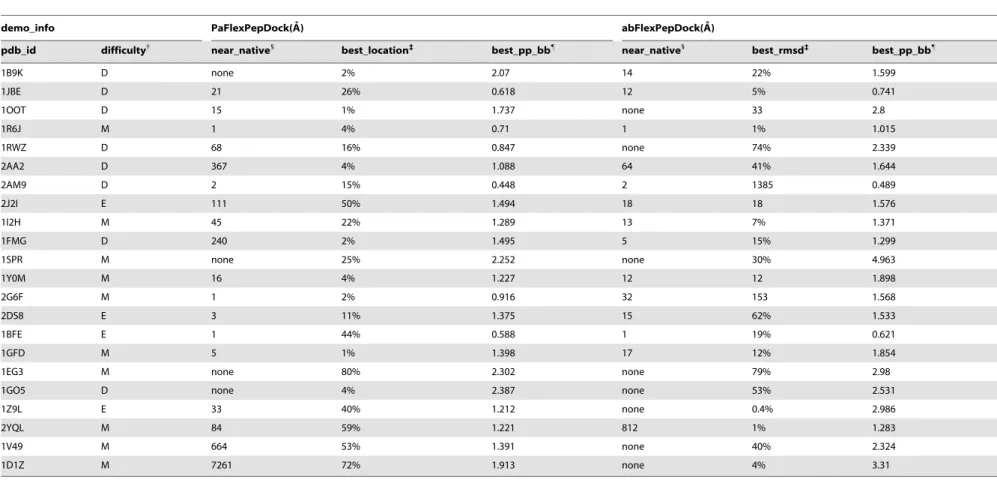
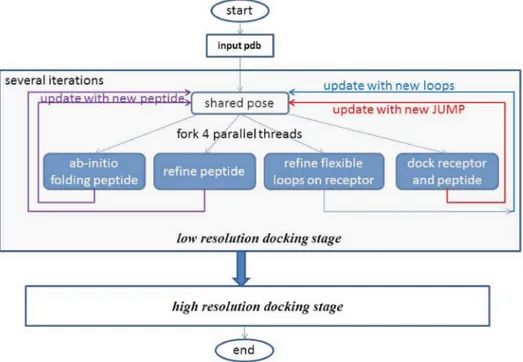
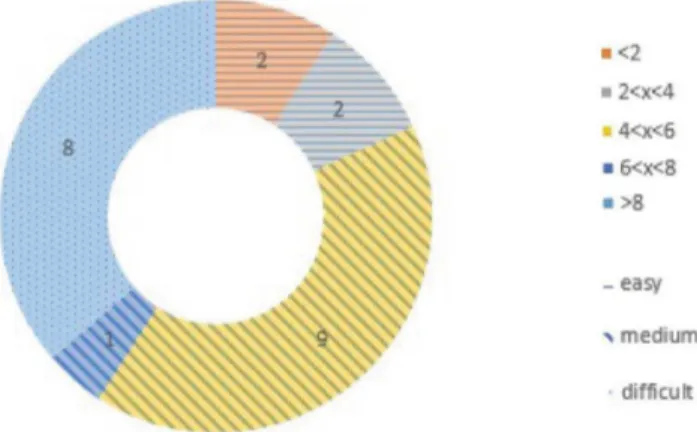
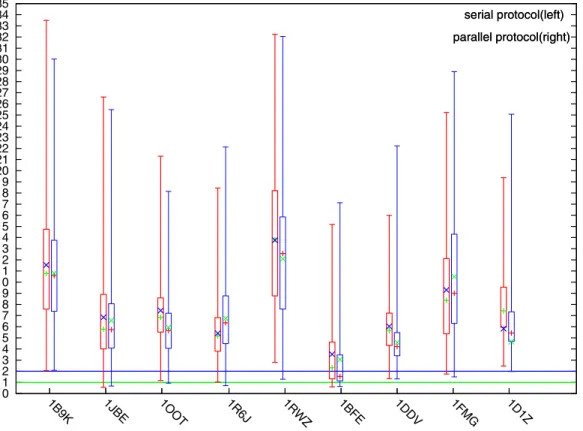
PaFlexPepDock: parallel ab-initio docking of peptides onto their receptors with full flexibility based on Rosetta.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Ar- bitrary atoms of thrombin active site which were selec- ted for the nearest atom filters and center of mass filter are shown in Fig 1.. Results
The superior performance of DMP323, when compared to the others ligands, may be due to a minor de- pendence among its dihedral angles and to the fact that its correct conformation
Thus, this study aimed to determine the digestible protein and energy requirement, and proper dietary protein to energy ratio for goldfish fingerlings based on
Then docking was performed with the screened molecules with ACE protein where docked results were compared with that of the existing drugs and the variations were noted which shows
Table S1 Energy Error of EFMO and FMO2/AFO compared to ab initio calculations on proteins and protein-like structures for different values of R resdim ~ R cor using one residue
(2013) Insight into the Intermolecular Recognition Mechanism between Keap1 and IKKβ Combining Homology Modelling, Protein-Protein Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulations and
Using the 3D structure of a protein, molecular recognition studies between protein-protein or protein- ligand can be achieved and used to explain biological
Table S1 The 1,460 proteins with both sequence and phenotype information retrieved from CYGD (the Comprehensive Yeast Genome Database) (Guldener U, Munsterkotter M, Kastenmuller