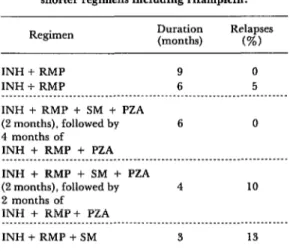
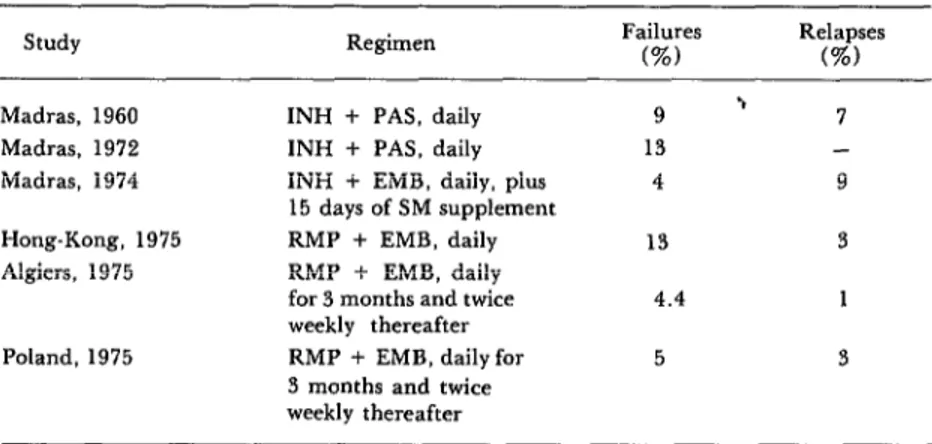
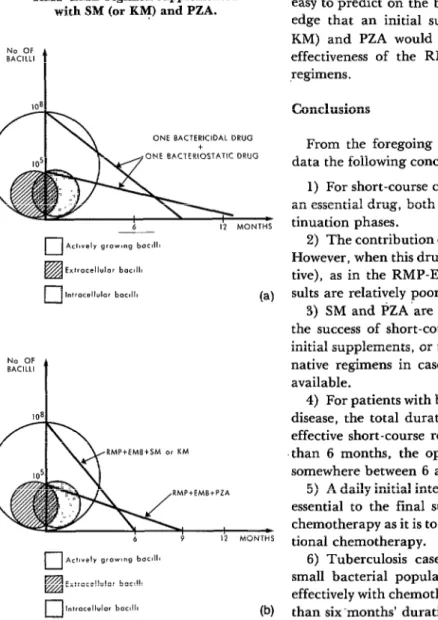
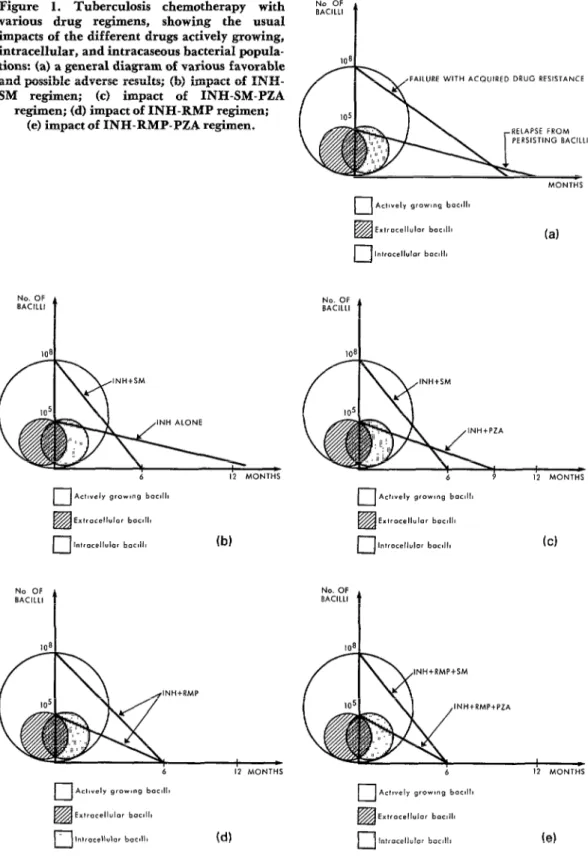
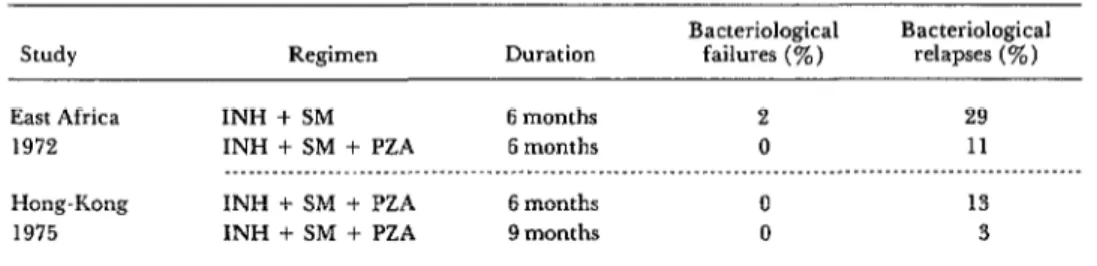
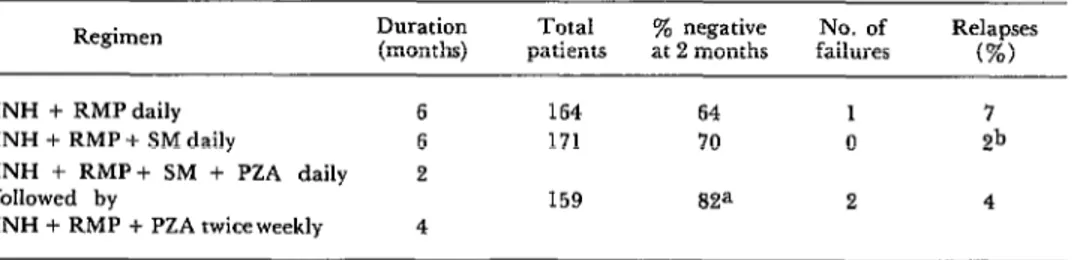
The efficacy of short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis
Texto
Imagem

Documentos relacionados
monary tuberculosis. Objective: To evaluate the sample quality in the performance of PCR fordiagnosisofpulmonarytuberculosis.
(2019) propõem o framework EiF (Elastic Intelligent Fog), cuja arquitetura geral é representada na figura 10. Esta plataforma utiliza redes neurais profundas para filtrar
O estilo de vida moderno da sociedade torna as pessoas sedentárias por conta da inatividade física, devido ao trabalho, renda, classe social e visão de mundo acerca
Técnica de incidentes críticos: aplicabilidade nas pesquisas de enfermagem Critical incident technique: applicability in nursing research.. Técnica de incidente crítico:
Tendo como referência os objetivos definidos, procurou-se ao longo deste estudo, alcançar uma compreensão mais aprofundada acerca dos processos de Tutoria no Contexto do
Objective: To estimate the prevalence of primary resistance to the drugs in the basic treatment regimen for tuberculosis in treatment-naïve patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and
In a survey conducted in referral hospitals for the treatment of HIV/AIDS patients with clinically suspected pulmonary tuberculosis in the city of Recife, Brazil,
The objective of the present study was to evaluate the hearing status of patients being treated for pulmonary tuberculosis at one of two referral hospitals for tuberculosis in the