Transcriptome sequencing and expression analysis of terpenoid biosynthesis genes in Litsea cubeba.
Texto
Imagem
![Figure 6. Monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes biosynthetic pathway in L.cubeba (adapted from Gahlan et al and Ma et al [57,58])](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_br/16455458.197864/7.918.97.816.121.706/figure-monoterpenes-sesquiterpenes-biosynthetic-pathway-cubeba-adapted-gahlan.webp)
Documentos relacionados
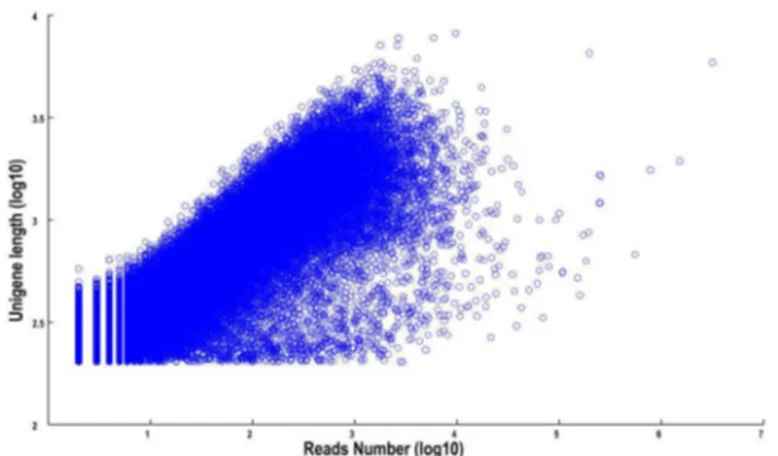
In order to technically validate the data from deep sequencing, five differential expressed unigenes and four miRNA genes were selected for real-time RT-PCR analysis.. The
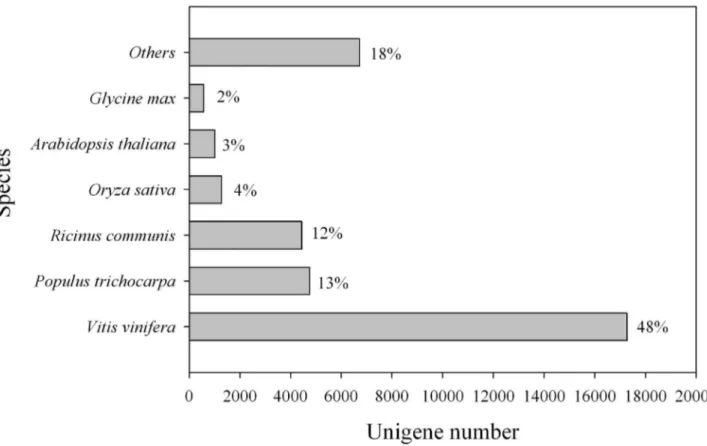
There were approximately 1,500 Unigenes involved in the lipid metabolic pathway of developing peanut seeds, and many were found to participate in fatty acid biosynthesis,
For this, we focused on 212 biological pathways on the KEGG website (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). We annotated the peptides and probesets according to their pathway member- ship
Eighteen top Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were significantly involved in physiological responses, particularly in lipid metabolism, including
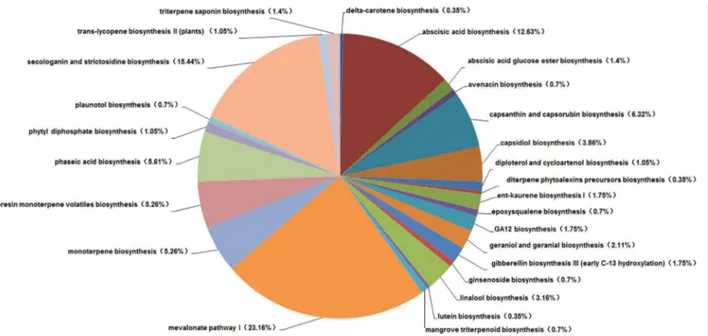
In this study, through transcriptome sequencing and KEGG database annotation, 40 kinds of enzymes are involved in terpenoid backbone biosynthesis, and 16 genes participate in
imaging showed that chitosan activated the PPAR activity in the brain and the KEGG pathway analysis showed that chitosan significantly regulated the expression of genes involved
Pathways of differential genes corresponding to the differentially expressed proteins identified in the KEGG database included regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, adhe- rens
By KEGG orthology assignment and comparative analysis of known haloarchaeal genomes, the amino acid biosynthetic pathways of this haloarchaeon were reconstructed (Figure
