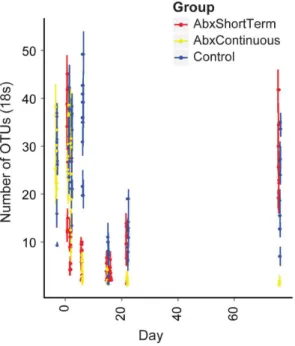
Fungi of the murine gut: episodic variation and proliferation during antibiotic treatment.
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
We aimed to describe the fre- quency of antibiotic use by children in the irst two years of life; determine the characteristics associated with antibiotic use; and estimate
Complement activation by anti-α-gal Abs is cytotoxic to sporozoites and thus is sufficient per se to prevent sporozoite migration to the liver and to inhibit
It is estimated that patients undergoing treatment for haematologic malignancies, such as leukaemia, have a mortality rate of 35% due to systemic fungal infections (Bhatt et
ABSTRACT: The murine model of OVA-induced immediate allergic reaction was used to evaluate the effectiveness of intraperitoneal sub-acute treatment with the leaf hydroalcoholic
Treatment of carotid disease has been in focus over the past years, especially with the advent of the endovascular technique, which supports use of carotid angioplasty and
Antibiotic therapy in combination with mediastinal drainage was used in 9 cases (42.9%) and antibiotic therapy in combination with specific treatment of the cause of mediastinitis
This study contributed to the knowledge about conidial fungi associated with Cedrela odorata , and to the expansion of the geographic distribution of several conidial fungi in
We present a case report of a patient with cerebral palsy that had oral myiasis treated successfully with ivermectin.. The use of this antibiotic in humans, its mechanism of action