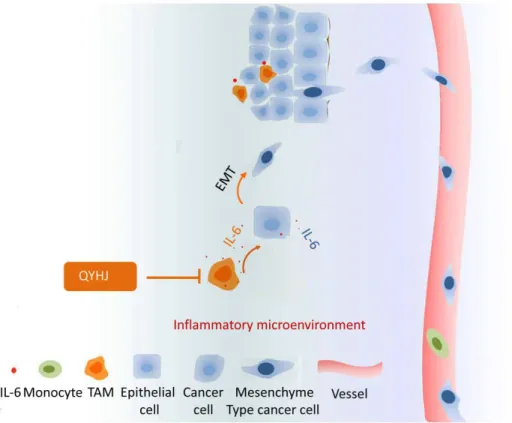
Targeting cancer-related inflammation: Chinese herbal medicine inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
There is ample evidence of the importance of E-cadhe- rins to inhibit tumor invasion and metastases: the metasta- tic potential of various cancer cell lines is inversely related to
In the present study, we have developed a spheroid-based, 3-D culture of pancreatic cancer cell lines MIAPaCa-2 and PANC-1 for pancreatic drug testing, using the acid
Using pancreatic cancer cell lines with or without expressing mutated K-ras , we demonstrated that the inhibition of endogenous PKC activity sensitized human pancreatic cancer
Forced expression of miR-7 in aggressive breast cancer cell lines suppressed tumor cell monolayer proliferation, anchorage independent growth, three-dimensional growth in
In this study, we have shown that soluble factors secreted by activated PBMC of healthy donors including TNF- α , IL-6 and TGF- β can induce a paradoxical co-expression of EMT
In the present study, we addressed the heterogeneity in pancreatic cancer cell lines BxPC3 [22] and PC3 [23] based on the morphology of colonies derived from single cancer cells
Heterogeneity tests indicated that studies analyzing the association between nine cancers (EC, gastric cancer, lung cancer, HCC, colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, female
These results indicate that miR-200c overexpression regulates MUC4 and MUC16 mucins in pancreatic cancer cells by directly targeting the mRNA coding sequence of