SEQUENTIAL MODELLING OF BUILDING ROOFTOPS BY INTEGRATING AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA AND OPTICAL IMAGERY: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
Texto
Imagem

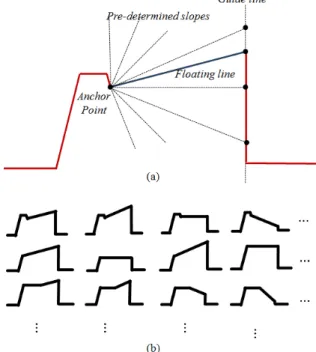

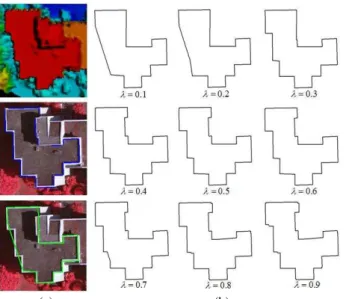
Documentos relacionados
Abstract — In this paper, we present a simple experimental method to generate a DP-16QAM optical signal for high spectral efficiency optical transmission.. A 16QAM optical
In this paper we establish results on existence and uniqueness of the weak solu- tions for a system modelling the motion of a charged particle driven by the action of an
In this paper, the performances of biomass estimation using airborne LiDAR and Hyperspectral data will be explored in a sub-tropical forest of Southwest China.. STUDY SITE AND DATA
PSC microphysical properties were retrieved by comparison of the measured particle depolarization ratio and PSC-averaged lidar ratio to theoretical optical data obtained for
We analyzed the mean optical properties of southern hemisphere midlatitude tropopause cirrus, such as optical depth, extinction coefficient and lidar ratio using lidar observations
International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume XXXVIII-5/W12, 2011 ISPRS Calgary 2011 Workshop, 29-31 August 2011,
In this paper, we proposed sequential Monte Carlo method (SMCM) to accurately estimate the location of the missing object and the extensive simulations are also shown to
In this paper, we have been mainly concerned with the in- fluences of two very different ice particle microphysical and optical models on the resulting optical thickness retrievals
