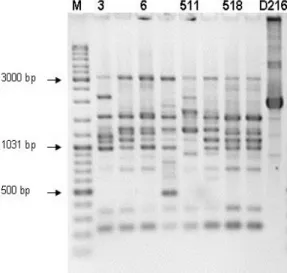
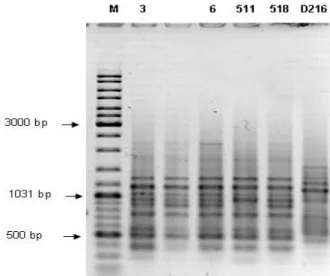
Osmotic stress tolerance, PGP traits and RAPD analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
The results showed that co-inoculation of Rhizobium and Pseudomonas strains containing ACC-deaminase ac- tivity significantly reduced the effect of salinity on total dry matter and
Studies were conducted to determine the effect of osmotic and matric stress on germination and growth of two Fusarium solani strains, the etiological agent responsible of peanut
Osmotic stress tolerance: in order to simulate osmotic stress, the seeds were placed in germination boxes with two sheets of blotting paper, moistened with distilled water
To understand the relationship between nutritional efficiency and stress tolerance to low nutrient availability the correlations between the ranking of the lines for the traits
A functional system was developed constituted by an application for smartphones that enables the monitoring of the geographic position, heart rate and physical activity being
RAPD analysis showed very similar patterns among low, moderate and high fumonisin-producing strains. Although RAPD markers were capable of discriminating the different
This study showed similar DNA profiles between Malassezia strains from healthy cattle and cattle with otitis, raised in the same herd, using the RAPD analysis.. However,
The tolerance of these strains to these metals was assessed in liquid culture medium containing different concentrations of Zn + Cd and in soil solutions and soils contaminated