Effects of Low-level Laser Therapy on Muscle Repair in Rats with Chronic Alcohol Intake
Texto
Imagem



Documentos relacionados
Effects of chronic low back pain on trunk coordination and back muscle activity during walking: changes in motor control. European
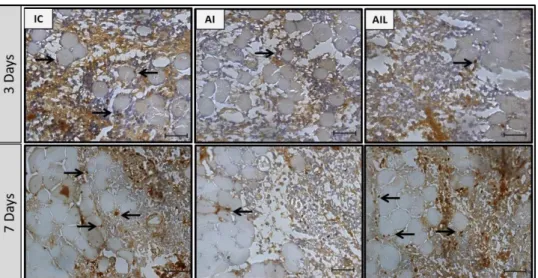
Fig 2. CARV counters alcohol-mediated effects on cytokine production in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury.. Histological examination of liver specimens in rats with
In previous studies from our labora- tory (7,8), the effects of acute and chronic treatment with a water-alcohol extract of the inflorescence of EM were investigated in rats
The Effects of Low-Level Laser Therapy on Bone in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Rats Photomedicine and Laser Surgery. The effects of infrared low-level laser therapy on
The rats were randomly distributed into two groups of 20 animals each for administration of bromopride in the postoperative period (study group - E) or saline (control -
Mean and standard deviation of the cross-sectional area of muscle fiber in μm2 of the tibialis anterior (injured and control) and soleus muscles of groups LE7 (7 days lesion), S7
To verify the effects of exercise on blood biomarkers of oxidative stress in diabetic rats, 40 rats Wistar, were distributed into four groups: control, diabetes, trained control
In this study, 32 rats were used which were randomly distributed into 4 groups: G1 - negative control; G2 - control treated with physiological solution; G3 - animals treated