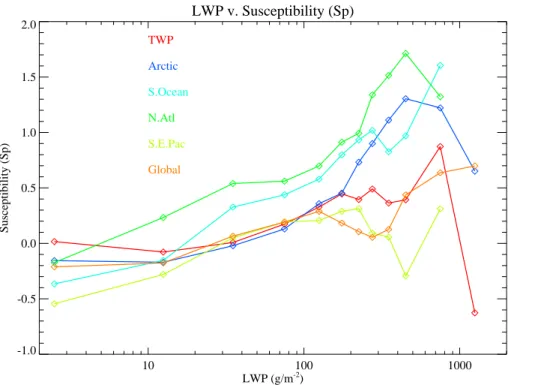
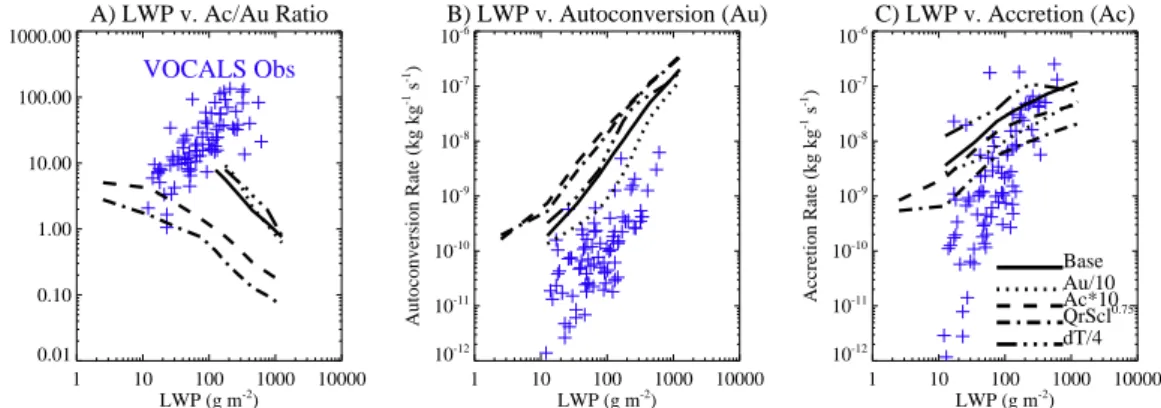
Microphysical process rates and global aerosol-cloud interactions
Texto
Imagem



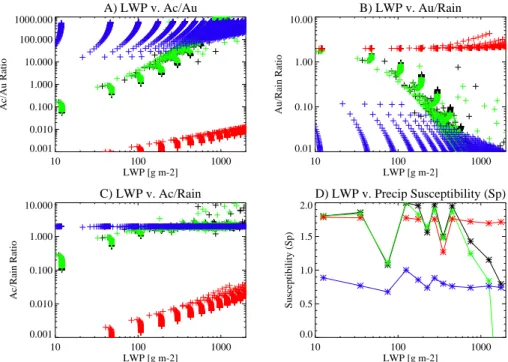
Documentos relacionados
Large variation in microphysical characteristics of the boundary layer clouds and the aerosol concentration were found, and in particu- lar the CDP cloud droplet number concentration
In such cases, knowing the event (rain or not-rain) may allow recalibration. For example, a forecaster might give rain on a particular day a probability of 80% and, hence, not-rain
Je to otázka ut ára ia ide tit žiako , štítko a ie (labeling). autoregulá iu pod ieňuje. Otázkou šak je, čo rozu ie e v tejto sú islosti pod ide titou? G.. Takáto s hop
mixing ratio of 5 hydrometeors (cloud water, cloud ice, rain water, snow, graupel/hail) in every time step using prognostic equation saturation process and microphysical in-
A detailed microphysical characterization is presented for aerosol spectra over three major areas over Greece, namely- the Area West of Crete (AWC), the Greater Thessaloniki
Thus, in order to design a rain rate estimation algorithm adapted si- multaneously to light and heavy rain rates, the reflectivity Z and the specific differential phase K dp must
The precipitation formation and changes in microphysical variables were investigated for a liquid cloud in the tropics (EPIC campaign) and a multi-layer mixed-phase cloud over
We analyze the modeled microphysical properties under the different aerosol conditions to gain insights into the effects of aerosols on cloud development, precipitation, and