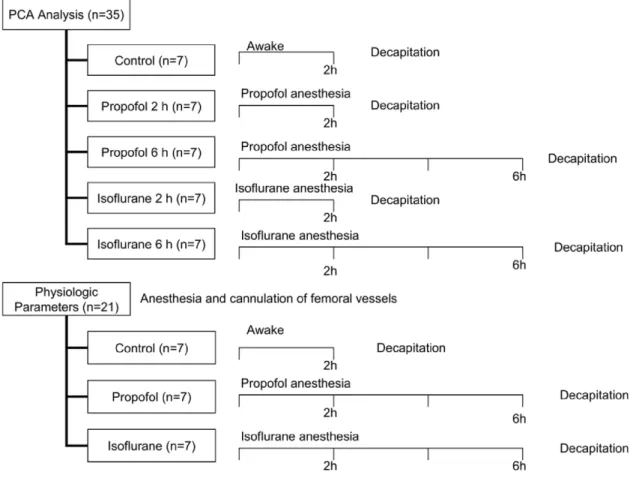
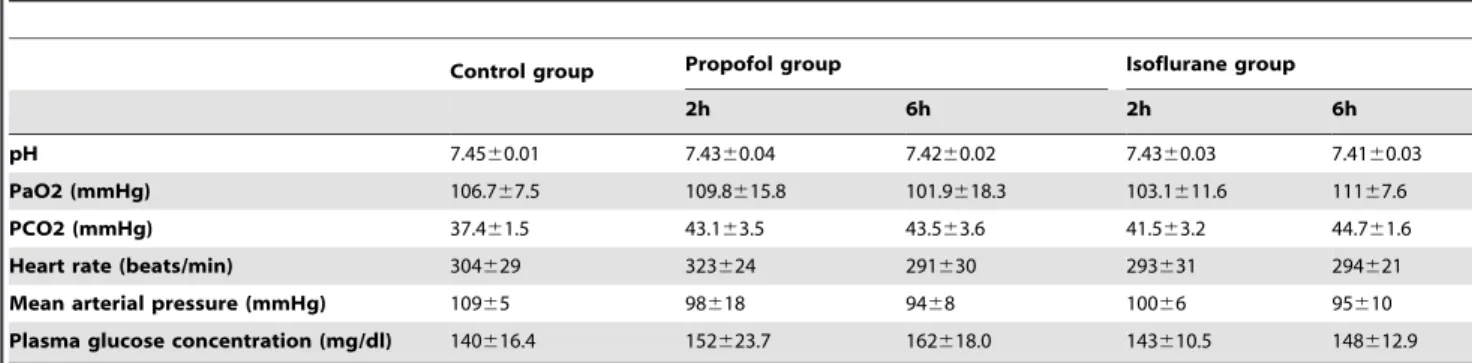
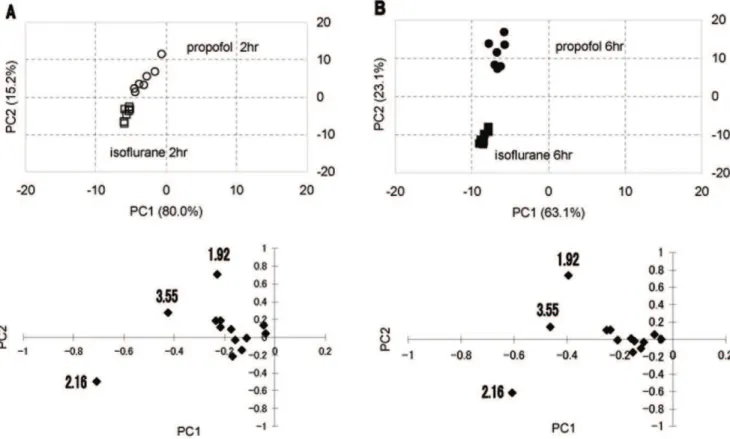
Pattern recognition analysis of proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of brain tissue extracts from rats anesthetized with propofol or isoflurane.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Objectives: To evaluate the use of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with β -thalassemia and to compare T2* magnetic resonance imaging results with
SSPE should be kept in mind when changes in basal ganglia signal are seen on brain magnetic resonance imaging with or without involvement of other regions of the human brain to
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the human brain has proven to be a useful technique in several neurological and psychiatric disorders and benefits from higher
Spectrum of indings on magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in patients with neurological manifestations of dengue fever..
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipments of high field, dedicated specifically to experimental uses, have been used to study the hydrocephalus in vivo of small rats carriers
In order to study metabolic changes within the brain, the authors performed a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) study in a 1- year-old girl with merosin-positive CMD (MP-CMD)..
In fact, the availabil- ity of functional magnetic resonance imaging for in vivo analysis of the normal brain has revolutionized the study of language. Another unexpected ind in
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry in the lateralization of temporal lobe epilepsy: a series of 100 patients. Connelly A,