Tropospheric aerosol microphysics simulation with assimilated meteorology: model description and intermodel comparison
Texto
Imagem


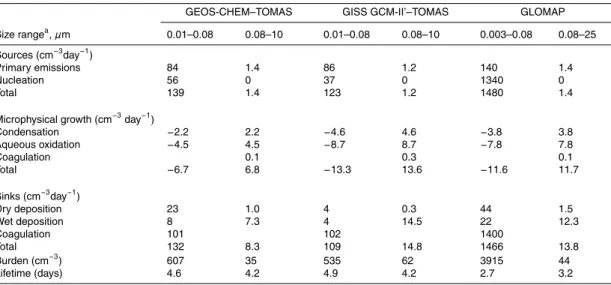

Documentos relacionados
present, the high concentrations of fine aerosol (PM 2. 5 ) and the resulting large numbers of Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) had a strong impact on clouds and microphysics,
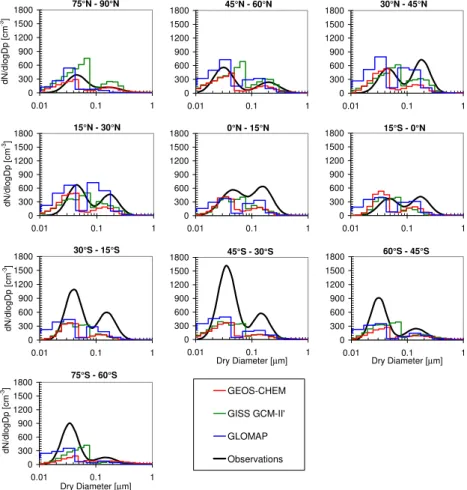
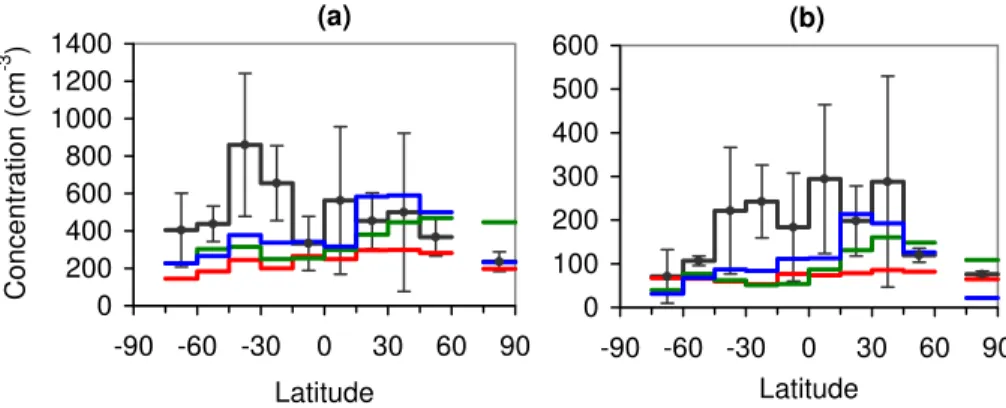
Simulated marine surface zonal-mean geometric mean particle diameters in the Aitken and accumulation mode compared to observed values from a compilation of 30-yr of measured
presents dynamical and chemical evolutions in the mass and size distributions of aerosols due to emissions, new particle formation, condensation, Brownian coagula- tion, dry
mixture within one size class (chemical and morphological internal/external mixture) with respect to CCN activation properties can be studied; 5) If aerosol number size
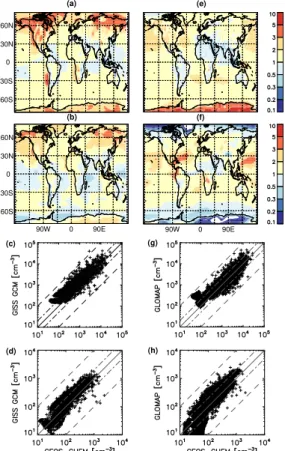
Although a detailed evaluation of the two schemes against observations is out of the scope of this paper, we do compare both models to benchmark global datasets of
We find that the variability in the CCN concentrations in the central Amazon is mostly driven by aerosol particle number concentration and size distribution, while variations in
We use a global aerosol microphysics model to estimate the effect of particle formation through activation nucleation in the boundary layer (BL) on cloud droplet num- ber
The well- predicted aerosol quantities, such as aerosol number, mass composition and optical properties, and the inclusion of full aerosol-cloud couplings lead to