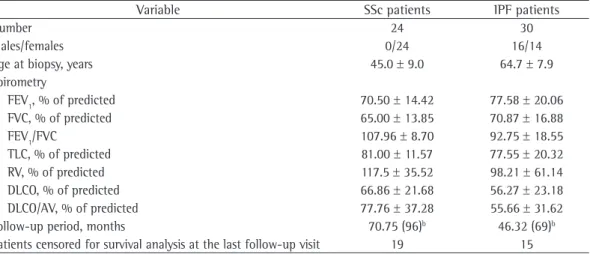
J. bras. pneumol. vol.39 número6
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
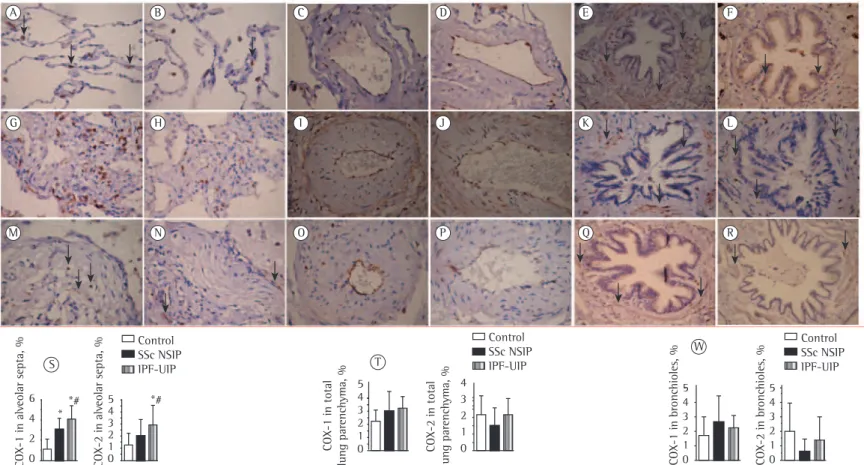
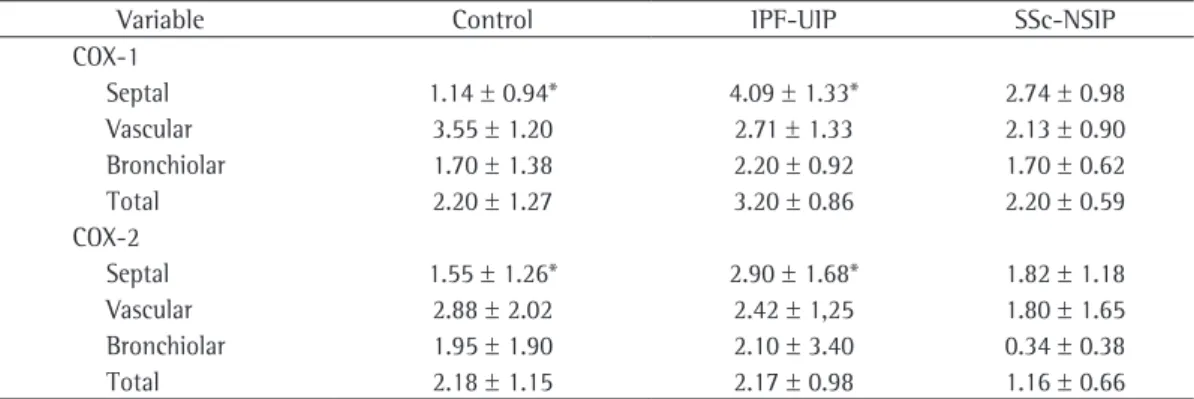
expression of COX-2 in stimulated fibroblasts from NP-AIA samples was almost undetectable. 4) Stimulation of fibroblasts with IL-1 β increased the expression of COX-1 in
Next, analysis of the other results, with a decrease in TNF-α and IL-6 production associated with a rise in plasma IL-10 and IL-4 (Figure 1 ) and lung tissue ( Figure 2 ), shows
In our study, we did not find any differences in HBD-1, HBD-3, and LL-37 expressions between pterygium tissue and normal tissue, whereas HBD-2 expression was significantly higher
lower levels (p<0.05) between the saline treated group and increased compared to the normal group. FIGURE 2 -Effects of Hev b 13 on cytokine production in lung tissue from
We did not detect significant differences in COX-2 and COX-1 levels between saline- and MCT-treated mice by Western blot, qPCR or immunostaining of lung sections and, as expected,
Figure 1 - Cellular expression of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AGTR-1) and AGTR-2 divided in septal areas and intrapulmonary vessels from normal control lungs, systemic
Wound inflammation-related miRNAs; digit wound healing and regeneration; regenerative myogenesis; rejuvenating muscle stem cells; immune control; post-natal and adult
Calorie-related rapid onset of alveolar loss, regeneration, and changes in mouse lung gene expression.. Am J Physiol Lung Cell