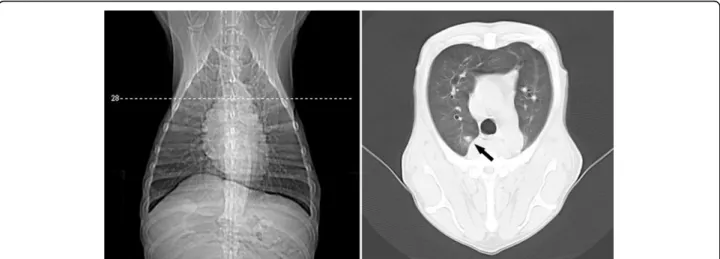
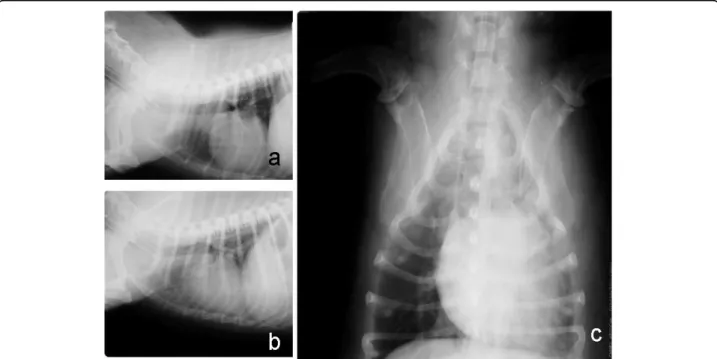
Survey radiography and computerized tomography imaging of the thorax in female dogs with mammary tumors
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
Among the 537 malignant tumors, 13.05% were simple tubular adenocarcinomas, 3.91% were complex tubular adenocarcinomas, 7.26% simple papillary adenocarcinomas, 4.28% complex
The aim of the present study was to study some of the proteins that form the extracellular matrix of 54 benign and malignant mammary neoplasms in dogs, using histochemical
There is a relationship between the presence of imma- ture myeloid DCs and malignant tumors in female dogs, su- ggesting one of mechanisms of immune evasion by tumor cells.
In female dogs with breast tumors, the results were similar to those of previous studies on animals with carcinoma (Saavedra et al. 2011) and when associated with tumor progression
molecular subtypes of human breast carcinomas were identified, based on gene expression profiling: luminal A, luminal B, HER2, basal-like, and normal type carcinoma, all.. of which
describe the utilization of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and perfusion mag- netic resonance imaging in the detection and differen- tiation of benign and malignant tumors,
Female dogs diagnosed with carcinoma in mixed tumors, invasive papillary carcinomas and tubular carcinomas had longer survival times and did not reach the median compared
Another study assessed miRNAs associated with metastatic progression in canine mammary tissue by evaluating 16 miRNAs that were relevant in human breast cancer in 10 samples