Voxel Based Morphometry Alterations in Mal de Debarquement Syndrome.
Texto
Imagem


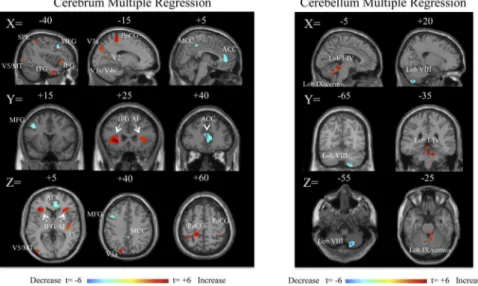
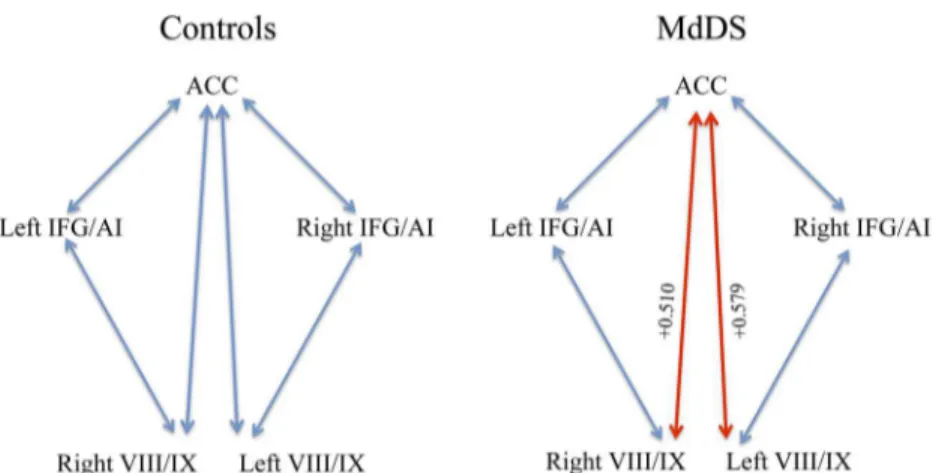
Documentos relacionados
The results of the present study show that the level of physical activity as measured by an accelerometer is lower in patients with COPD than in healthy controls, as well as
Concluding, the present study describes morphometric brain changes in a large necropsy series from Brazil and highlights that brain weight and volume (with or with- out
Here, we investigated changes in the postural balance of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and in healthy controls undergoing different proprioceptive and
which investigated both these domains found no differences between schizophrenics and healthy controls regarding identity processing, but found patients impaired in emotion
These brain areas overlapped only partially with regions characterized by changes in GM and effect sizes were in the range and above for cortical thickness and GM-volume,
Longitudinal local volume ratios (percent, y-axis) during follow-up examination (months, x-axis) of different cortical and subcortical regions that revealed no significant
Single patients showed a marked relative hippocampal volume reduction, but the patients were not different from controls in the volumetric measurements of hippocampal and whole
Our previous PET-CT study [8] indicated that, compared to the HS, the meal-related FD patients showed a higher glycometabolism in the insula, and that the abnormal hyperactivity of
