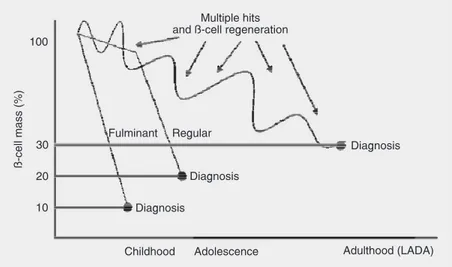
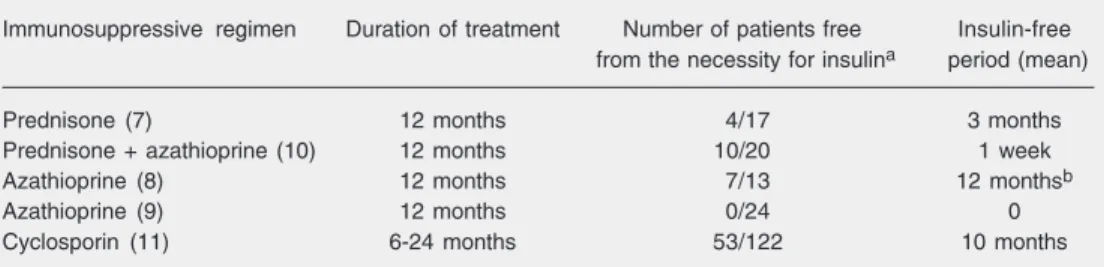
Secondary prevention of type 1 diabetes mellitus: stopping immune destruction and promoting ß-cell regeneration
Texto
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
O legislador ao definir o direito do consumidor à inversão do ônus, busca equilibrar a condição processual das partes litigantes, para efetivação das normas de ordem
A feasibility of useful cell-based therapy by bone regeneration with deciduous tooth stem cells, dental pulp stem cells, or bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for
Por fim, concluímos que a interpretação temporal da completiva de infinitivo regida por verbos perceptivos e causativos é determinada por uma interacção complexa de
α -Catenin correlates with Yap intracellular localization To find adhesion- and cytoskeleton-associated proteins that might act as cell density sensors in the blastema and mediators
In this work we describe the establishment of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and the role of bFGF in adipocyte differentiation.. The
In this context, the objective of this study was to evaluate in vitro resistance of Enterococcus faecium (ATCC 8459) and Lactobacillus helveticus (ATCC 15009) against
Esses espaços, fundamentais na prática da saúde coletiva, ainda encontram-se bastante fragilizados nos contextos dos serviços de saúde, seja pela baixa adesão por parte
Apesar disto parece relevante constatar que: — 77% dos casos de internamento ocorreram com valores de pressão atmosférica abaixo da normal 760 mm58; — 50% dos casos de