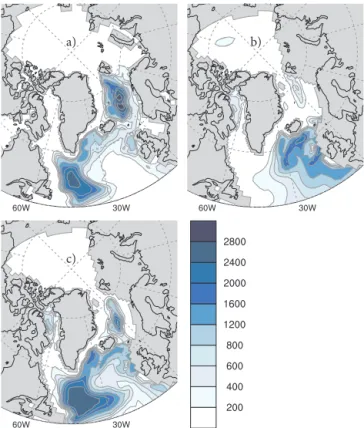
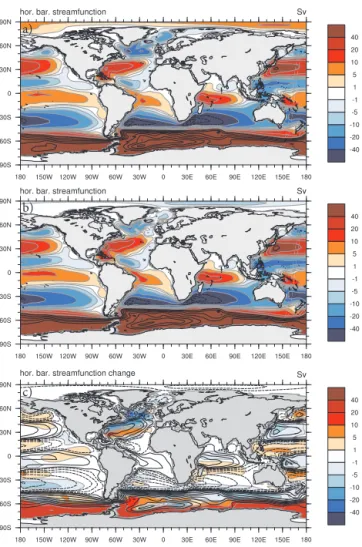
Coupled ice sheet–climate modeling under glacial and pre-industrial boundary conditions
Texto
Imagem

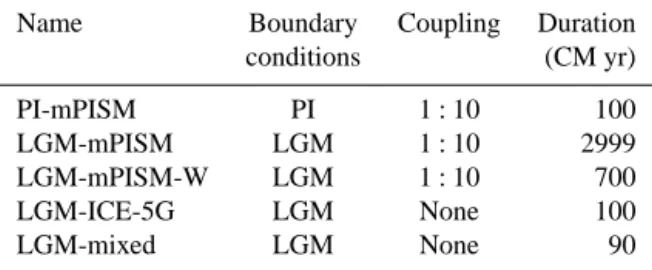
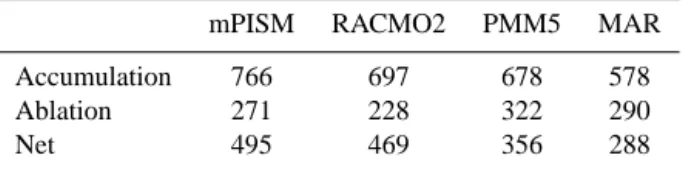
Documentos relacionados
Boundary condi- tions such as sea surface temperatures (SSTs), topography, ice-sheet extent and vegetation are derived from the ones imposed by the Pliocene Model
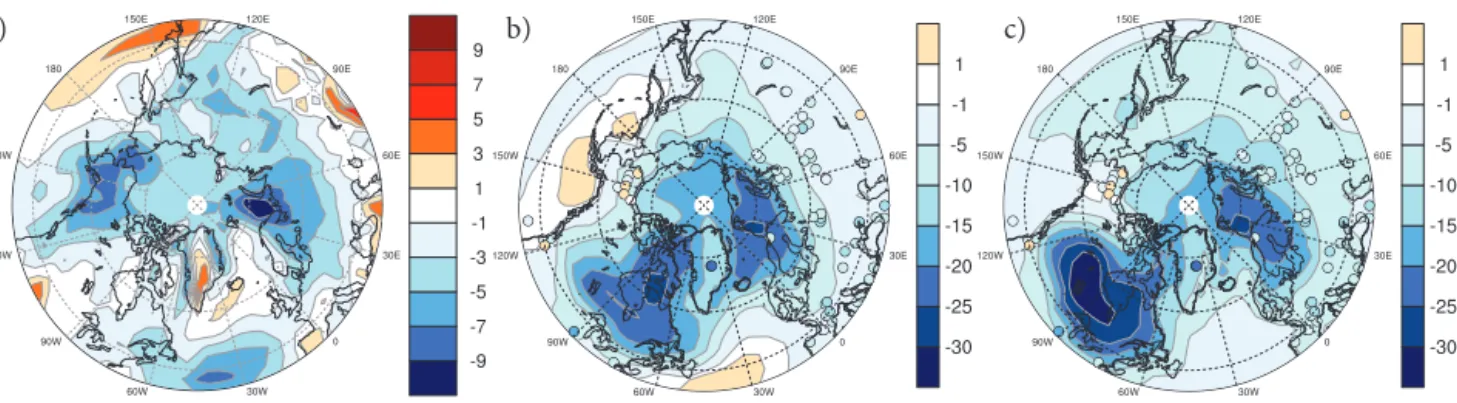
We have described and demonstrated a new procedure for generating 1850 preindus- trial ice sheet states for use in fully coupled ice-sheet/climate models which results in
Consequences of a warmer climate on the Greenland Ice Sheet (GrIS) mass balance will be a thickening inland, due to increased solid precipitation, and a thinning at the GrIS
Annual Arctic-wide solar heat input (and relative changes) under sea ice ( Q T ) in 2007 for the reference method and sensitivity studies: changes in melt season duration by (1) 7
The SMB anomaly projection for k = a/b =− 1 as well as the cumulated sea level rises equivalent are shown in Fig. This record surface mass loss rate is likely to become com- mon at
Impacts of sea-ice reduction on the future projection of pH and aragonite saturation values in the Arctic surface waters have been investigated by comparing the rates of
and Marsiat, I.: Simulations of the Northern Hemisphere through the last glacial- interglacial cycle with a vertically integrated and a three-dimensional thermomechanical ice-
Unstructured finite element mesh and model surface velocities after optimisation of the basal friction with the Robin inverse method, on the whole ice sheet and zooms on