Comparative Study of Coal and Biomass Co-Combustion With Coal Burning Separately Through Emissions Analysis
Texto
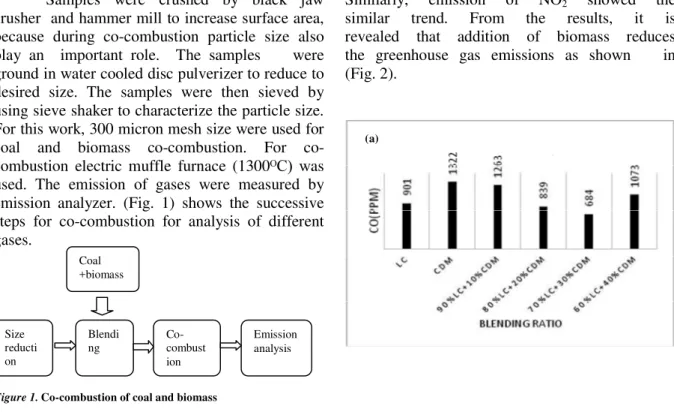
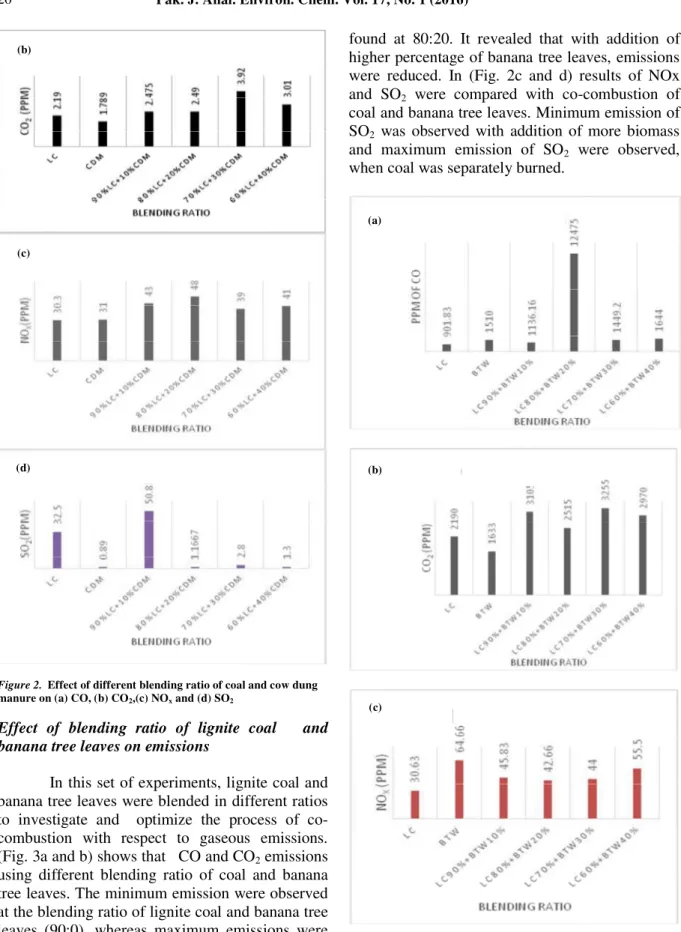
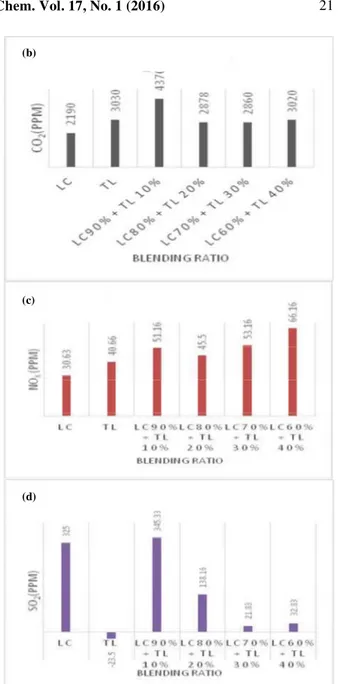
Imagem
Documentos relacionados
Time-series of daily contributions from each identified source, including soil dust, coal combustion, biomass burning, tra ffi c and waste incineration emission, industrial
pogenic NMVOCs emission inventories covering six major sources of vehicle, fossile fuel combustion, biomass burning, storage and transport, solvent utilization, and in-
In the case of blends that were made of Ashland + C Coal, and Carbocol + C Coal (Figures 7 and 8), involving one coal rich in inertinite (C Coal) and two others rich in
The utilization of reflected-light microscopy and SEM allowed the identification of coal particles thermally affected, tectonized, weathered, coarse min- eral matter, bind fine coal
Among coal chars, char A areas are the highest (parent coal shows the highest rank) in agreement with the higher combustibility of parent coal.. But for reactivity to CO 2 we
The paper investigated the synergistic effect that exists during the co-gasification of biomass and coal through thermogravimetric analysis of the two materials and their
In order to study the role of biomass burning on GHG’s over study site we have analysed GHG’s emissions from biomass burning using long term (2003–2013) Fire Energetics and
Global distributions of the C2H2 and C2H2/CO ratio con- firm significant features associated with both the Asian mon- soon anticyclone and biomass burning for this important