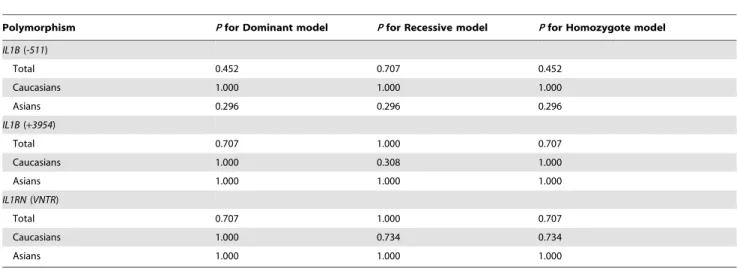
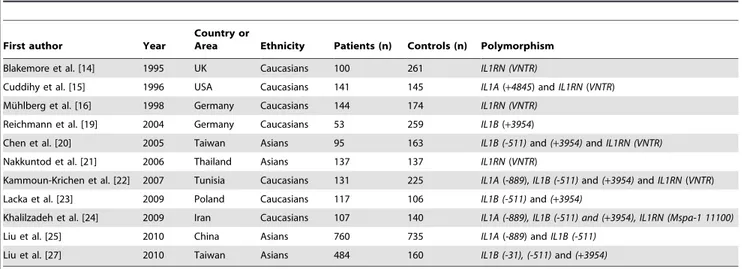
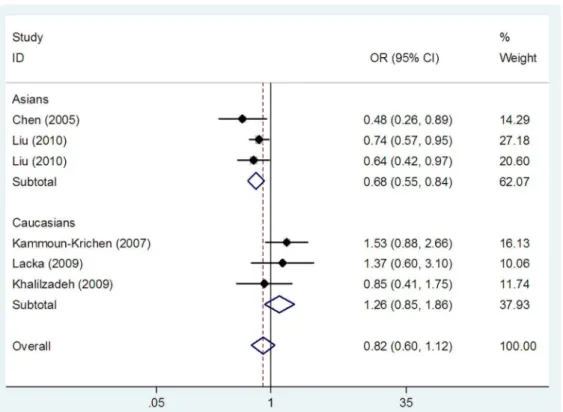
Association between the IL1B (-511), IL1B (+3954), IL1RN (VNTR) polymorphisms and Graves' disease risk: a meta-analysis of 11 case-control studies.
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Conclusions/Significance: This meta-analysis indicates that ADPRT Val762Ala and APE1 Asp148Glu polymorphisms are not associated with increased breast cancer risk.. Citation: Wu B,
This meta- analysis explored the association between the CYP1A1 exon7 gene polymorphisms and lung cancer risk, and performed the subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity,
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (1) the study as- sessed the association between hepatocellular carcinoma risk and COX-2
Considering the relatively small sample size in each single study might have low power to detect the effect of the polymorphisms on cancer risk and the underlying heterogeneity
Association of folate-pathway gene polymorphisms with the risk of prostate cancer: a population-based nested case-control study, systematic review, and meta- analysis.. Cancer
In order to better understand the genetic role of PDE4B for schizophrenia sus- ceptibility, we recapitulated the association of different PDE4B SNPs with schizophrenia risk
The inclusion criteria for the gene association studies in this meta-analysis were as follows: (1) independently published case-control studies explored the association between
Although the association in this study suggested a modest risk of 20% for both-819T and -592A alleles in leprosy susceptibility, these results support the role of these polymorphisms