Integrative meta-analysis of differential gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia.
Texto
Imagem
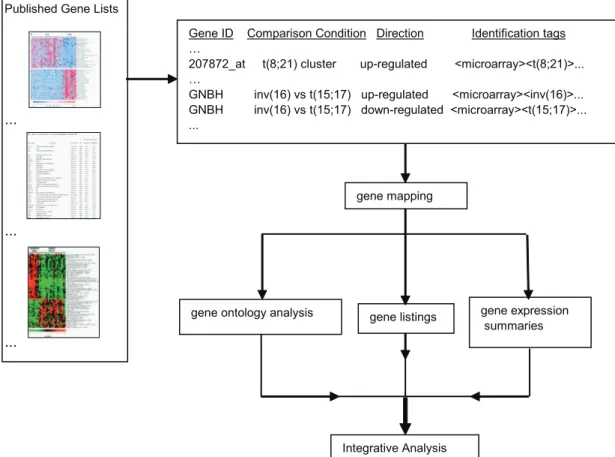
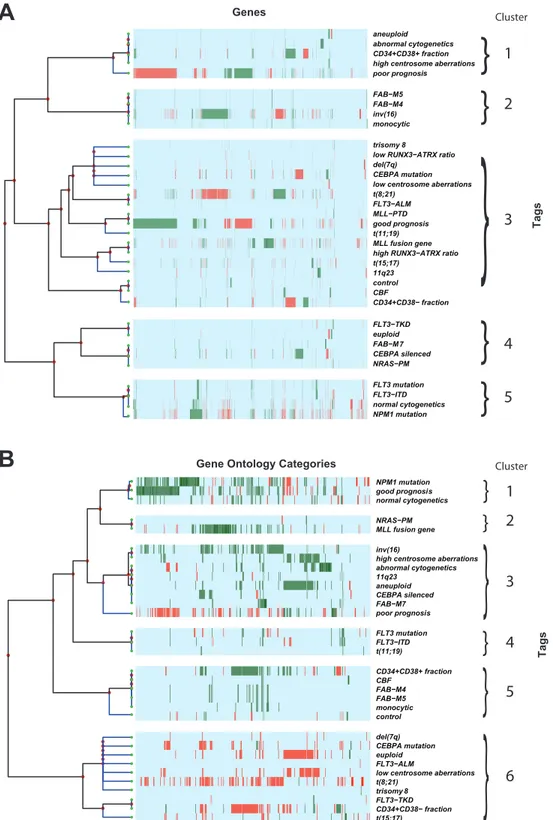
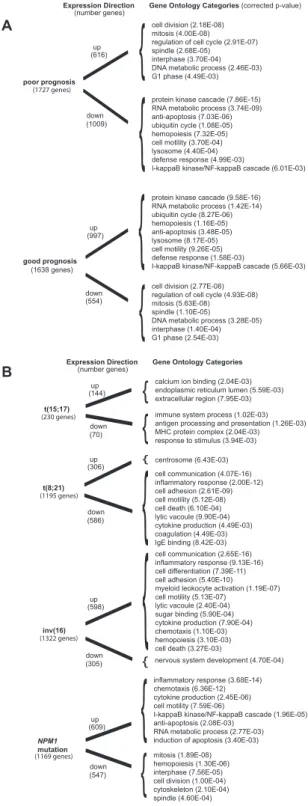
Documentos relacionados
In myelodysplastic syndrome, mutations of TP53 gene are usually associated with complex karyotype and confer a worse prognosis.. In the present study, two mutations in this gene
In line with that, microarray stud- ies of gene expression during trypomastigote (a non-di- viding stage) to amastigote differentiation also identified several genes encoding
The expression of the CD56 antigen is associated with poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.. Hematology and Oncology Department, Faculdade de Medicina de
The integration of functional gene annotations in the analysis confirms the detected differences in gene expression across tissues and confirms the expression of porcine genes being
Herein, we identified that Zn, Mg and retinoic acid (Figure 5) are involved in fatty acid metabolism, which are associated with expression regulation of DEG between
Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and
We sought to identify patterns of gene expression in the MI during pod differentiation, determine biological processes associated with pod differentiation and determination,
Differential expression of genes in the CA1 region of KA-treated rats compared to control rats: genes associated with neuronal damage, calcium-binding, gliosis and inflammation..