychological AssociationInc, Vol.53, No.1. 6 Hafeznia, MR, 2009, An introduction to
Research Methods in Human Sciences, Sixteenth Edition, Tehran, SAMT publication.
7 HajiBabaee, H, (2012), "The features of " The school I love * "according to revolution document in Education," Journal of innovative education, No. 42, year 11, p. 52. - KamelNia, H. (2007), "grammar of learning environments design", Sobhan Noor publication, Tehran.
8 LotfAta, Aynaz, (2008), "The effect of environmental factors on learning and behavior in learning environments (primary level) in the city", Journal of Urban Management, No. 21, pp. 73-90.
9- Mardomi, K ;delshad, M, (2010), "flexible learning environment of investigative children, changeability of educational systems", scientific- research Journal of Iran urbanization and architecture scientific association, pp. 109-118.
10- Mortazavi, Sh (1997), "educational spaces
from environmental psychology
perspective", National school renovation organization, Tehran.
-11 Nasr Abadi, B, Hassan Ali, Amna; Ansari, M., (2013), "An Analysis of aesthetic elements in the architecture of educational facilities according to Islamic Approach", Journal of Islamic Education, No. 17, pp. 29-49.
12 Purjamshidi, M; Momeni Rad, A, (2010), "constructivist instructional design mode based on social cognitive theory of Bandura", JOURNAL OF EDUCATION, Year 13, No. 32.
13 Safavid and Salehi, (2012), "the advantages and challenges of using teamwork in online environments", the Journal of Media, year 3, No. 1, p. 53.
14 Yamini et al., (2008), "The relationship between the perception of social constructivism learning environment,
thinking styles with an approach to learning and its rewards and challanges", Journal of Psychology, University of Tabriz, No. 12, p. 114.