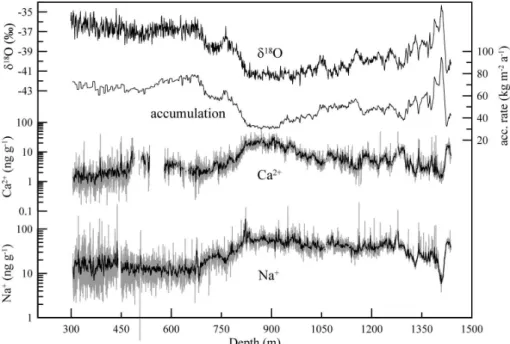
High-resolution mineral dust and sea ice proxy records from the Talos Dome ice core
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Here we report on the development of the common timescale AICC2012-Antarctic Ice Core Chronology 2012 over the last glacial period (0–120 ka BP) constructed for four Antarctic,
In this study we quantified the ice production in the Laptev Sea polynyas for the winter 2007/2008 based on simulations with a regional atmospheric model (CCLM) and remote sens-
Proxy records for the western South Atlantic and south- eastern South America spanning Termination 1 based on marine sediment core GeoB6211-2 together with ice core
W.: Accumulation variability over a small area in east Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica, as determined from shallow firn cores and snow pits: some implications for ice-core records,
this section we focus on four simulations that represent well the sensitivity of the cloud and precipitation properties to aerosol loading through the modification of aerosol
The top 2 cm section of the sea ice had relative high bulk salinity on 20 January (Fig. 3) likely due to the granular nature of the sea ice in this part of the core creating
Vertical thinning due to ice flow has been estimated both for the EDC and Dome Fuji ice cores based on a 1-D ice flow model (Parrenin et al., 2007b) with prescribed ice
Since treatments to remove and/or deactivate organic matter have a small impact on the ice nucleating ability of China loess soil dust, the key ice nucleation active sites contained





