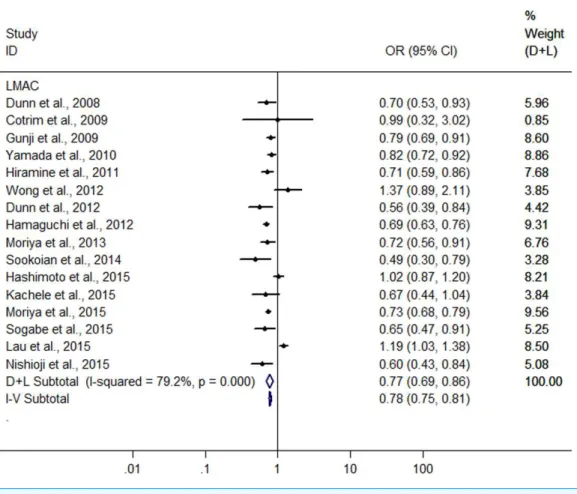
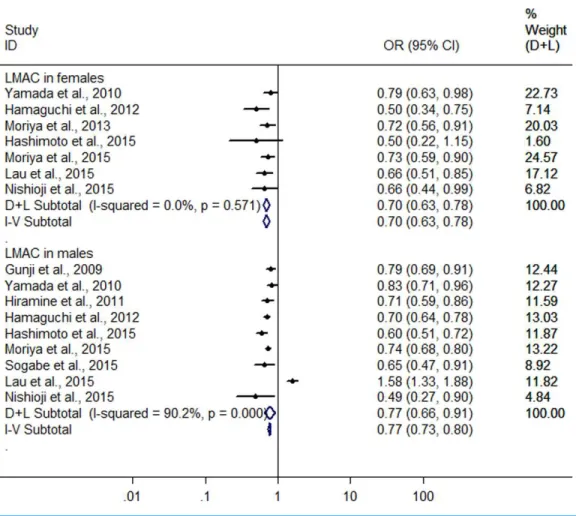
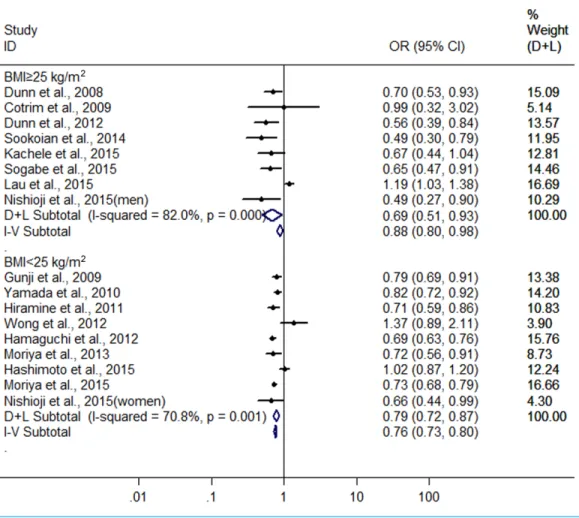
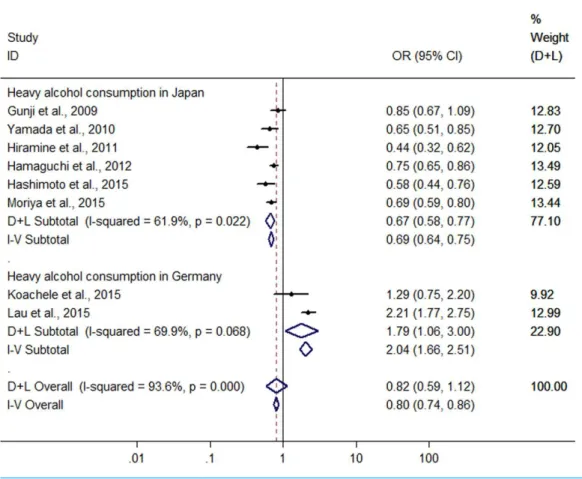
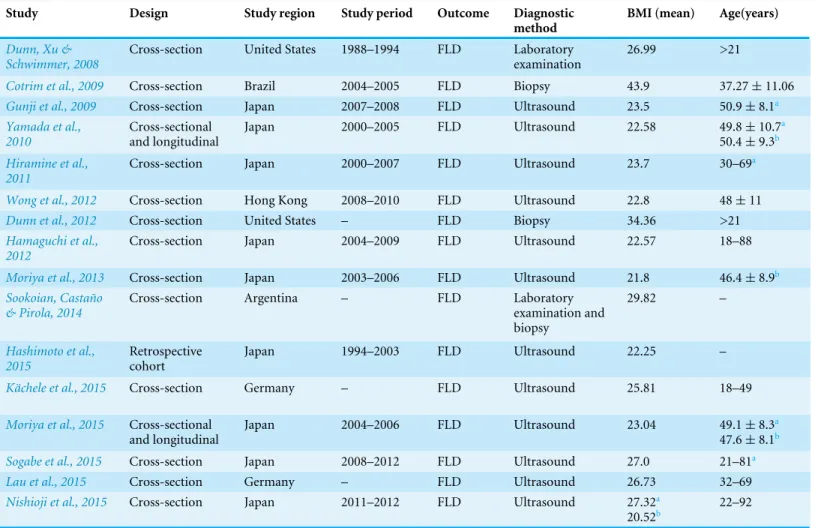
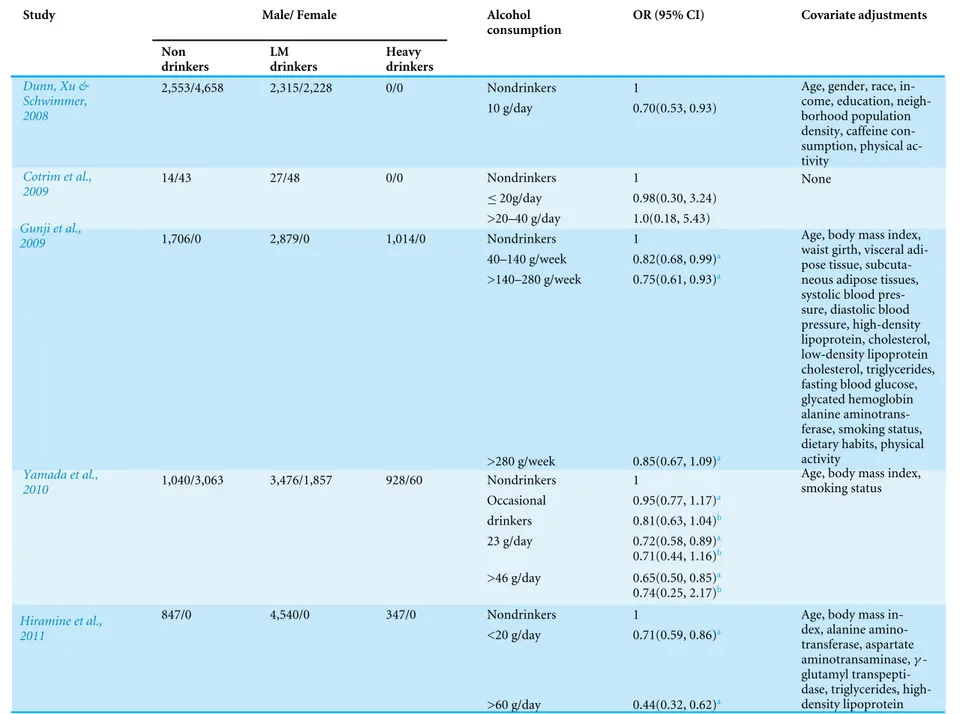
Alcohol consumption and risk of fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Os espaços religiosos estão estreitamente vinculados com a identidade cultural e histórica de determinada comunidade local, podendo promover o deslocamento de pessoas
Combination of extended donor criteria and changes in the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score predict patient survival and primary dysfunction in liver transplantation:
Liver transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients with cirrhosis, decompensated disease, acute liver failure and hepatocellular cancer within Milan
Cryptogenic cirrhosis (CC) is observed in 15-30% of patients with advanced liver disease, and certain studies have suggested that nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) may be a
By comparing with numerical solution of the ori- ginal distributed parameter formulation, it is shown that the high- er order improved lumped model (H 1;1 =H 0;0 approximation)
A tentativa de uniformização das condutas conexas ao consumo e cultivo da Cannabis, por meio unicamente vinculado ao direito penal, retrata o intuito falho de
The presence of hepatopulmonary syndrome was significantly associated with severity of liver disease assessed by the MELD (Model for End-Stage Liver Disease) score, but not with
Alcohol in alcoholic liver disease is a causative factor for development of allergic skin manifestations. Urticaria and angioedema: a