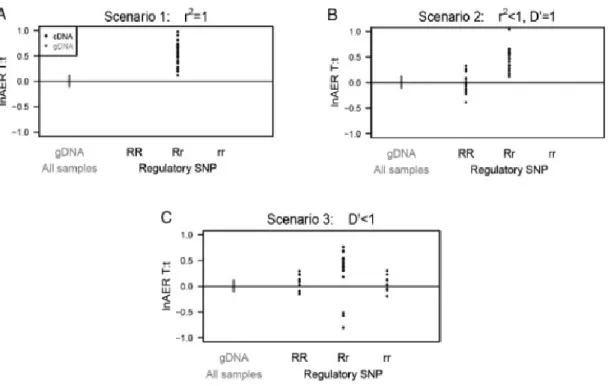
Functional analysis of genetic variants associated with risk for breast cancer: 12q24, a candidate risk locus
Texto
Imagem


Documentos relacionados
To determine the association of genetic variants and obesity and/or obesity-related risk factors, we analyzed the genotype and allele distributions of five
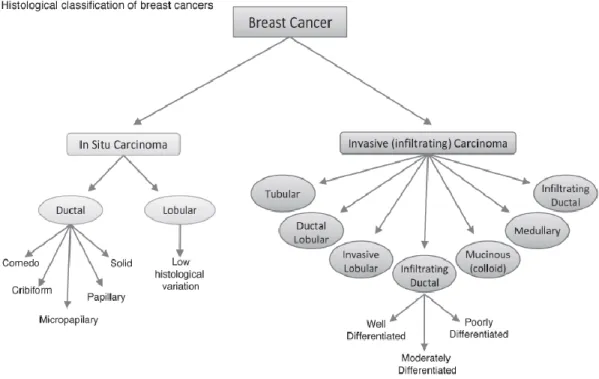
The study of risk factors can permit the identiication of modiiable factors that increase the incidence of breast cancer cases, highlighting women’s lifestyle,. including
To determine the association of genetic variants and obesity and/or obesity-related risk factors, we analyzed the genotype and allele distributions of five
In various populations worldwide, common variants of the TCF7L2 (Transcription factor 7-like 2) gene are associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).. The aim was
Genetic Risk Analysis of Coronary Artery Disease in a Population- based Study in Portugal, Using a Genetic Risk Score of 31 Variants Andreia Pereira, 1 Maria Isabel Mendonça, 1
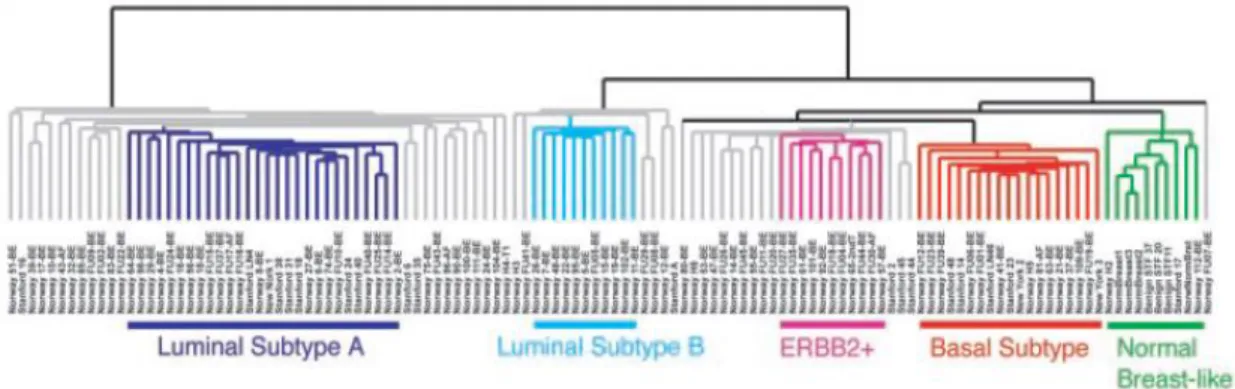
Population-based, case-control study of HER2 genetic polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Biology of HER2 and its importance in
ARPE-19 cells were transduced using lentiviral particles containing vectors either for the expression of wtSTUB1, STUB1K30A and STUB1H260Q or with adenoviral particles containing