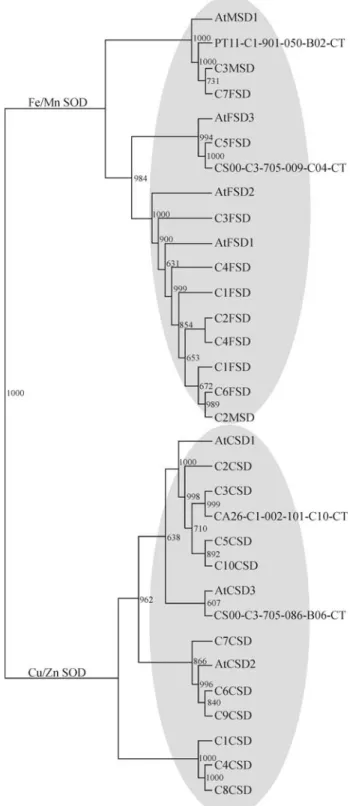
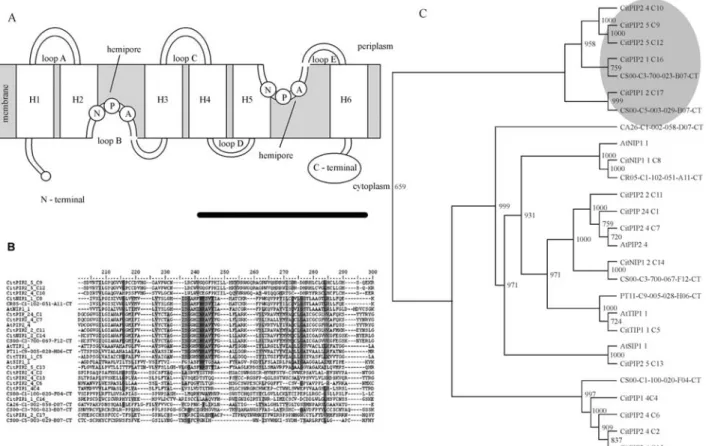
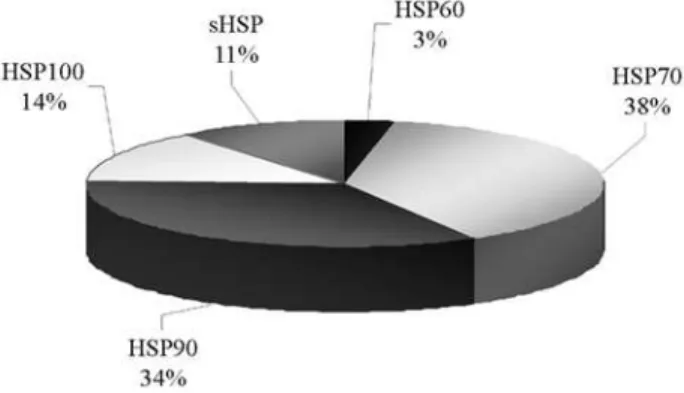
Identifying water stress-response mechanisms in citrus by in silico
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
Ao Dr Oliver Duenisch pelos contatos feitos e orientação de língua estrangeira Ao Dr Agenor Maccari pela ajuda na viabilização da área do experimento de campo Ao Dr Rudi Arno
Ousasse apontar algumas hipóteses para a solução desse problema público a partir do exposto dos autores usados como base para fundamentação teórica, da análise dos dados
This log must identify the roles of any sub-investigator and the person(s) who will be delegated other study- related tasks; such as CRF/EDC entry. Any changes to
keywords Digital images analysis, feature extraction, image segmentation, classifica- tion, content-based image retrieval, similar images, image histogram, edge detection
In preliminary cyto- genetic studies, after in vitro irradiation with a test dose of gamma rays, a strong cytogenetic AR was induced in the lymphocytes of residents of the very
É imperativo o despontar de novos paradigmas sócio-culturais, onde os valores e o respeito mútuo, quer pelos seres humanos, quer pelo mundo natural, se sobreponham ao modo egoísta
In the present study, the response of ‘Sunki Tropical’ mandarin to water stress favoured sexual embryo development, contrary to its behavior in the presence of a normal water
With this goal, we have used the sequences of the key proteins of the different developmental pathways involved in the regulation of flowering-time available from Arabidopsis as bait