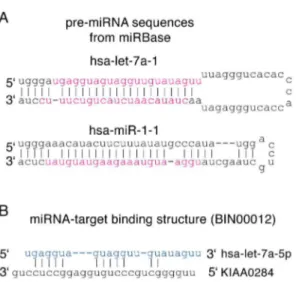
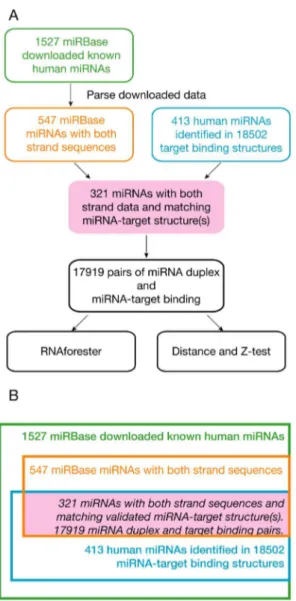
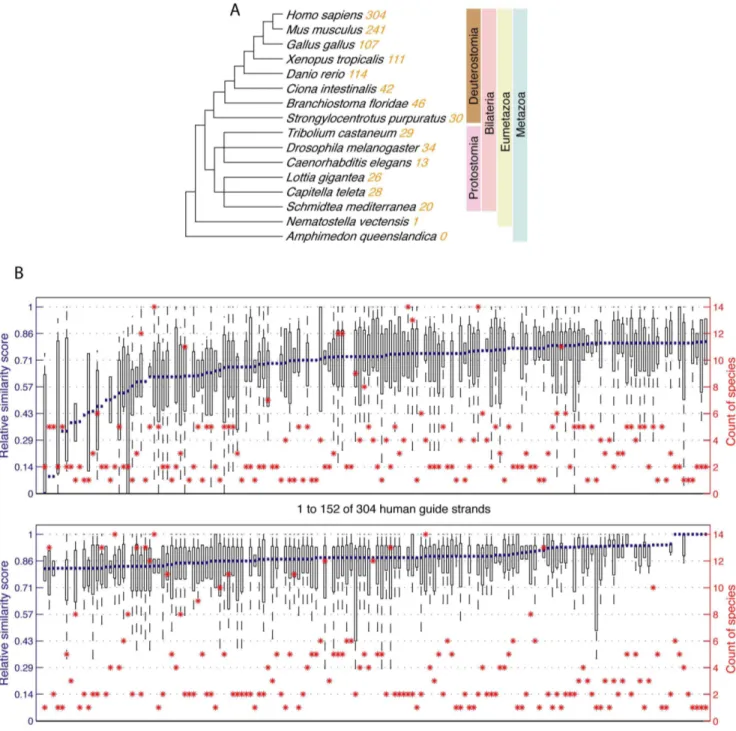
MicroRNA-target binding structures mimic microRNA duplex structures in humans.
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
In this study, using bioinformatic algorithms and luciferase reporter assay, we found that ZNF217 is a target of miR-203, a tumor suppressor miRNA. To explore the potential roles
MiRNA related single nucleotide polymorphisms (miR-SNPs), defined as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in miRNA genes, miRNA binding site and miRNA processing machinery,
Relative expression estimates for the target miRNAs (miRNA-21, miRNA-125b, miRNA-145, and miRNA-630) were obtained by image analysis of the ISH-stained slides ( Table 1 ).The
In order to determine the structural basis for the binding of the substrate and molecular mechanism for the hydrolysis and transglycosylation activities, we solved the structures
Then, we developed a webtool to allow the analysis of the miRNA genomic context in inter and intragenic regions, the access of miRNA and gene expression data
inverse regulation of expression of mRNAs and their specific miRNAs, we determined (MicroCosm Target algorithm) for each miRNA its potential target(s) and the regulatory pathways
Because of the similarity of miRNA target interactions between different plant species, we tend to filter miRNA-target interactions of other plant species using the proposed
fU1-miR- [miRNA] and fU1-miR-[miRNA]-m: miRNA expression vectors containing the primary sequence of a specific miRNA gene (wild type and mutant, respectively) (for details,