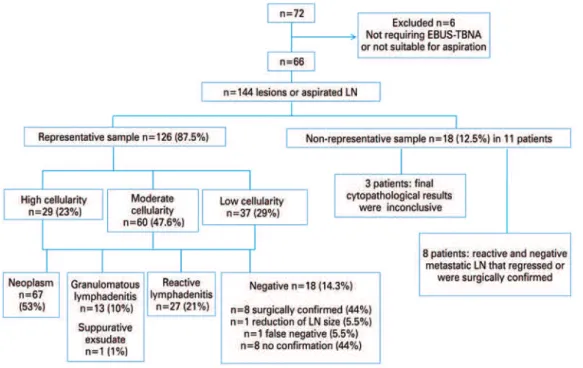
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) in diagnosis of mediastinal lesions
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Objective: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS- TBNA) is a new method for the diagnosis and staging of lung disease, and its use is
Objective: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) is a minimally invasive diagnostic test with a high diagnostic yield for suspicious
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA), a minimally invasive method, has been shown to be safe and accurate for collecting samples
Punção aspirativa transbrônquica por agulha no diagnóstico e estadiamento do câncer de pulmão Transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer..
Objetivo: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA, punção aspirativa por agulha guiada por ultrassom endobrônquico) é um método novo em
Rapid On-Site Cytologic Evaluation During Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for Nodal Staging in Patients With Lung Cancer. Ann
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA, punção aspirativa por agulha guiada por ultrassom endobrônquico) tem desempenhado um papel fundamental
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) has played a key role in the diagnosis of mediastinal, paratracheal, and peribronchial lesions, as well