Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on new trabecular bone during bone-tendon junction healing in a rabbit model: a synchrotron radiation micro-CT study.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
What distinguishes the healing of muscle injuries from bone healing is that in muscles there is a repair pro- cess, while in bone tissue there is a regeneration process.. Healing
The low intensity and long duration aggressions to the periosteum induce the formation of new layers and can increase the volume of bone and change its shape. In intrusive
Osteoporosis is a metabolic disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to enhanced bone fragility and
Bisphosphonate therapy normalizes bone turnover, reduces the number of bone remodeling sites and stress risers, restores the balance of bone remodeling, prevents bone loss
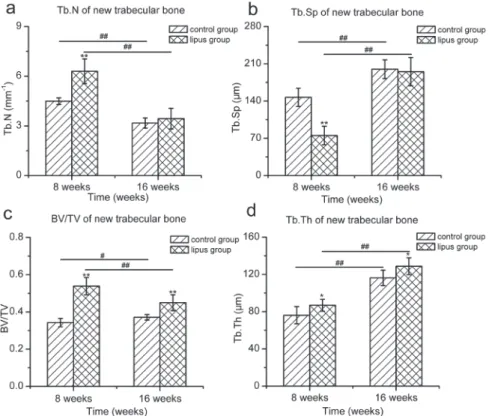
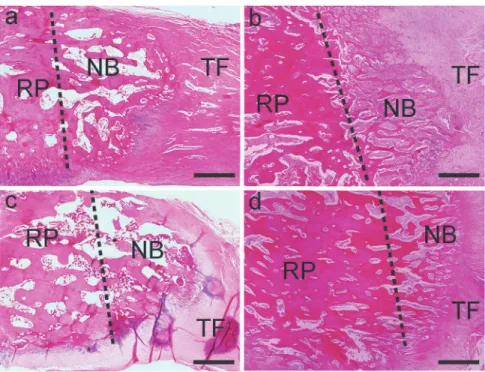
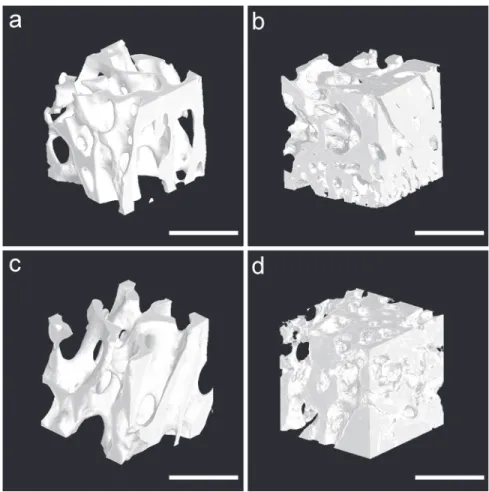
Considering the importance of bone quality and healing in several medical and dentistry situations, the aim of this study was to evaluate bone healing and trabecular
Since several changes have been described in the bone metabolism of hypertensive subjects, the pur- pose of this study was to evaluate bone healing in defects
As collagen is an important component of the extracellular matrix of bone and increased amounts, as seen in this study, may indicate a positive effect of LLLT on bone healing
TNbF, total new bone formation; NbFP, new bone formation on the periosteal side; NbFMC, new bone formation in the medullar canal; BIpCC, bone/implant contact in the cortical