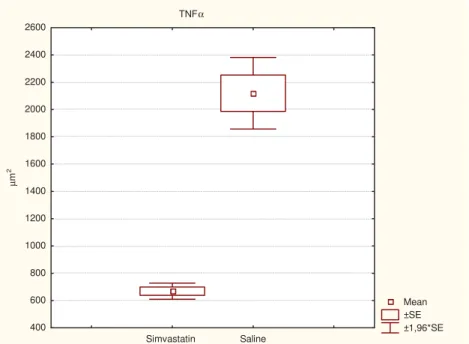
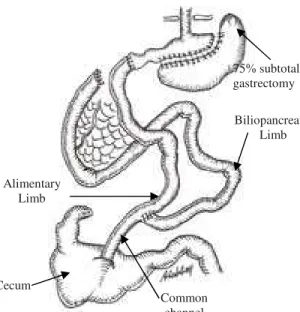
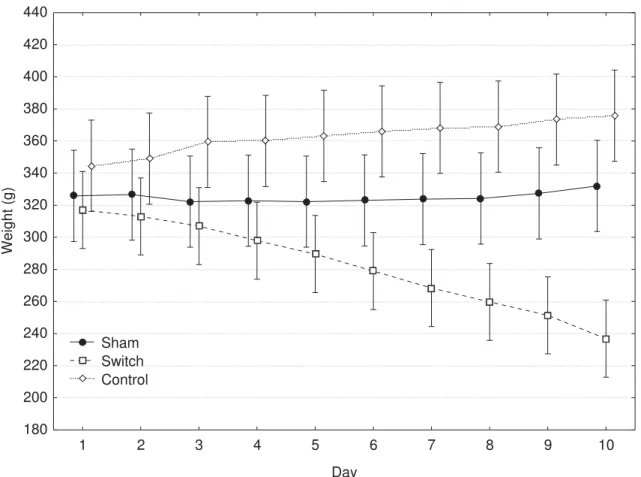
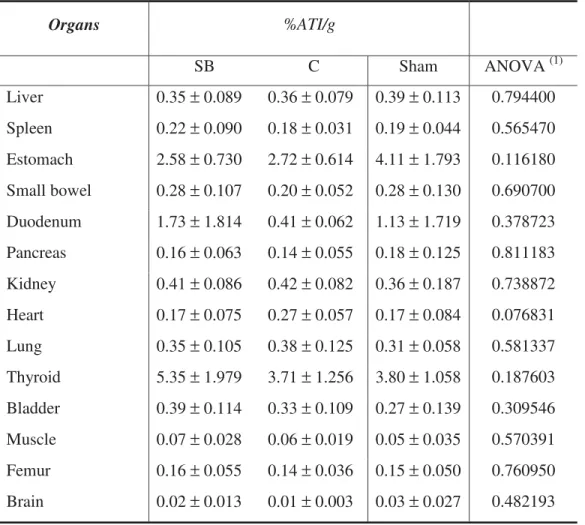
Biodistribuição do pertecnetato de sódio após cirurgia do Switch Duodenal
Texto
Imagem

Outline
Documentos relacionados
136 Figura 63 - Effect of the pH conditions at cathodic and anodic reservoirs during the ESR for removing petroleum from soil by applying different currents see Table 12.. 137 Figura
e) Intensificar, junto à comunidade, campanhas educativas de conscientização ambiental; f) Incentivar a participação e a colaboração das famílias dos alunos na execução
After a quarantine period of 7 days, 24 rats were randomly divided into four groups, each consisting of six animals as follows: Rats in group 1 were control; Rats in group 2
After demineralization, the samples were randomly divided into five equal experimental groups: Group 1 (control), the brackets were bonded without any surface treatment; Group 2,
The animals were randomly divided into four groups: Group I: positive controls (n=7 rats in permanent estrus), Group II: negative controls (n=7 castrated rats treated with vehicle
Were randomly assigned three groups of five rats: Group I (GI), laparotomy, resection of 70% of the small intestine and jejunoileal end-to-end anastomosis; Group II
The rats were randomly divided into fi ve groups: normal control group (NCG), long-term model group (LTMG), short-term model group (STMG), combining disease with syndrome group
The present experiment was developed to study the behavior of TGF-ß1 levels and concentration in pleural effusion over time, after induction of infected and