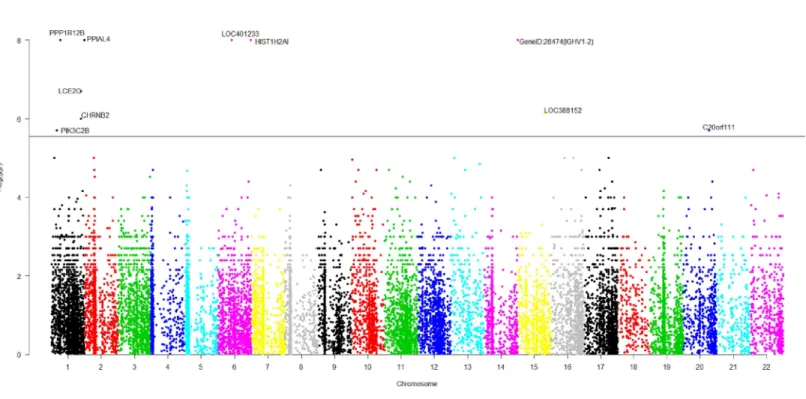
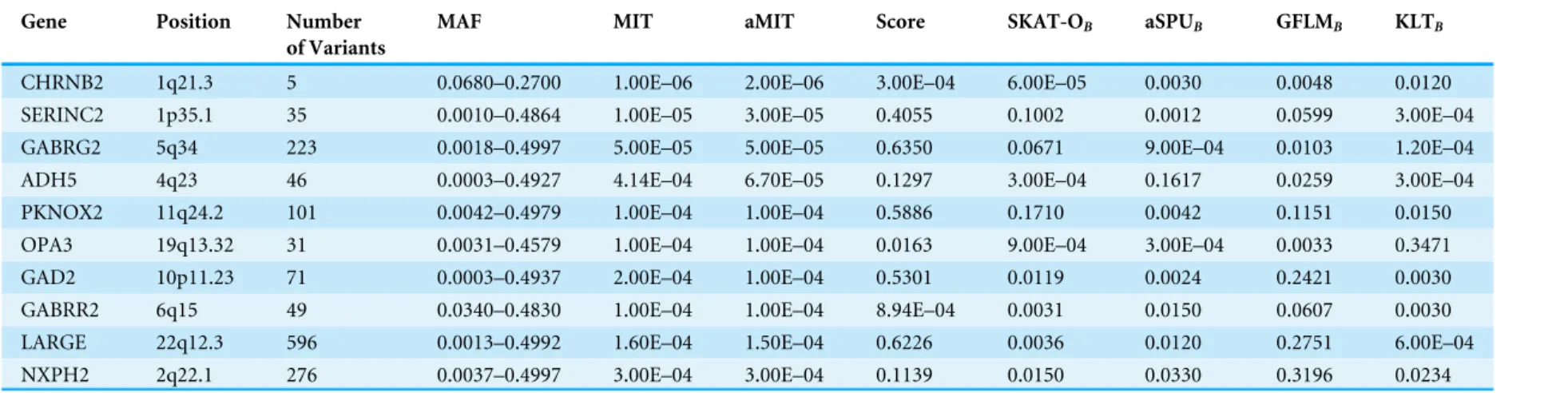
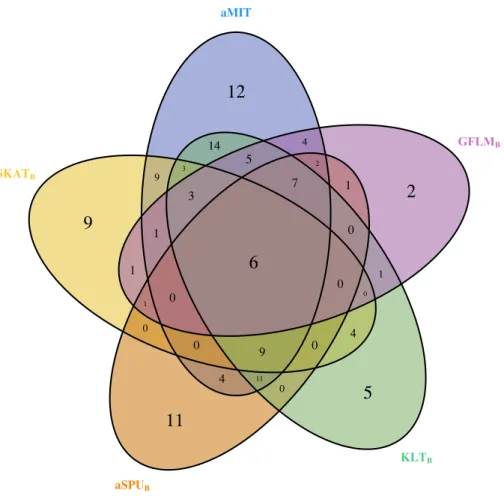
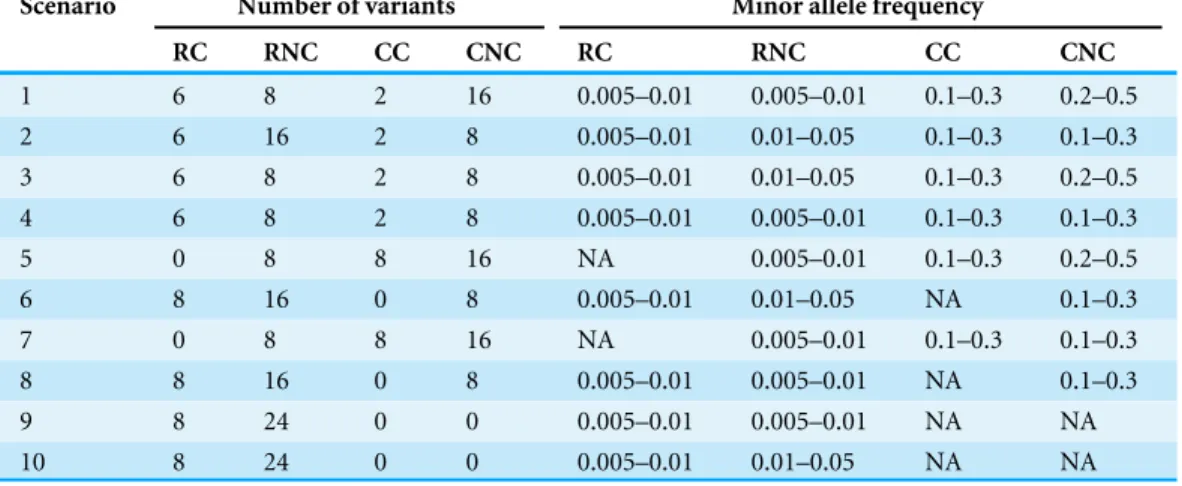
Utilizing mutual information for detecting rare and common variants associated with a categorical trait
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Genetic variants in the microRNA machinery gene GEMIN4 are associated with risk of prostate cancer: a case-control study of the Chinese Han population. Genetic variants in the
We developed a unified method for detecting secondary trait associations with rare variants (STAR) in selected and random samples, which can flexibly incorporate all rare
The modules showing the highest enrichment for rare and common variants in ASD included highly connected genes that are involved in synaptic and neuronal plasticity, and are
Multiple genetic variants in chemokine receptors and chemokines have been identified as modifiers of HIV-1 infection or disease progression [12,13], including CCR5 - D 32 (a
A statistical model for detecting and estimating multiple change points in a finite batch of retrospective (phase I) data is proposed based on Likelihood Ratio Test..
in females 2,10,11 , with the parotid gland most af- fected 2,8,10,12,13 ; the most common histological variants were pleomorphic adenoma 2,9,12,14,15 and mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Literature review and illustrative cases with pathologic confirmation. Results: In LCH, the most common findings are 1) osseous lesions in the craniofacial bones and/or skull base;
In particular, the results obtained with geometric semantic genetic pro- gramming are significantly better than the ones produced by standard genetic programming and other state of